This state of matter has the least particle kinetic energy & particles simply vibrate in place.
What is a solid?
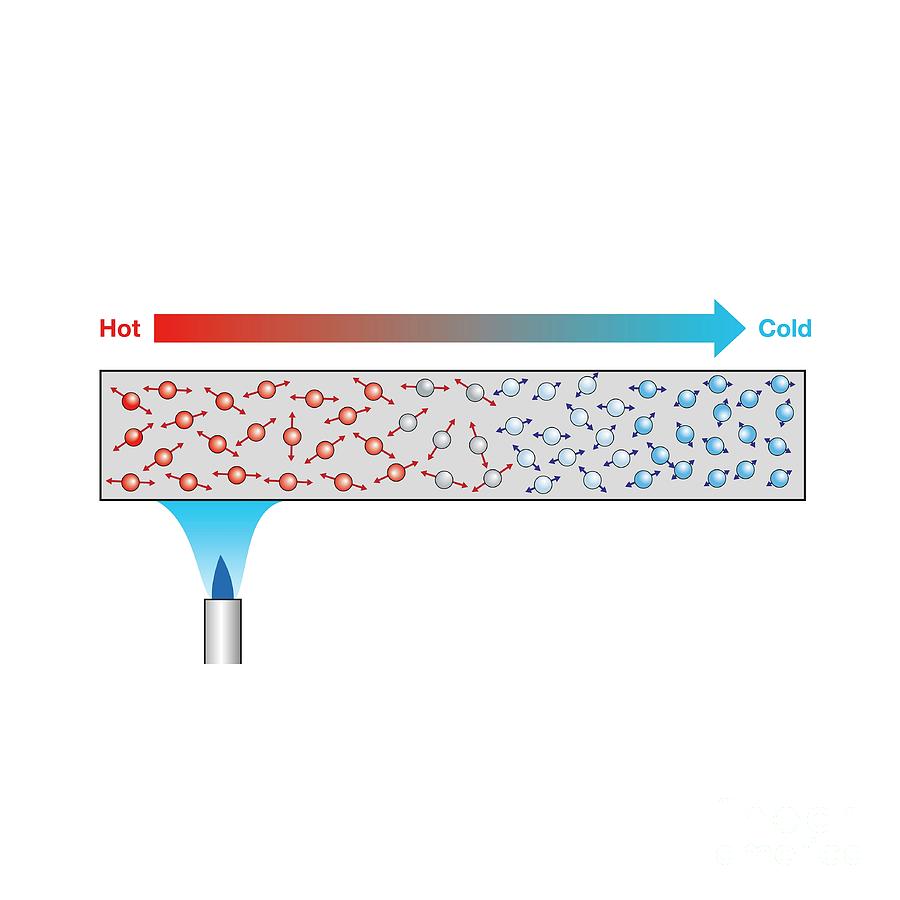
This method of heat transfer involves the direct contact of particles & is how the atmosphere is heated by the Earth's surface.
What is conduction?

The general term for the wearing away of rocks at the Earth's surface by wind & water.
What is weathering?
 At this type of plate boundary, plates slide past each other horizontally, often resulting in earthquakes.
At this type of plate boundary, plates slide past each other horizontally, often resulting in earthquakes.
What is a transfor boundary?
This is the name of the Earth's outer layer that is broken into several large and small pieces that move slowly over time.
What is the crust (lithosphere)?
This state of matter has particles that slide past each other and fit to fill their containers.
What is a liquid?
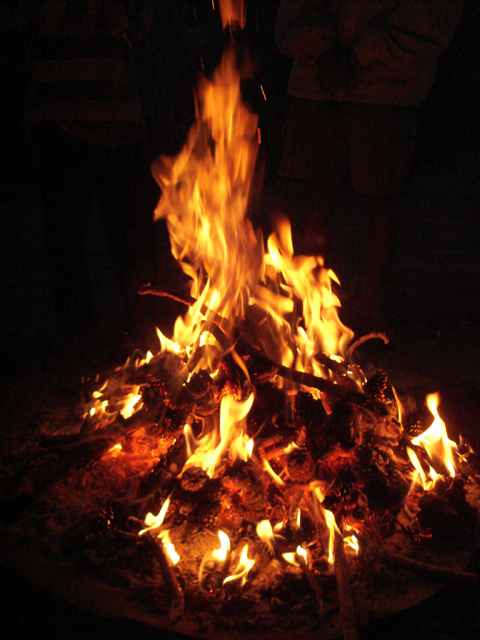

You feel the warmth of a campfire even though you're not touching the flames because of this type of heat transfer.
What is radiation?
Wind, water, and ice act as agents of this process, moving weathered material from one place to another.
What is erosion?
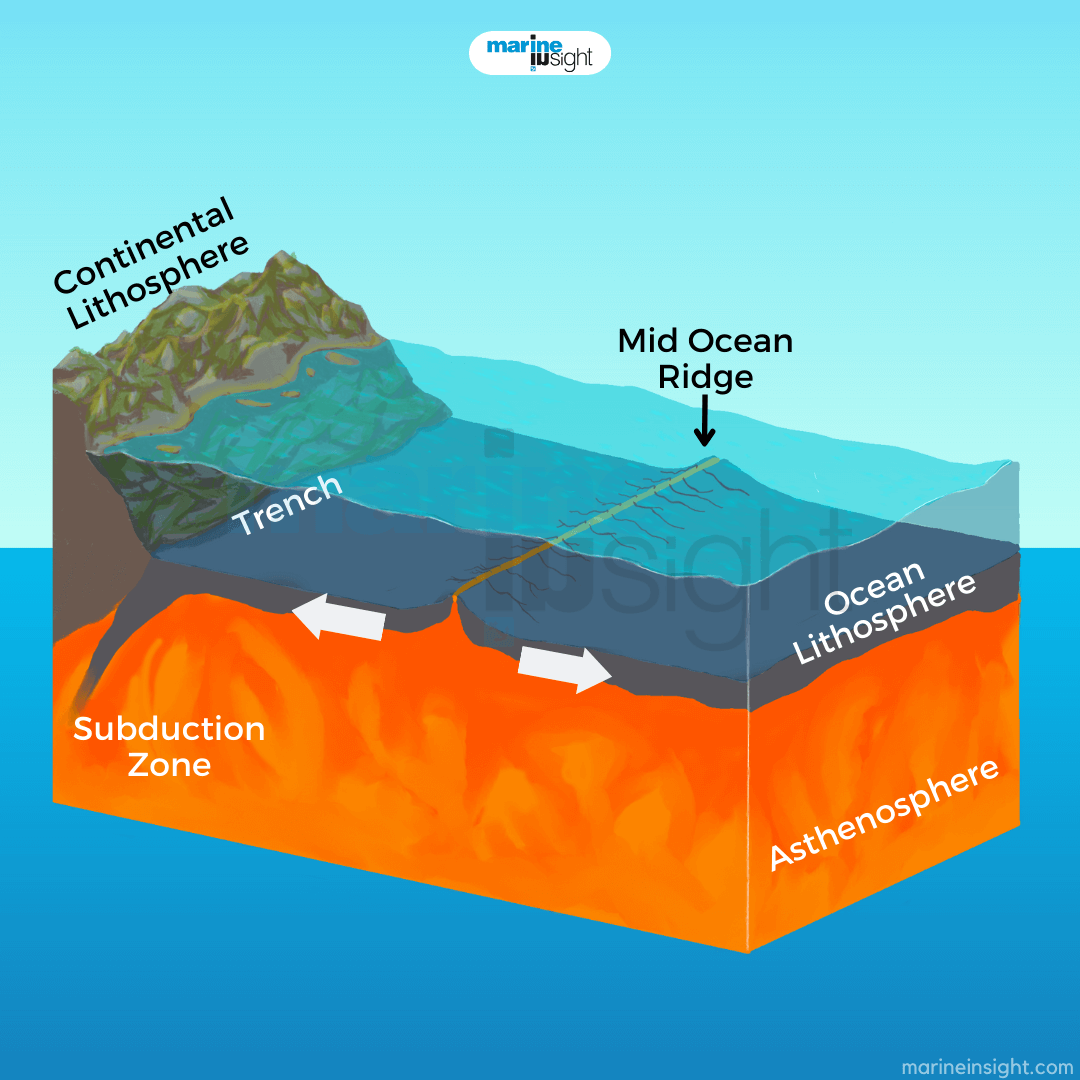
Mid-ocean ridges, where new crust is formed as plates move apart, are examples of this type of plate boundary.
What is a divergent boundary?
Located directly beneath the crust, this is the thickest layer of the Earth.
What is the mantle?
This state of matter has the most kinetic energy & expands to fill its container.
What is a gas?
In the Earth's atmosphere, heat is transferred through this method of heat transfer where hot air rises and cool air sinks.
What is convection?

The buildup of sediment in a river delta at the mouth of a river is an example of this surface process.
What is deposition?
Volcanic island arcs, like those found in Japan, are typically formed at this type of boundary, where two oceanic plates collide.
What is a convergent boundary?
This layer of the Earth is liquid and made of mostly iron and nickel - generates Earth's magnetic field.
What is the outer core?
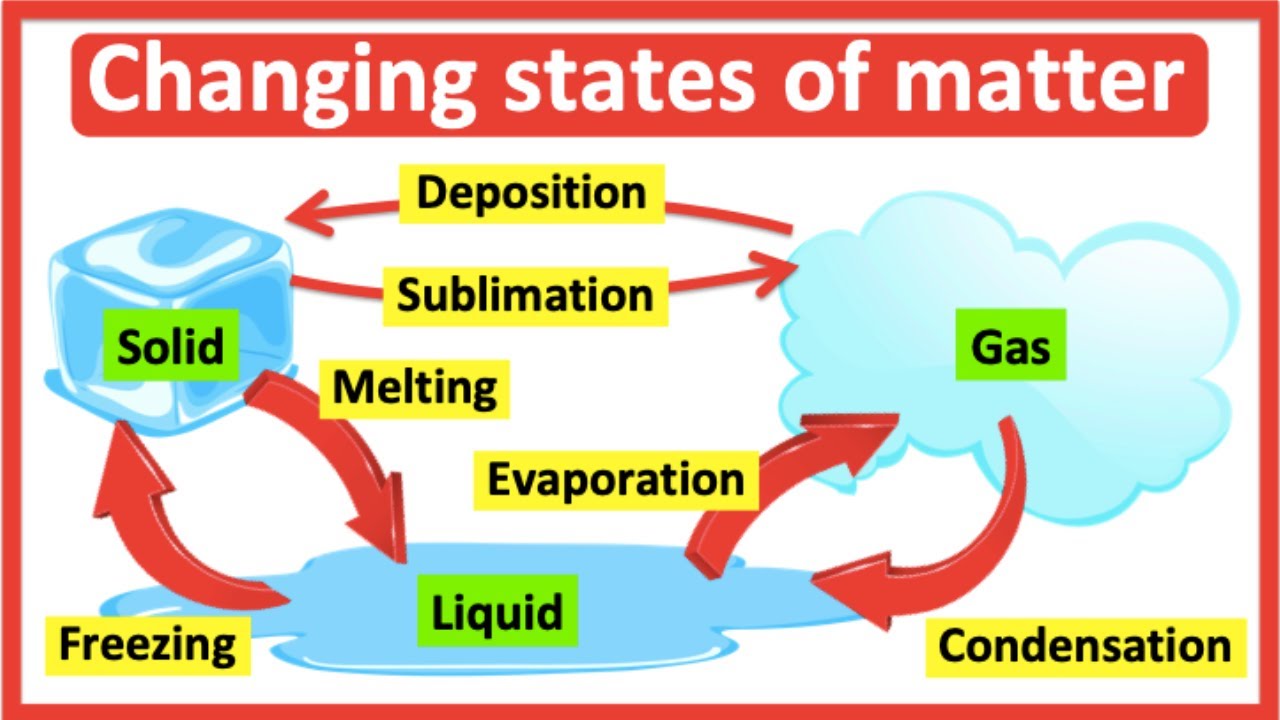
This is required for a phase change like condensation & freezing.
What is a decrease in thermal energy?

These materials are a poor conductor of heat, which is why we often use these materials for pot holders.
What is an insulator?
Windblown sand accumulates over time to create these shifting hills in deserts and along coastlines.
What are dunes?
The process where a denser oceanic plate slides beneath a less dense continental or oceanic plate is called this.
What is subduction?
This layer of the Earth is a solid sphere made of mostly iron and nickel and is the hottest layer of the Earth.
What is the inner core?

This is required for a phase change like evaporation & melting.
What is an increase in thermal energy?

The sun's energy travels through the vacuum of space as electromagnetic waves to Earth through this method of heat transfer.
What is radiation?
The continuous erosion by a river carves out this steep-sided valley.
What is a canyon?


The collision of two continental plates, without subduction, often resulting in formation of these large landforms, like the Himalayas.
What are mountains?
The mantle has this type of heat transfer where hot fluid rocks rise and cool fluid rocks sink.
What is convection (convection currents)?