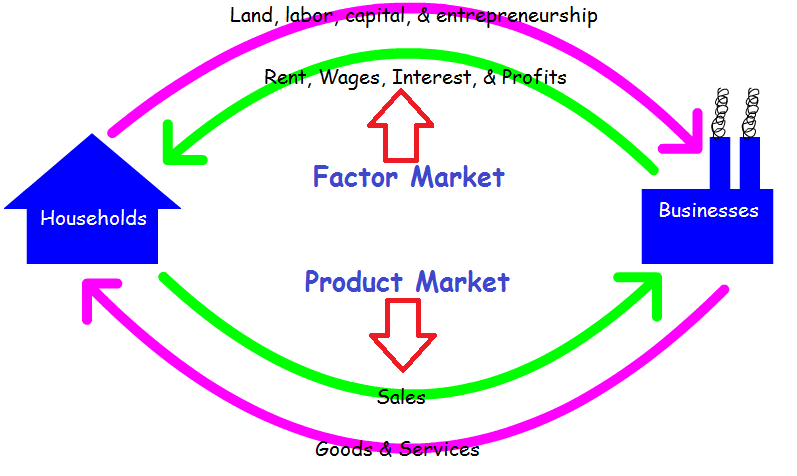
 This model represents
This model represents
What is a Circular Flow model?
The value of the next best alternative foregone when making a decision.
What is opportunity cost?
A government-imposed maximum price that is set below the equilibrium price, leading to shortages.
What is a binding price ceiling?
If consumer preferences shift toward healthier foods, what happens to the demand for fast food?
Decreases
Quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded, causing downward pressure on price.
What is surplus?
Prices adjust in a market to bring supply and demand into balance.
What is the law of supply and demand?
A rise in consumer income typically does what to demand?
Increases
A market structure dominated by a few large firms, where each firm’s decisions affect the others.
What is an oligopoly?
A market structure where many firms sell identical products, and no single firm can influence the market price.
What is perfect competition?
Changes in production costs, technology, taxes, and the number of suppliers.
Factors that can shift the supply curve?
A market structure where one firm controls the entire market for a good or service.
What is a monopoly?
The limit on the consumption choices a consumer can make, given their income and the prices of goods.
What is a price floor?
when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded at a certain price.
What is market equilibrium?
As the price of a good increases, the quantity supplied increases, and vice versa.
What is the law of supply?
A curve showing the maximum possible output combinations of two goods given available resources and technology.
What is a production possibility frontier (PPF)?