The Ophthalmic Artery is a Branch of Which Artery?
The Internal Carotid Artery
Patient "X" Has a Visual Acuity of 6/12. Interpret this Result
What a Person with Normal Vision can See at 12m, Patient "X" Can Only See at 6m
Which Type of Skin Cancer Has the Greatest Propensity to Metastasise?
Melanoma
Which Nerves Innervate the Extrinsic Muscles of the Eye?
Oculomotor Nerve: All Except Superior Oblique & Lateral Rectus
Trochlear Nerve: Superior Oblique
Abducens Nerve: Lateral Rectus
Identify the Following Condition:
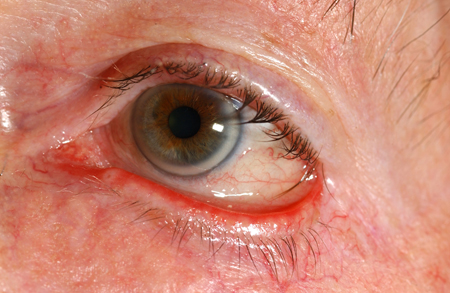
Ectropion: Outward Turning of the Eyelid Margin
Identify the Metastatic Routes of Melanoma
Lymphatic or Haematogenous Spread
A Pituitary Tumour Compresses the Optic Chiasm. Which Visual Field Defect is Expected?
Bitemporal Hemianopia

What is the ABCDEFG System for Examining a Nodular Melanoma?
1. Asymmetry
2. Irregular Border
3. Two or More Colours
4. Diameter >6mm
5. Evolution (History of Change in Shape/Size/Colour)
6. Elevated
7. Firm
8. Growing
Test "X" Has a Specificity of 80%. Interpret What This Means
The Test Correctly Identifies the Absence of Disease in 80% of Individuals. While 20% of Healthy Individuals are Incorrectly Identified as Positive.
80% True Negative, 20% False Negative.
What is Breslow's Thickness a Predictor of in the Context of Melanoma?
Breslow Thickness is a Key Predictor of Metastasis
What is the Physiological Basis of Horner's Syndrome?
Apical Lung Tumour Compresses Sympathetic Trunk. Disruption of Sympathetic Pathway to Eye & Face Leading to Ptosis (Paralysis of Levator Palpebrae Superioris), Miosis (Loss of Input to Dilator Pupillae) & Anhidrosis (Loss of Sweat Gland Stimulation).
Describe the Findings of the Following Fundoscopy. What is the Most Likely Diagnosis?

Hypertensive Retinopathy:
1. AV Nipping
2. Cotton-Wool Spots (Ischaemia)
3. Microanuerysms
Diagnosis: Chronic or Malignant Hypertension
What are Three Points You Can Use to Educate a Patient About Sun Cancer Prevention?
1. Skin Protection: Slip, Slop, Slap, Seek, Slide
2. Sunscreen: SPF50+, 5mL (~1tsp) Per Body Part, Apply 20min Before Exposure, Reapply At Least Every 2hrs or After Swimming, Sweating, Towel Drying etc.
3. UV Index: Sun Protection is Required When the UV Index Exceeds 3.
4. Educate About Vitamin D: Most Australians Are Not Deficient. Aim for 25% of Body Exposure (Forearms) for 10-15min in Summer or 30-45min in Winter.
Name Four Risk Factors for the Development of Melanoma
1. Excessive UV Exposure
2. History of Sunburn, Particularly Severe Ones Resulting in Blistering
3. Fiztpatrick Type I or II (Fair Skin, Burn Easily)
4. Personal/Family History of Melanoma
5. Solarium Use
6. Immunosuppression
7. Late Age
8. Light Eye Colour
A 65 Yo Male Presents to the ED w/ a Sudden, Painless Loss of Vision in His Right Eye that Resolved Spontaneously. He has a History of Hypertension, Hyperlipidaemia & Smoking. What is the Most Likely Diagnosis?
Amaurosis Fugax Secondary to Carotid Artery Disease: Occlusion of the Central Retinal Artery (End Artery) Leading to Monocular Vision Loss as a Result of Poor Collateral Circulation.
Name Three Red Flags for the Presentation of "The Red Eye".
1. Moderate/Severe Eye Pain
2. Photophobia
3. Marked Redness of Eye
4. Reduced Visual Acuity on Snellen Chart
5. Foreign Body or Penetrating Eye Trauma
Define Positive Predictive Value (PPV)
The Positive Predictive Value is the Probability that a Person Actually Has the Disease Given they Tested Positive
PPV = True Positives / (True Positives + False Positives)
Name Three Differentials for Melanoma
2. Seborrheic Keratosis
3. Pigmented Actinic Keratosis
4. Solar Lentigo
5. Pigmented BCC