What is the difference between the base and apex of the heart?
Base of the heart- top surface
Apex of the heart- bottom of the heart
AV Node has an intrinsic rate of?
40-60bpm
Which Sinus Rhythm originates in the SA Node and is common with breathing?
Sinus Arrhythmia
In A-fib the PR interval is usually....
NOT MEASURABLE!!
Ventricular Rate of Junctional Bradycardia?
Slower than 40bpm
Name 2 Characteristics of the Atria of the heart
Thin
Receive blood
-Pumped into ventricles
-70% with each AV valve opening
-30% with each contraction aka “Atrial kick”
PR-interval is considered long if it is longer than____ seconds in duration.
.20 seconds
Sinus Block is a disorder of impulse_____ and Sinus Arrest is a disorder of impulse______.
a) Formation/conduction
b) Conduction/formation
B!
Most common sustained dysrhythmia in adults?
A-fib
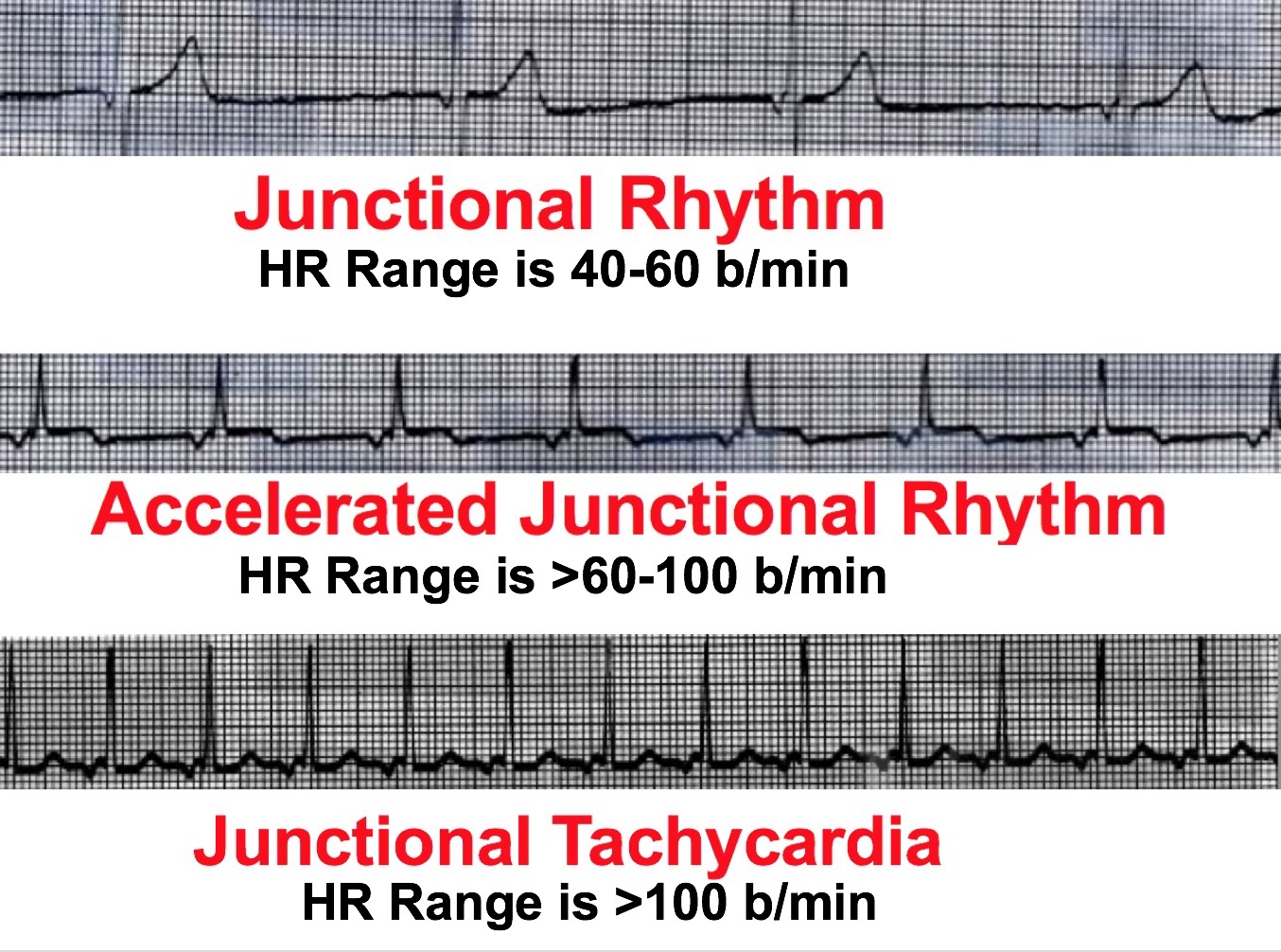
What is the difference between Accelerated Junctional Rhythm and Junctional Tachycardia?
RATE!
Accelerated Junctional- 61-100bpm
Junctional Tachycardia- Above 101
Name the Atrio-Ventricular Valves “AV Valves” and Semi-Lunar Valves
AV: Tricuspid and Bicuspid
Semi-Lunar:Pulmonic and Aortic
Which part of the conduction system receives an impulse from the SA node but delays relaying that impulse to the bundle of His, allowing time for the atria to empty their contents into the ventricles before the onset of ventricular contraction?
AV Node
Sinus Arrest is a disorder of?
*Hint impulse formation or conduction
Impulse formation!
Sinus Block is the disorder of impulse conduction...
Intravenous access has been established. A repeat set of vital signs reveals the following: blood pressure 140/82 mm Hg; pulse 188 beats/min; ventilations 20 breaths/min. The patient's anxiety has increased. She denies chest discomfort and shortness of breath. Her skin is pink and warm, but moist. Based on the information provided, your standard orders/ treatment are?
Attempt vagal maneuvers!
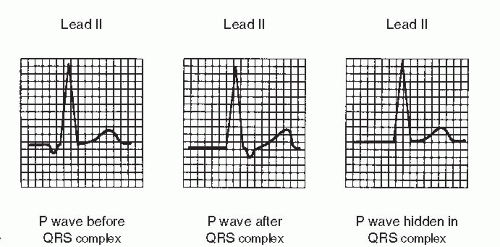
In a junctional rhythm viewed in lead II, where is the location of the P wave on the ECG if ventricular depolarization precedes atrial depolarization?
*Hint occurs low in the junction..
After QRS
Define preload and afterload..
Preload:
-Defined as the amount of pressure exerted on the ventricular walls during diastole
-Influenced by volume of blood returning to the heart
Afterload:
-Defined as the pressure or resistance the ventricles must pump against to distribute the blood
-Direct correlation to diameter of the arteries and veins
On EKG the time necessary for the spread of an electrical impulse through the atria, AV node, Bundle of His, R/L Bundle Branches and the Purkinje fibers are reflected by the_____.
PR-interval
A pulse oximeter has been applied to an adult patient. The patient's oxygen saturation level on room air is 97%. The cardiac monitor reveals a rhythm recorded in lead II. The rhythm rate is 148 bpm. It is regular. It contains a P wave for every QRS complex. A QRS for every P wave. The PR interval and QRS duration are within normal limits. What rhythm is this?!
Sinus Tachycardia!
Short PR interval, delta waves, widening QRS
Which of the following statements is true regarding the differences between premature atrial complexes (PACS) and premature junctional complexes (PJCs)?
a) A PAC has a narrow QRS complex and a PJC has a wide QRS complex
b) A PAC has a negative P wave before the QRS complex and a PJC has a positive P wave before each QRS complex
c) A P wave may or may not be present with a PAC, whereas a PJC typically has a positive P wave before the QRS complex
d) A PAC typically has a positive P wave before the QRS complex, whereas a P wave may or may not be present with a PJC
D!!
The contribution of blood that is added to the ventricles and results from atrial contraction is called?
Atrial kick!
True or False:
Automaticity is defined as the cardiac cells ability to receive an electrical impulse, and conduct that impulse to an adjacent cardiac cell.
False! This is conductivity!
An ECG rhythm strip shows a ventricular rate of 46, a regular rhythm, a PR interval of 0.14 seconds, a QRS duration of 0.06 second, and one upright P wave before each QRS. This rhythm is?
Sinus Bradycardia!
The most common type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is?
*Hint it is just the other name for SVT!
AVNRT
What are the characteristics (6-steps) of a Junctional Tachycardia??