An FEV1/FVC under .7 both pre and post bronchodilater treatment
Spirometry findings in spirometry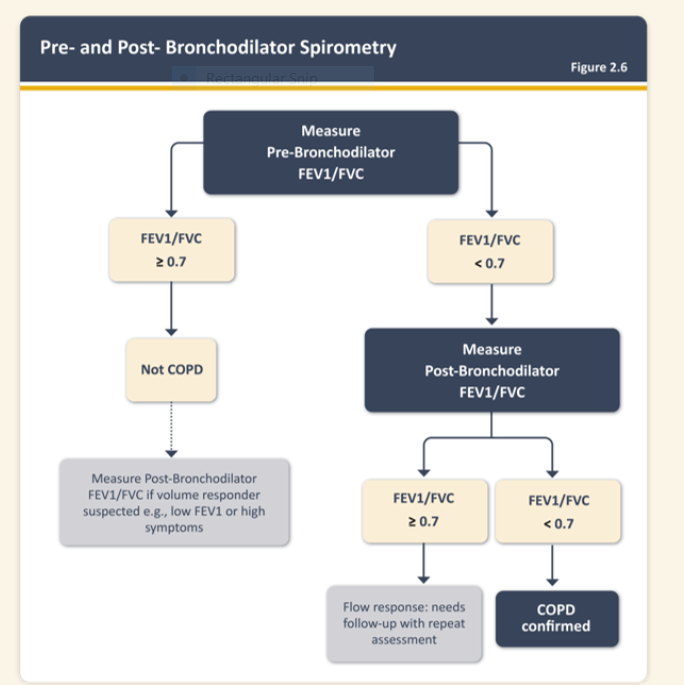
This is an oral antibiotic commonly used in UTIs is contraindicated in patients with CKD5, patients with megaloblastic anemia, and patients with severe liver disease
What is bactrim?
Aerobic gram-positive bacteria: Streptococcus pneumoniae
• Aerobic gram-negative bacteria: Escherichia coli (including susceptible enterotoxigenic strains implicated in traveler's diarrhea), Klebsiella species, Enterobacter species, Haemophilus influenzae, Morganella morganii, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Shigella flexneri, Shigella sonnei
• Other microorganisms: Pneumocystis jirovecii[1
Side effects associated with Bactrim include:
• Severe adverse reactions: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis (AFND), acute generalized erythematous pustulosis (AGEP), fulminant hepatic necrosis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, other blood dyscrasias, acute and delayed lung injury, anaphylaxis, circulatory shock.[2][3]
Contraindications for Bactrim include:
• Known hypersensitivity to trimethoprim or sulfonamides
• History of drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia with use of trimethoprim and/or sulfonamides
• Documented megaloblastic anemia due to folate deficiency
• Marked hepatic damage
• Severe renal insufficiency when renal function status cannot be monitored
• Concomitant administration with dofetilide.[1-2]
GDMT in HFrEF
What is a combination of an ARNI, MRA, SGLT2 and a beta blocker?
Angiotensin Receptor-Neprilysin Inhibitors (ARNI): Preferred over ACE/ARB alone for most patients due to superior outcomes in reducing mortality and hospitalization.
Beta-Blockers: Such as carvedilol or metoprolol succinate which reduce mortality and morbidity.
Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists (MRAs): Such as spironolactone or eplerenone, which further reduce mortality and hospitalization.
4. Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors (SGLT2i): Such as dapagliflozin or empagliflozin, which have shown benefits in reducing heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular death.
COPD treatment for a patient with 3 exacerbations in last year and one hospitalization.
What is LAMA+LABA+ICS?
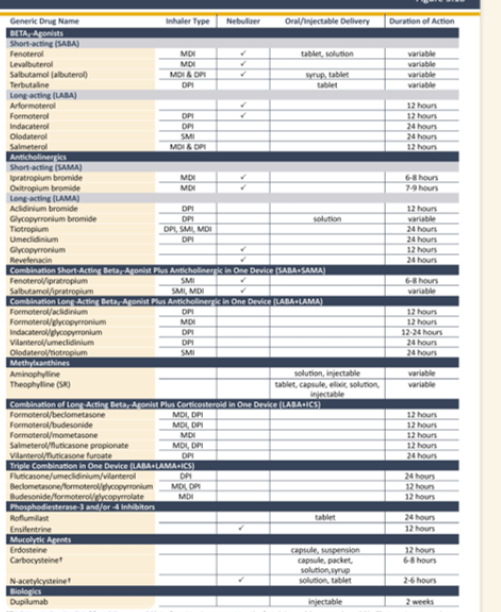
This is an IV antibiotic commonly used inpatient with good gram negative, gram positive, pseudomonal, and some oral anaerobe coverage; this medication is always suspected when a patient suddenly becomes encephalopathic.
What is cefepime?
Basic diagnostic approach to patient with suspected CHF exacerbation
Diagnostics: CMP, CBC, BNP, ECG, CXR, POC US, Trop, continual o2 monitoring
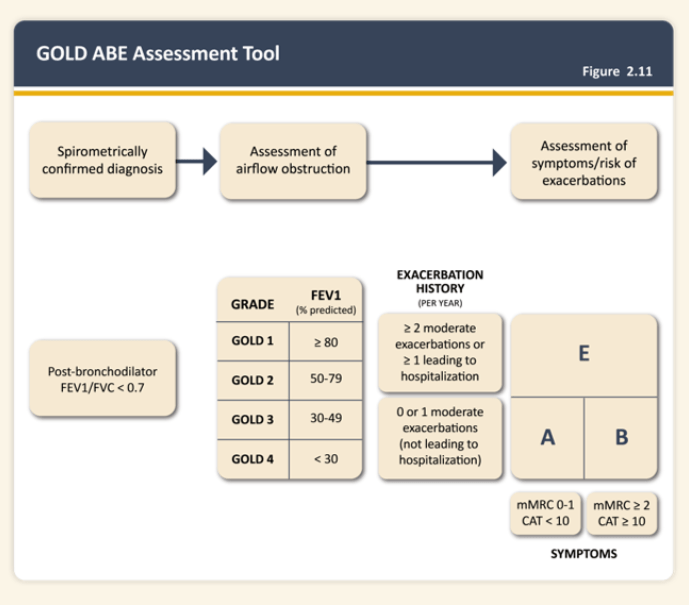
COPD classificatoion for a patient with an mMrc >2, 0-1 exacerbations per a year, and no hospitalizations
COPD GOLD Class 2
Gold classification:
Group A: Low risk, fewer symptoms. Patients have fewer symptoms (e.g., mMRC 0-1 or CAT <10) and a low risk of exacerbations (0-1 exacerbations per year and no hospitalizations).
Group B: Low risk, more symptoms. Patients have more symptoms (e.g., mMRC ≥2 or CAT ≥10) but a low risk of exacerbations (0-1 exacerbations per year and no hospitalizations).
Group C: High risk, fewer symptoms. Patients have fewer symptoms (e.g., mMRC 0-1 or CAT <10) but a high risk of exacerbations (≥2 exacerbations per year or ≥1 hospitalization).
Group D: High risk, more symptoms. Patients have more symptoms (e.g., mMRC ≥2 or CAT ≥10) and a high risk of exacerbations (≥2 exacerbations per year or ≥1 hospitalization).
Abx regimen for patient hospitalized for inability to tolerate PO with fever, cough, recent sick contacts with the following x ray finding:

Ceftriaxone 1-2 g Q24 + doxy 100 mg Q12 IV.
Diagnosis suggested by this imaging finding in a patient with crackles on their lungs and two weeks of leg swelling and DOE:

B lines.
Think B for BAD.
B-lines on an ultrasound represent extravascular lung water (EVLW) and are indicative of pulmonary congestion in the context of diagnosing and managing heart failure exacerbations. These comet-tails come from the pleural line and extend to the bottom of the ultrasound screen without fading, moving with respiration.

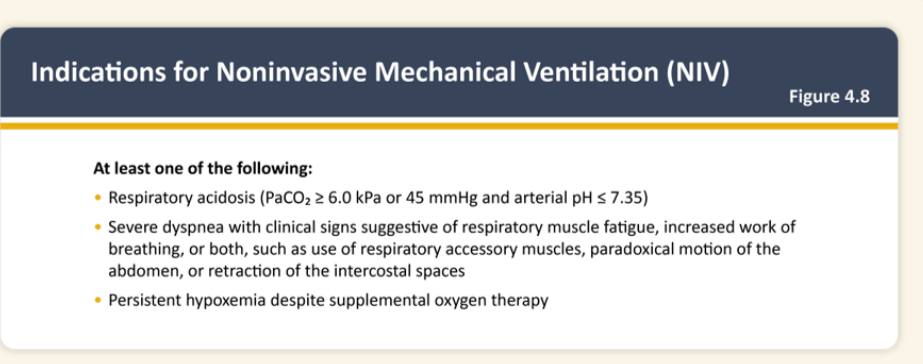
Respiratory acidosis with CO2 over 45, pH 7.35
Severe dyspnea with respiratory muscle fatigue and/or increased work of breathing
Persistent hypoxemia despite supplemental O2
What are indications for noninvasive mechanical ventilation?
Antibiotic regimen for salt water related cellulitis
- Doxycycline 100mg PO/IV q12hrs daily + Cefepime 1g IV q12hrs x 10 days
- Ciprofloxacin 400mg IV q12hrs x 10 days
Cover for v vulnificus, leading cause of shellfish associated death in US. Can progress rapidly, leading to death in 2-3 days.
Imaging findings in a patient with suspected CHF exacerbation w/ DOE, new O2 requirement and BNP to 3000 starting a few weeks ago after a "head cold":
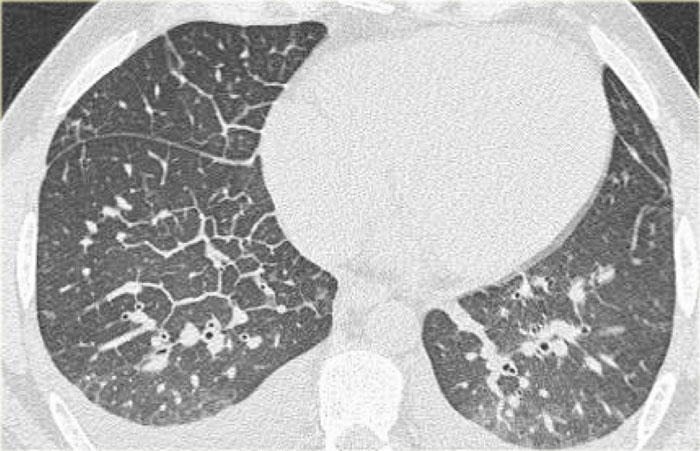
What are thickened septal lines, ground glass opacities, and bilateral pleural fluid?
- Thickened septal lines due to interstitial edema
- Subtle ground glass opacity in the dependent part of the lungs
- Bilateral pleural fluid.
In a patient with a known malignancy lymphangitic carcinomatosis would be high in the differential diagnostic list.
Ground glass opacity is the first presentation of alveolar edema and a precursor of consolidation.