The primary cell type responsible for gas exchange in the lungs.
What is a type 1 pneumocyte?
An immune-mediated disease caused by intermittent bronchoconstriction and airflow obstruction in response to environmental stimuli.
What is Asthma?
A lung disease most commonly caused by left heart pathology.
What is pulmonary hypertension?
The first-line treatment for asthma.
A high blood carbon dioxide level.
What is hypercapnia?
The mucin secreting cell in this image.
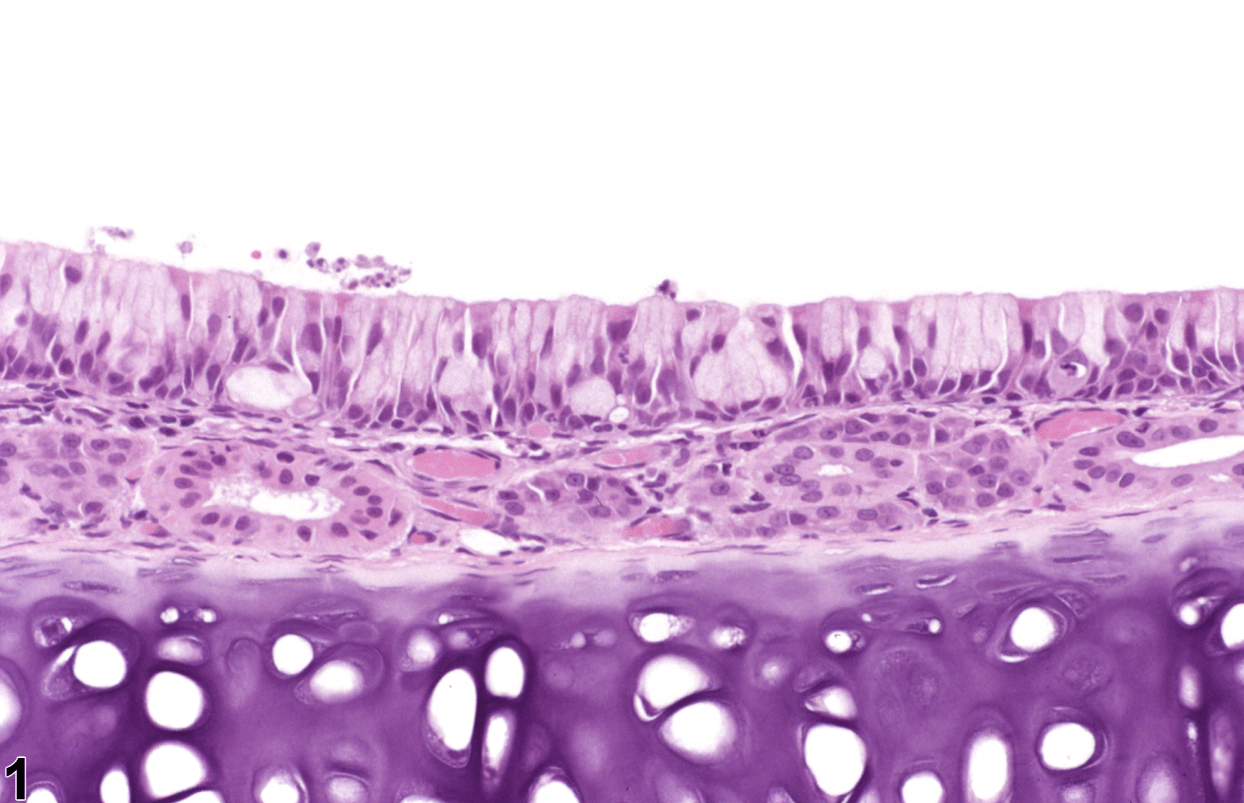
What is a goblet cell?
A lung disease caused by chronic inflammation from exposure to noxious particles.
What is COPD?
A lung disease that results in inflammation of the bronchi.
What is bronchitis?
A drug with a mechanism of action similar to a beta-2 agonist, but targeting the parasympathetic nervous system instead.
What is a muscarinic receptor (M3) antagonist?
A rapid, deep, and labored breathing pattern.
What is Kussmaul Breathing?
Destruction of the alveolar sacs.
What is emphysema?
A heterogeneous set of pulmonary disorders defined by restrictive patterns on spirometry.
What is restrictive lung disease?
A lung condition that may cause obstructive shock.
Ivacaftor, lumacaftor, and Orkambi.
What are the drugs that treat cystic fibrosis (CF)?
A condition in which part of the lungs receive oxygen without blood flow or blood flow without oxygen.
What is a V/Q mismatch?
A physiologic process where the pulmonary arteries constrict in response to hypoxia in the lung parenchyma.
What is Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction (HPV)?
A disorder causing cyanosis at birth that is associated with pulmonary venous flow.
What is total anamalous pulmonary venous return?
A lung disease that most commonly presents with shortness of breath, cough, hemoptysis, and weight changes.
What is lung cancer?
The most commonly inappropriately prescribed medication for bronchitis.
What are antibiotics?
Enlargement of the terminal phalanx that may indicate lung malignancy.
What is clubbing?
The phenomenon observed where the pressure-volume curve of the lung is different during inhalation and exhalation; at any given pressure, the lung volume is greater during exhalation.
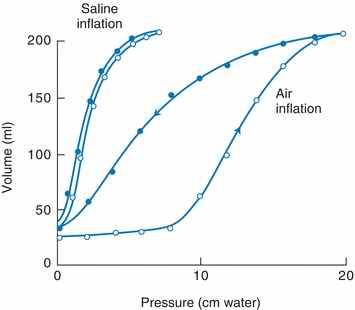
What is hysteresis?
A lung disease that may lead to distributive shock.
What is pneumonia?
A condition resulting in respiratory failure commonly associated with pinpoint pupils.
What is an opioid overdose?
Erlotinib (EGFR inhibitor), crizotinib (ALK inhibitor), and bevacizumab (VEGF monoclonal antibody).
What are biologic medications used to treat lung cancer?
A type of pulmonary function test in which someone enters a plastic box where machines measure how much air goes into and out of the lungs.