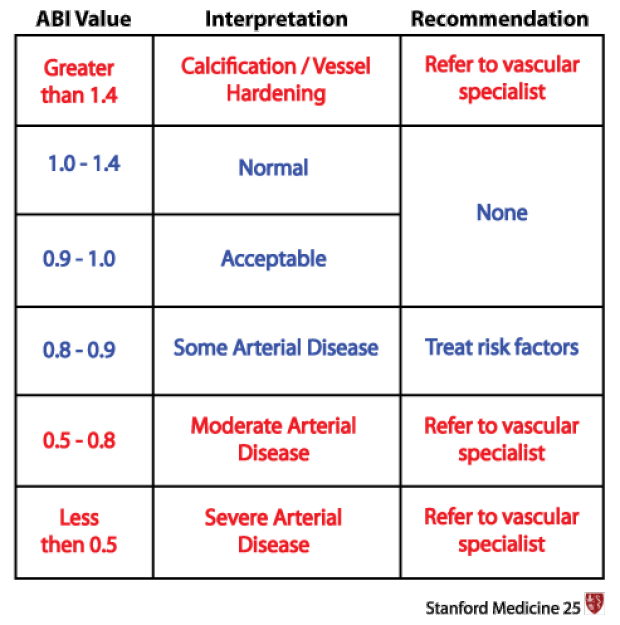
The ankle-brachial index (ABI) is considered abnormal below this threshold.
<0.9
This eponym describes the paradoxical rise in jugular venous pressure on inspiration, classically seen in constrictive pericarditis.
Kussmaul sign
This paradoxical tissue Doppler finding—medial e′ velocity exceeding lateral e′ velocity—is seen in constrictive pericarditis
Annulus reversus
What is the problem with this dual chamber pacemaker?
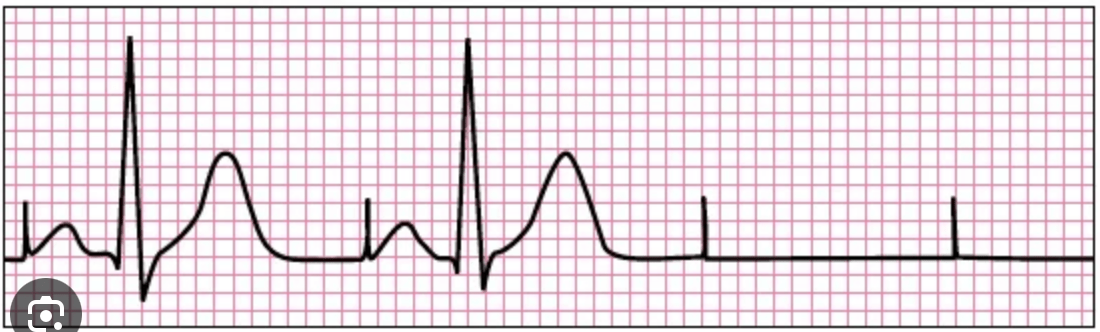
Failure to capture
Calculate the corrected QT interval using the bazett formula if the QT interval is 450 ms at a heart rate of 60 bpm.
450 ms (same)
The hepatic artery is a branch off of which artery?
Celiac trunk
In congenitally corrected transposition of the great arteries (L-TGA), this conduction abnormality develops in up to 30% of patients by adulthood.
Complete heart block
Associated with 22q11 deletion, this syndrome features conotruncal anomalies such as tetralogy of Fallot and interrupted aortic arch.
DiGeorge syndrome
This vascular syndrome results from compression of the left common iliac vein by the right common iliac artery.
May-Thurner Syndrome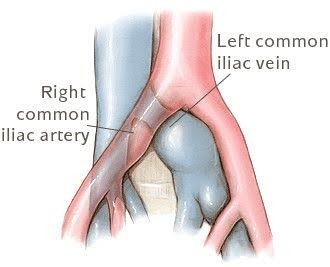
Head bobbing with each heartbeat, seen in aortic regurgitation
de Musset's sign
This echocardiographic parameter is defined as the slope of early diastolic transmitral inflow and reflects LV compliance.
Deceleration time

This funny sounding acronym can be adjusted to prevent pacemaker mediated tachycardia from recurring
Increase the PVARP

What is the simplified equation to calculate "strain" on echocardiography

This X-ray finding can be seen as a clue suggesting coarctation of aorta
Rib notching and the “figure 3 sign"

This congenital lesion results in a “snowman” appearance on chest X-ray
Total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)

Includes coarctation of the aorta, sub aortic stenosis, and parachute mitral valve
Shone complex (syndrome)
Also supravalvular mitral membrane and LVH as well as LV hypoplasia
After an EVAR, the two most common vessels causing type 2 endoleaks are (name 1)
Lumbar arteries and inferior mesenteric artery

This three cardiologist named sign refers to the dynamic LVOT obstruction/gradient in the setting of PVCs in Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy.
Brockenbrough-Braunwald-Morrow sign
The decrease in pulse pressure after a PVC or extrasystole is due to the following:
- The increased inotropy (contractility) of the heart after the extrasystole, along with the reduced afterload (pressure the heart must pump against), exacerbates the LVOT obstruction.
- This leads to a significant increase in left ventricular systolic pressure, but the arterial pulse pressure may paradoxically decrease due to the increased obstruction
In prosthetic aortic valve evaluation, this Doppler parameter helps differentiate patient-prosthesis mismatch from prosthetic stenosis
Acceleration time
In Long QT Syndrome, this subtype carries the highest risk of cardiac events during sleep or rest
LQT3 (SCN5A mutation)
This formula (name it) is used to calculate the aortic valve areas during cardiac catheterization
Gorlin formula

In the bovine aortic arch variant, the left common carotid artery has this location
LCC off the right brachiocephalic artery or shared
True:

This type of tumor is associated with tuberous sclerosis. Don't resect it, they almost always regress spontaneously.
Cardiac rhabdomyomas in infants
This autosomal dominant syndrome includes prolonged QT interval, ataxia, and intermittent attacks of muscle weakness or paralysis.
Andersen-Tawil syndrome
"Hypokalemic periodic paralysis" can be treated with acetazolamide
Associated with bidirectional VT

In vascular ultrasound, this is the percentage cutoff attributed to a PSV ratio of greater than 4, or to describe severe stenosis in the renal arteries?
60%
This syndrome refers to upper extremity venous thrombosis often caused by repetitive activity, such as in athletes.
Paget-Schroetter syndrome
The "modified" Bernoulli equation ignores what 3 other forces/factors? Name 2 of them.
Viscous losses (frictional forces due to blood viscosity)
Inertial forces
Changes in momentum due to accelerating or decelerating flow
Proximal velocity (v₁) when it’s small relative to distal velocity (v₂)
Gravitational energy differences
This vagally mediated reflex may cause paradoxical worsening of hypotension when bradycardia is treated with pacing.
Bezold–Jarisch reflex
(Not Jarisch–Herxheimer reaction, Adam)
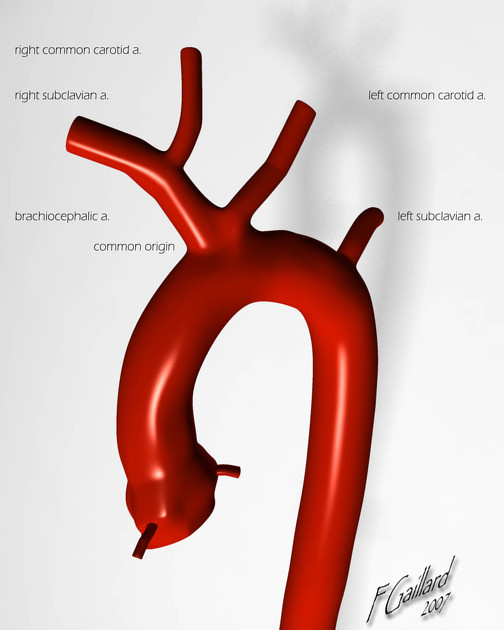
A patient has an PW LVOT velocity of 2 m/s and an CW aortic valve velocity of 4 m/s. What is the aortic valve gradient?
48 mmHg
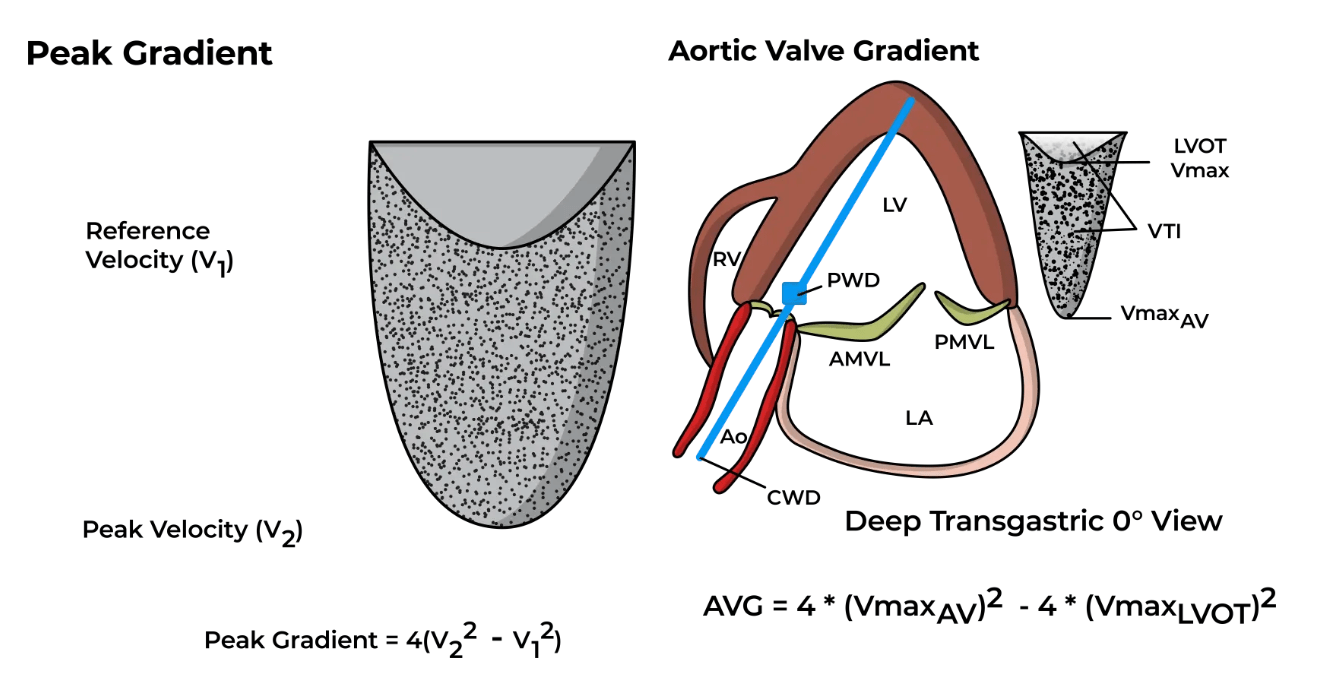
This vascular anomaly results from this vessel encircling the trachea and esophagus.
double aortic arch
This angiographic sign, classically described as a “gooseneck deformity,” is seen due to elongation and narrowing of the left ventricular outflow tract and leftward displacement of the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve found in this condition.
Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD), also known as endocardial cushion defect
This X-linked syndrome involves immunodeficiency, eczema, thrombocytopenia, and a risk of vasculitis and coronary artery aneurysms.
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
What is the most common site of peripheral artery aneurysms?
Popliteal Artery
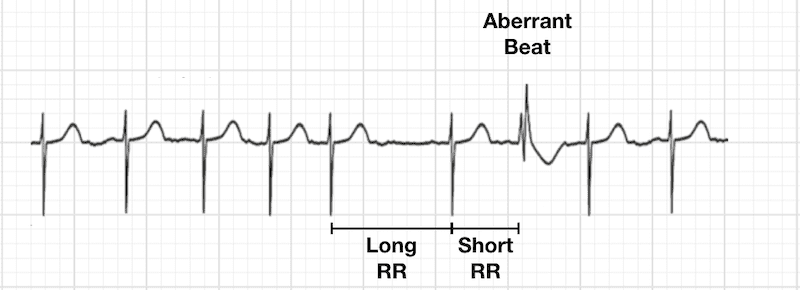
This phenomenon describes aberrant ventricular conduction, usually of right bundle branch block morphology, following a short RR interval and a preceding relatively long RR interval
Ashman phenomenon
Name 5 ways to quantify RV function (15 second timer)
TAPSE, S' Velocity, RV FAC, RIMP (Tei), 3D RVEF, RV Free wall strain
When ventricular lead noise mimics ventricular fibrillation, how might a device discriminate between the two?
Comparing near-field and far-field electrograms, lead integrity alert (LIA) or noise discrimination algorithm (rate stability/onset)
The law of Laplace states that if the wall thickness doubles, the wall stress.....
Halves
σ = (P × r) / (2h), the Law of Laplace, where σ = wall stress, P = pressure, r = radius, and h = wall thickness
Due to compression of this vein between these two structures, patients will present with hematuria and flank pain, often called "nutcracker syndrome"
Compression of the left renal vein between the aorta and SMA

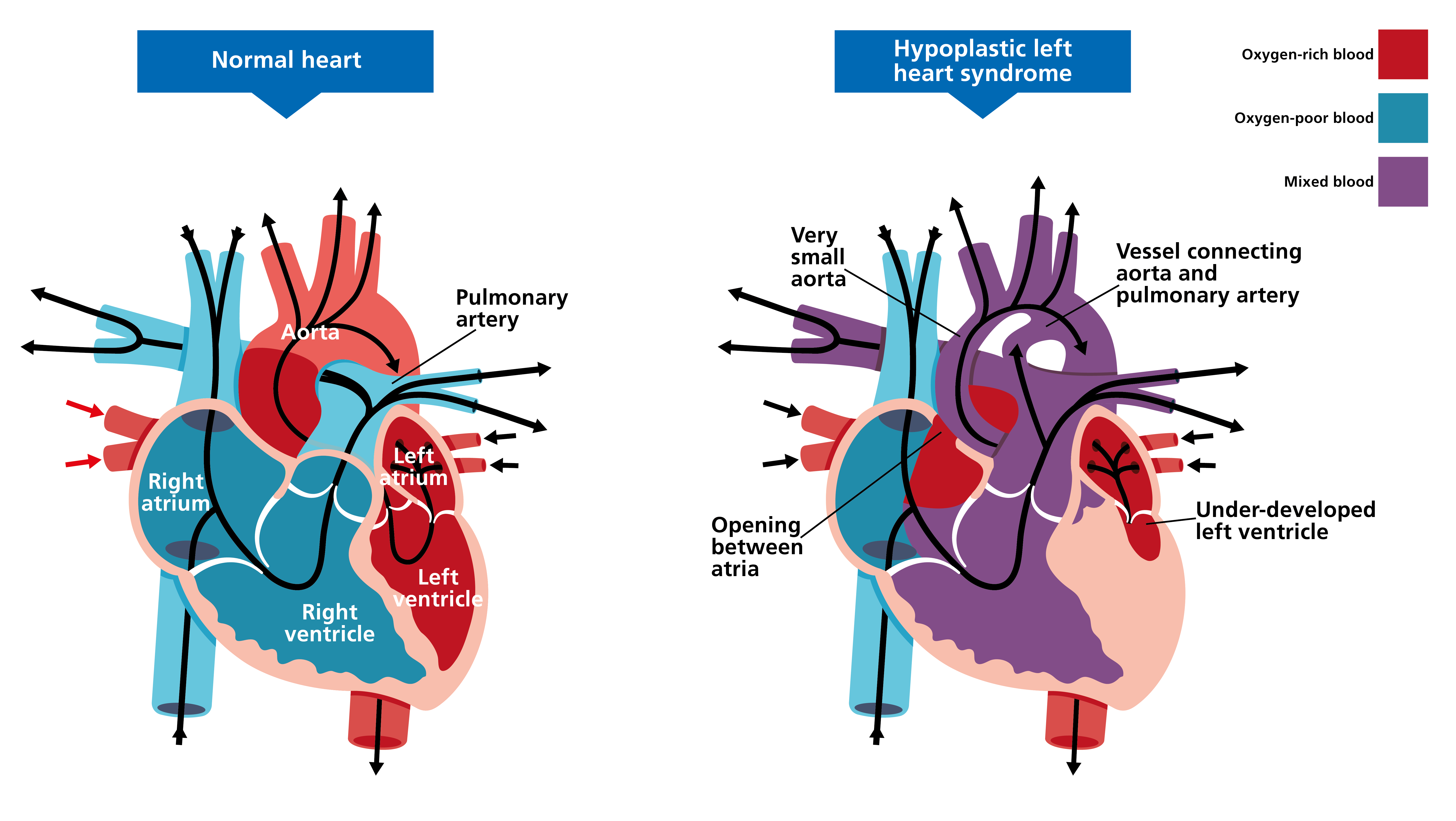
In hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS), survival after birth depends on patency of these two key structures
Ductus arteriosus and atrial septal defect (or foramen ovale)
This rare X-linked disorder causes cardiomyopathy, neutropenia, and growth retardation.
Barth Syndrome