This protects the x-ray tube from physical damage and isolates the tube electrically, protecting the radiographer and patient
What is the protective housing (steel)?
Primary purpose of glass or metal enclosure around x-ray tube
What is to maintain a vacuum?
(So electrons from the air do not disturb the x-ray production)
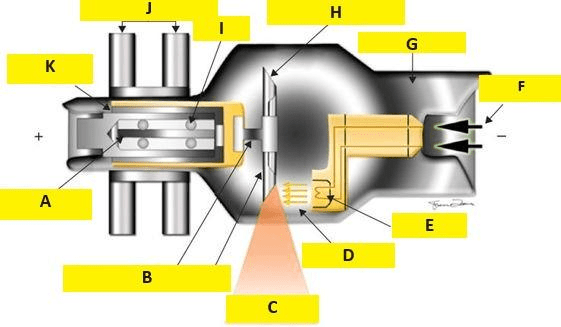
In the image below, the letter 'B' identifies this structure made of this material.
What is the molybdenum neck and base of the anode?
Material (and Z#) used as part of the rotating anode shaft because of its electrical and thermal properties.
What is Copper (Z#29)?
The x-ray tube motor operates on the principle of this type of electrification.
What is electromagnetic mutual induction?
Material that lines the tube housing
What is lead?
Glass tube enclosures are made of this type of glass because it is very heat resistant
What is borosilicate (Pyrex)?
In the image below, letter "J" is this structure and located here.

What are stators (electromagnets) and outside the envelope?
Material (and Z#) used as part of the rotating anode disc base and core (neck) because it has a low thermal conductivity and is a light, but strong alloy.
What is Molybdenum (Z#42)?
Average anode RPM for general purpose tubes.
What is 3400?
The 2 parts of the tube housing that helps protect the tube from thermal damage by dissipating heat
What are cooling fans and an oil bath?
The area in the envelope where the primary beam exits.
What is the target window?
(Thinned glass or metal area on the envelope)
In the image below, letter "H" is this structure made of this material.

What is the tungsten (Z#74) anode?
Melting point of Tungsten (and Z#).
What is 3400 degrees Celsius and Z#74?
Purpose of rotating anode design.
What is to dissipate heat?
(heat-load capacity and exposure techniques that can be used increases)
The meaning of 'x-rays are produced isotropically'
What is x-rays are produced in all directions?
Radiation that is produced at the anode other than the focal spot.
What is off-focus or extrafocal radiation?
In the diagram below, the letter "I" is this structure made of this material.

What is the silver coated ceramic tube bearings?
Material (and Z#) added to the rotating anode coating material to increase thermal capacity and tensile strength.
What is Rhenium (Z#75)?
Sizes of the filaments in the cathode (length and width).
What is 7-15 mm long and 1-2 mm wide?
Amount of leakage radiation required by regulation
What is less that 100 mR/hr?
Technically, it is 0.0258 millicoulumbs/kg per hour in SI units ;)
Suntanning, that can result in arcing and damage of the tube, is a result of this event
What is deposits of vaporized tungsten that causes a bronzing discoloration?
In the diagram below, the letter "A" is this structure made of this material.

What is the iron core of the rotor?
(surrounded by a copper shaft)
DOUBLE JEOPARDY
Material (and Z#) that is added to the filament to increase thermionic emission and extend filament life.
The filament (focal spot size) only affects recorded detail. The smaller the focal spot, the ________________ the recorded detail in the image.
What is greater?