What should be in the resident/patient chart before using the PICC or Central line or Port
An order to use the PICC/ Central Line/ Port
Why do you discard a waste sample when drawing labs from a CVAD?
What is to remove diluted blood or residual flush/medication?
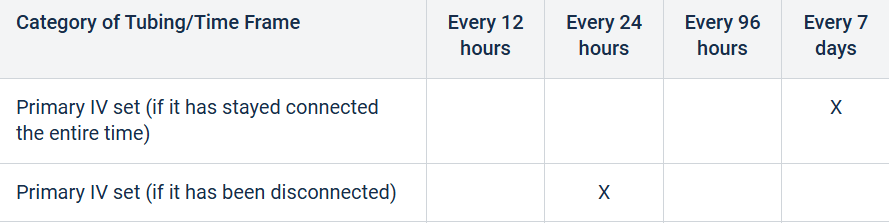
How often should primary IV tubing be changed for continuous infusions?
Primary IV set (If it has stayed connected the entire time) Every 7 days according to Blessing Hospital Policy.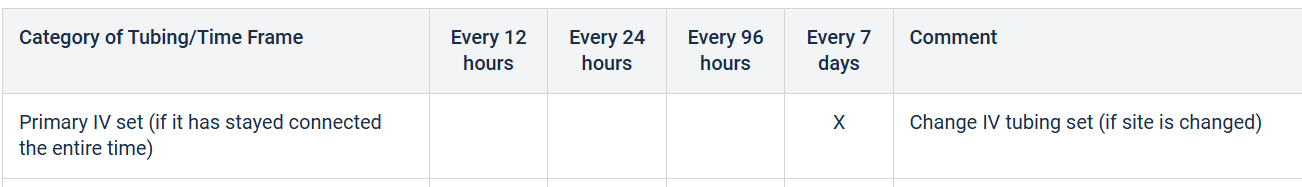
What is the purpose of the in-line 0.22-micron filter used with TPN?
What is to remove bacteria and particulate matter from non-lipid TPN solutions?
When using the patient/resident own parenteral nutrition, what does the nurse need to do first?
Get the consent form signed

True or False: Labs should be drawn from the same lumen used for TPN
False
How much blood is typically discarded before collecting samples?
What is 5 ml according to Blessing Hospital Policy

How often should primary IV tubing be changed if it has been disconnected?
What is every 24 hours
What life-threatening metabolic complication can occur if TPN is stopped abruptly?
What is hypoglycemia?
Name 2 clinical or laboratory signs that suggest fat overload syndrome during lipid infusion
What is hypertriglyceridemia (Elevated TG levels) and acute fever
Resource: NIH- "Fat overload syndrome after the rapid infusion of lipid emulsion"
A patient's central venous catheter flushes easily but has not blood return. What are the possible causes of this finding?
Absence of blood return could indicate catheter tip malposition, partial occlusion, or fibrin sheath formation.
After blood is drawn for testing, flush with how much of this using pulsatile flush.
What is with 20mL normal saline

You are doing bedside shift report and see your patient's TPN tubing has been in place for 30 hours, and the infusion appears clear with no signs of contamination. What should your next action be?
According to Blessing Hospital policy, TPN tubing must be changed every 24 hours.
prevents central line associated bloodstream infections.
include tubing for both TPN and lipids that are co-infused.
A patient receiving TPN suddenly develops shortness of breath, chest pain, and a drop in oxygen saturation. What is your priority action, and what complications might this indicate?
These are classic signs of an air embolism.
Stop the infusion
Position the patient in left Trendelenburg
Call Rapid
Administer oxygen
Notify provider
A patient is receiving TPN with lipids piggybacked into the same line. What is the correct setup for the infusion and why is this important?
Lipids are typically Y-connected below the TPN filter using a 1.2-micron filter.