Location of the deletion resulting in low set ears, hypertelorism, epicanthal folds, high-pitched cry
Short arm of chromosome 5
Confirmatory tests for Down Syndrome
Amniocentesis and Chorionic Villous Sampling
Cytogenetic nomenclature of male with Edward syndrome
47,XY,+18
Name the lab technique that allows identification of small deletions and duplications
FISH and Array Comparative Genome Hybridization (CGH)
aCGH detect copy number variation, do not detect balanced rearrangements
More than one karyotype in a person or tissue
Mosaicism
Reciprocal translocations are more likely to result in miscarriage when the breakpoint in the chromosome is located more...
Proximally
(When breakpoint is distal, offspring is more likely to survive)
Hypotelorism, micrognathia (small jaw), polydactyly, polycystic kidney disease, cutis aplasia
Patau Syndrome
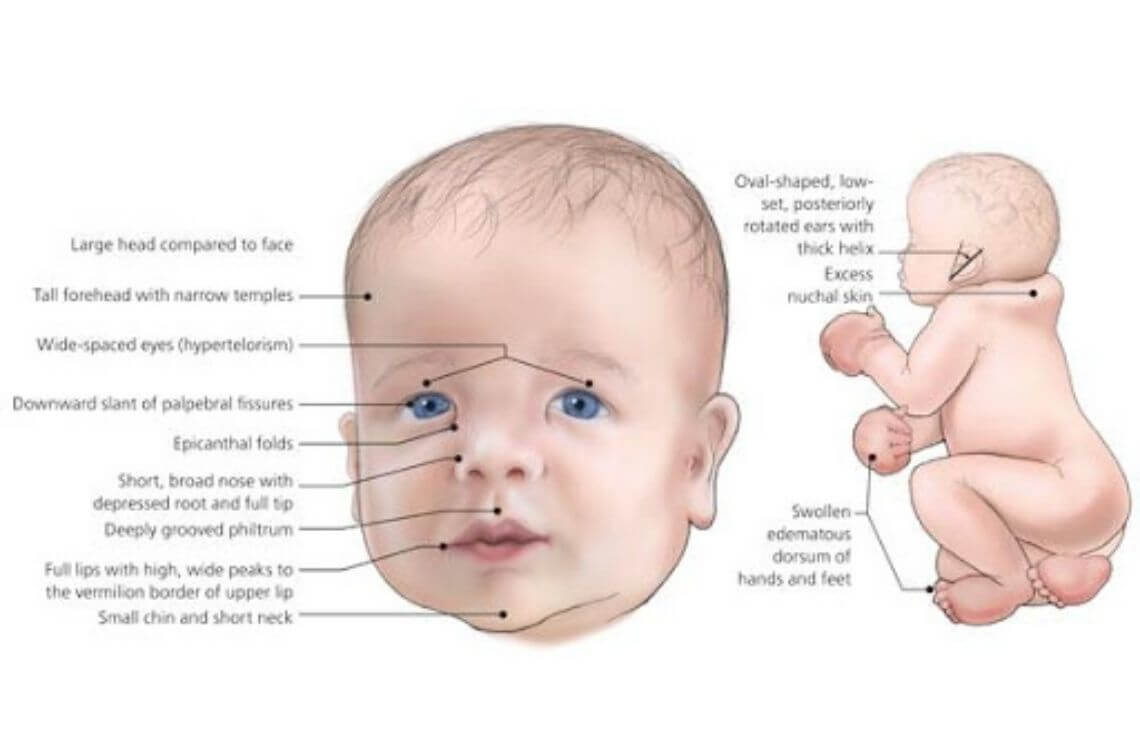
A baby has excessive skin at nape of the neck, flat nasal bridge, brachycephaly, and protruding tongue. 

Down Syndrome
Number of Barr bodies in Klinefelter syndrome
1
Phase of mitosis involved in non-disjunction
Anaphase
Location of deletion in a pt with hyperacusis, a heart murmur, wide mouth and long medial cleft.

Long arm Chromosome 7 (7q11.23)
ELN, LIMK1
Anomalous ears, hypotonia, hyperflexible joints, space between the first and second toes (sandal gap) and these findings:
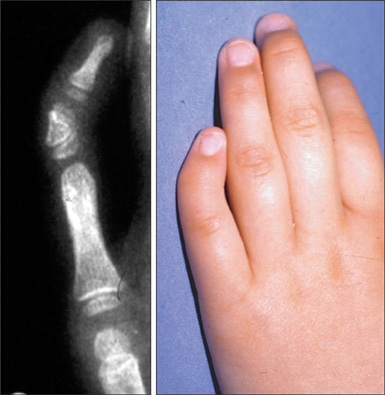
Down syndrome
Prominent occiput, rocker bottom feet, renal and cardiac defects.
Edwards syndrome
Classification of chromosomes 13, 14, 15, 21, and 22
Acrocentric chromosomes
If centromere is involved in a chromosomal inversion, this is called...
Pericentric inversion
(Paracentric inversion does not involve centromere)
Pt with hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy, high arches, hammer toes, drop foot. Condition is an example of which aberration?
Duplication
Chromosome 17, PMP22 (encodes myelin protein gene) and it is an Autosomal Dominant condition
Pt is tall, has learning disabilities, and infertility. Follicle Stimulating Hormone would be...
Increased
Baby is born with widely spaced nipples and these findings:
Turner syndrome
When females have mutations in X chromosomes, clinical manifestations vary due to the process of...
X-chromosome inactivation (Lyonization)
Origin of trisomy where aneuploidy is confined to some tissues.
Somatic origin (Post-zygotic non-disjunction)
Meaning of mnemonic CATCH22
Cardiac defects, abnormal facies, thymic hypoplasia, cleft palate, hypocalcemia, in chromosome 22 (22q11.2)
(>30 genes, including tbx1)
Mother carries a Robertsonian translocation. The chance that her child will have Trisomy 21 is...
1/3 -> 33%
In a woman who is tall and has mild learning disabilities, her chromosomal abnormality most likely resulted from extra chromosomes from which parent?
Mother
Name gene that is expressed when there is more than one X chromosome
XIST gene
Most likely origin of trisomy where aneuploidy is present in all tissues
Meiotic origin