Stance phase
Swing phase
What is the most common acquired pediatric upper limb deficiency?
Left terminal transradial
Name that K level
The patient has the ability or potential for ambulation with variable cadence. Typical of the community ambulator who has the ability to traverse most environmental barriers and may have vocational, therapeutic, or exercise activity that demands prosthetic utilization beyond simple locomotion.
K3
List the 5 parts of the motor unit
Anterior horn cell
Motor nerve axons
Peripheral nerve
NMJ
Muscle fibers
This spontaneous activity is regular, and derived from a single muscle fiber. Sound like rain on a roof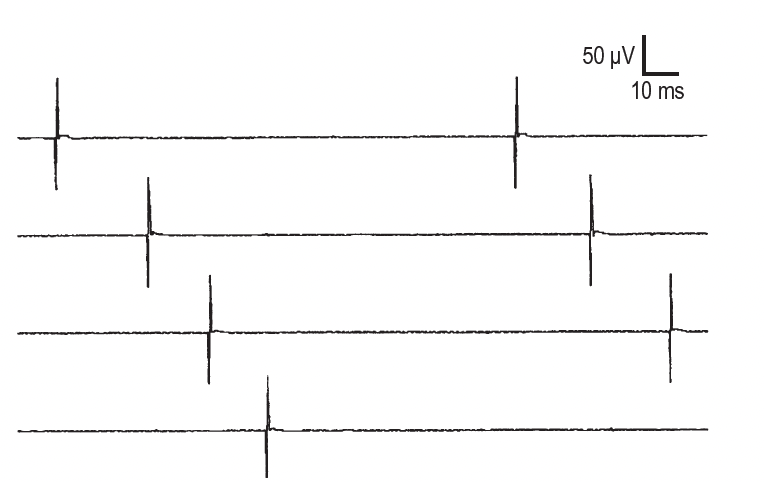
What is the appropriate sizing for walker fit in relation to the upper extremity?
~ 20 deg elbow flexion in upright standing
What % of gait cycle is spent in double limb support?
This is the most common primary malignant bone tumor in children, commonly occurring in the knee and proximal humerus.
Osteosarcoma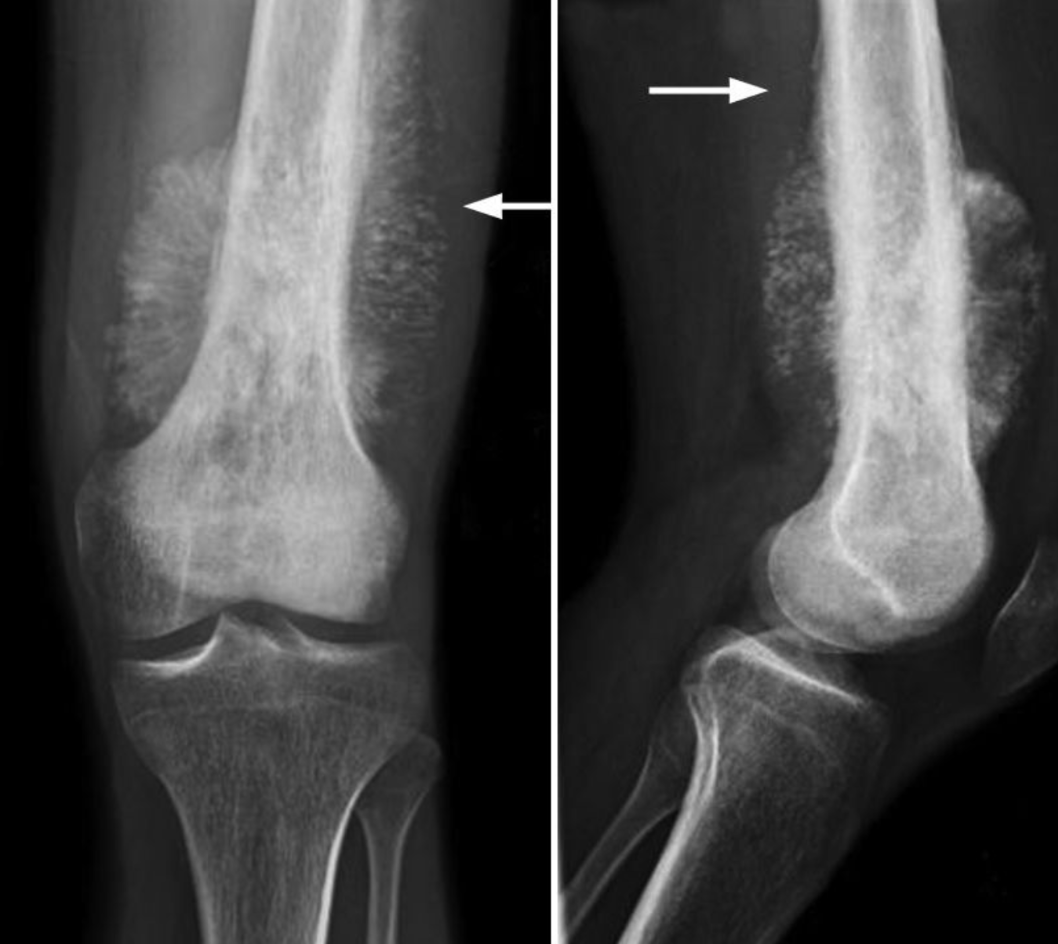
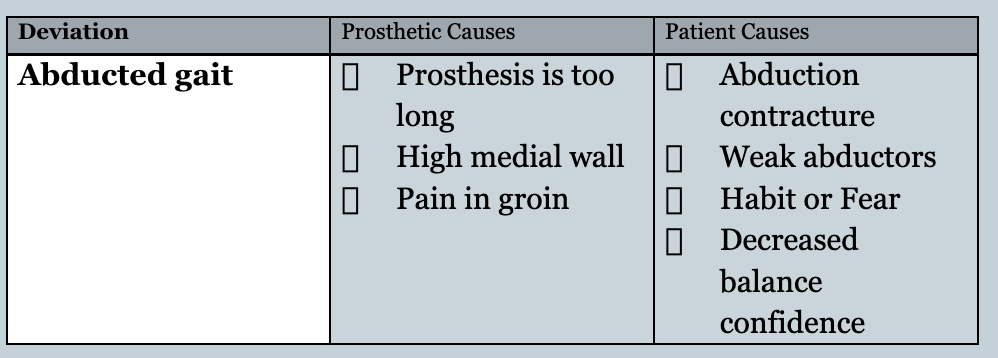
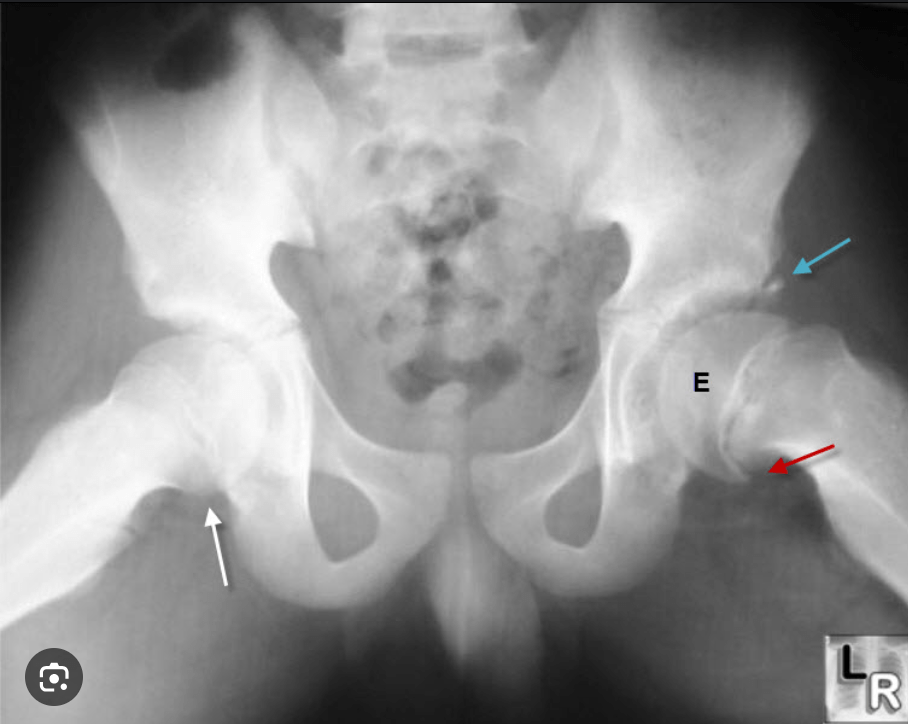
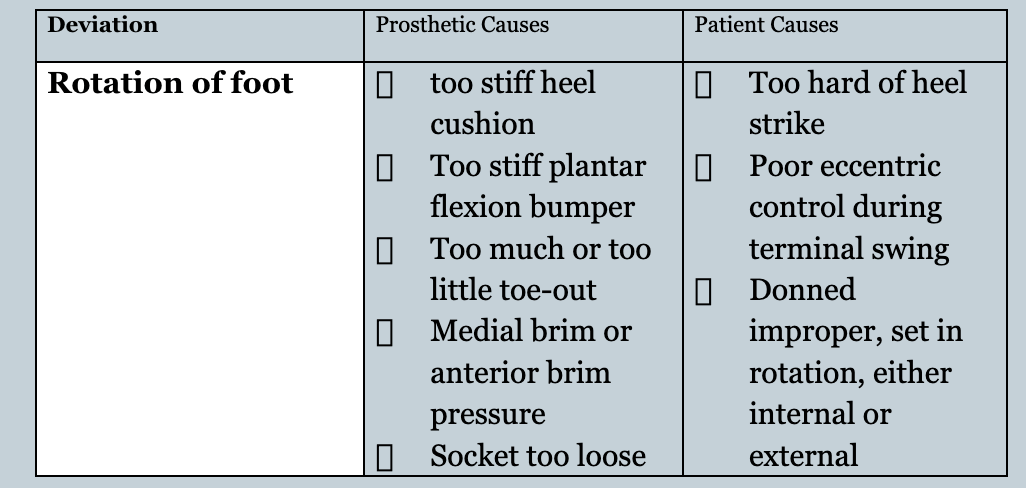
Name 1 prosthetic and 1 patient cause for an abducted gait
What is considered normal conduction velocity in the upper extremity?
Lower extremity?
Upper extremity >50 m/sec
Lower extremity >40 m/sec
This type of spontaneous activity is from multiple muscle fibers time-linked together and is stable in nature
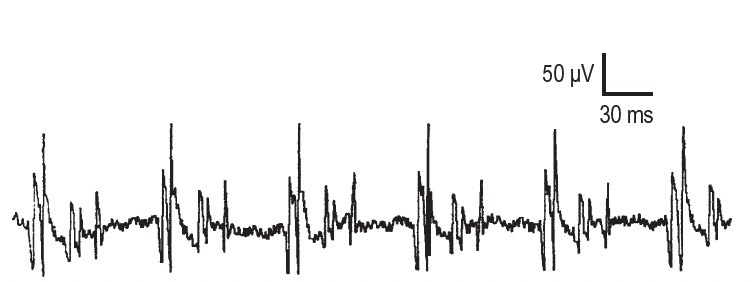
Complex repetitive discharge
What is the most common hip disorder of preadolescence and adolescent children which involves proximal epiphysiolysis?
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis.
More common boys>girls, physis on involved side is wider and irregular on XR
What are the 5 subdivisions of stance phase?
Initial contact
Loading response
Midstance
Terminal Stance
Preswing
"I Like My Team Presweetened"
A prosthetic replacement is recommended yearly until 5 years of age. Between ages 5-12, how frequently does a prosthetic need to be replaced?
Every 18 months
How much increased metabolic cost above normal is a vascular transtibial bka?
Give a %, closest to % wins the points
(Price is right rules)
40%
AND
Lower limbs?
Normal is
32 degrees centigrade in upper limbs
30 degrees centigrade in lower limbs
Irregular, hissing, seashell ar 20-40 Hz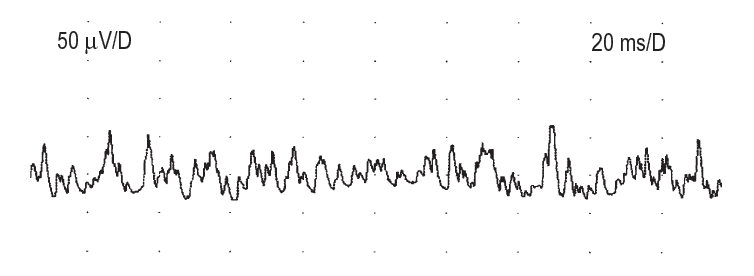
Endplate noise
Name the seddon classification:
Nerve crush injury
Axonal interruption. Connective tissue/schwann cell ntact.
Conduction looks like neuropraxia for 4-5 days, until wallerian degeneration occurs
Name 2 determinants of gait
1. Pelvic rotation
2. Pelvic tilt
3. Knee flexion in stance
4. Foot mechanisms (ankle extension/flexion mechanisms)
5. Knee mechanisms
6. Lateral displacement of the pelvis
What's the latest month baby should be able to sit upright?
9 months
How much increased metabolic cost above normal is a vascular transfemoral AKA?
Give a %, closest to % wins the points
(Price is right rules)
100%
These biphasic single muscle fiber action potentials are triggered by needle movement, percussion or voluntary contraction. Wax and wane in rhythm, Sound like dive bomber and can be caused by chronic radiculopathy, peripheral neuropathy, myotonic dystrophy, acid-maltase deficiency, propranolol use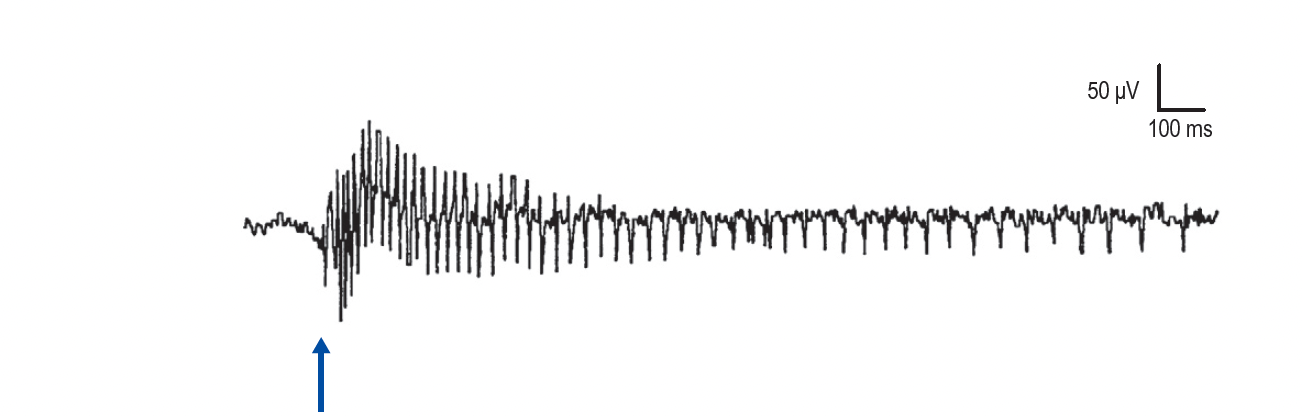
Myotonic discharge
What nerve is being tested in this picture?
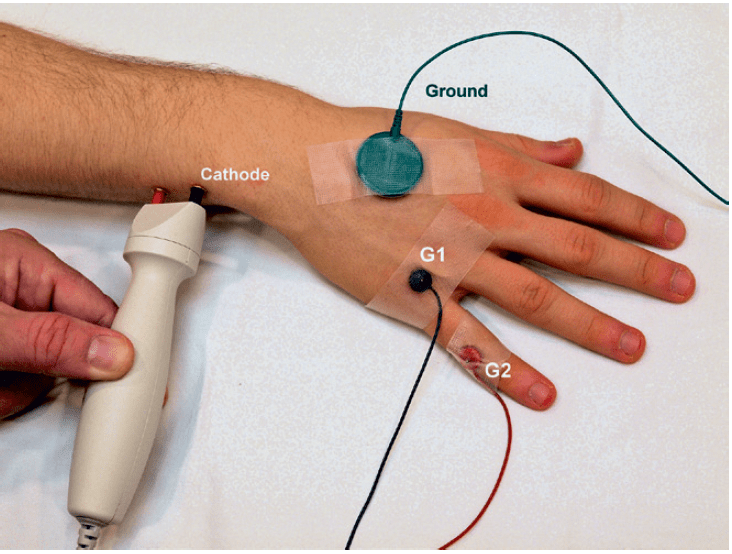
Dorsal ulnar cutaneous n
Which of the following describes the typical location of the center of gravity in an adult
Need a measurement in cm
Need a vertebral level
5 cm anterior to the 2nd sacral vertebra
Name 1 prosthetic or patient cause for the gait deviation of excessive foot rotation
Name that milestone (closest age by months will win)
Begins running, jumps on both feet in place, two word phrases are common,
2 years
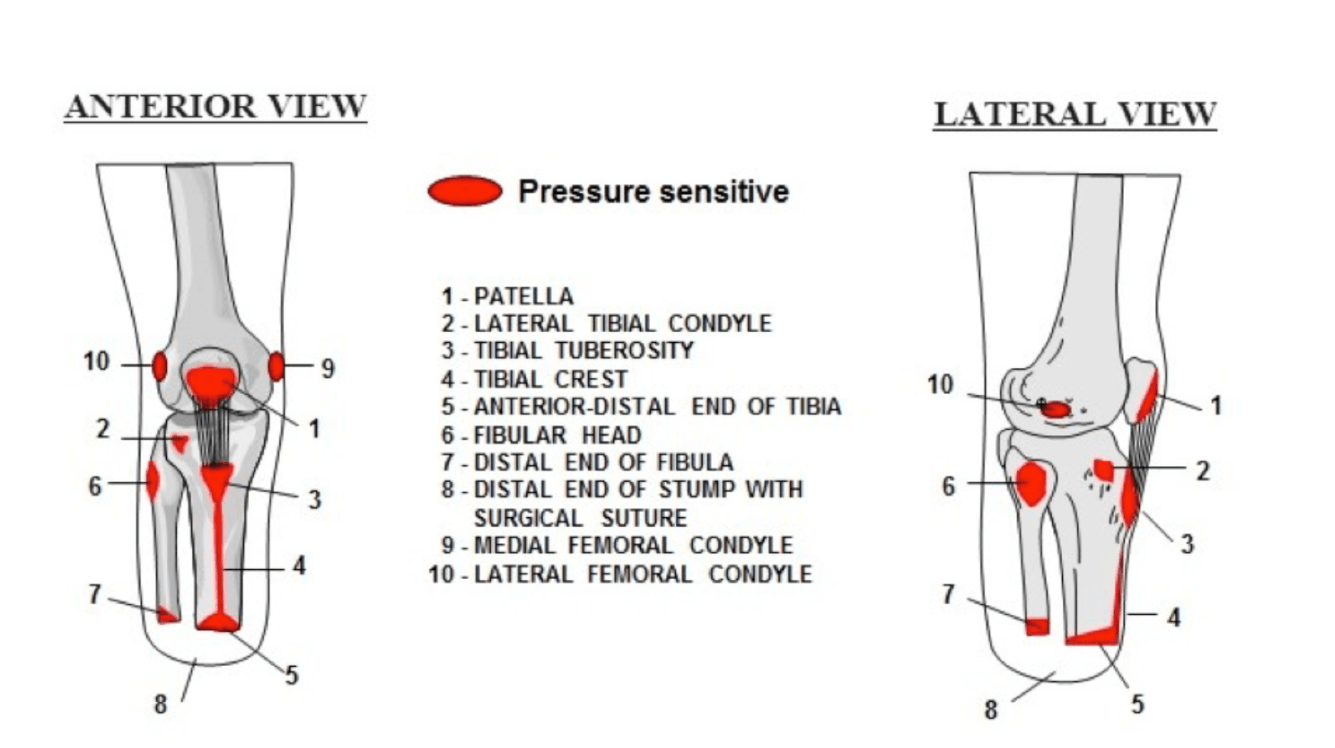
Name 3 pressure sensitive regions in the lower extremity when fitting a below the knee amputation?
1. Tibial crest, tubercle, condyles
2. Fibular head
3. Distal tibia and fibula
4. Hamstring tendons
5. Patella
Name the Seddon Classification:
Nerve compression injury
Axon is intact, local injury to myelin
Signal normal with stimulation distal to the lesion but abnormal proximal to it
Neuropraxia
Froment's Sign tests what nerve lesion and what muscle(s) affected?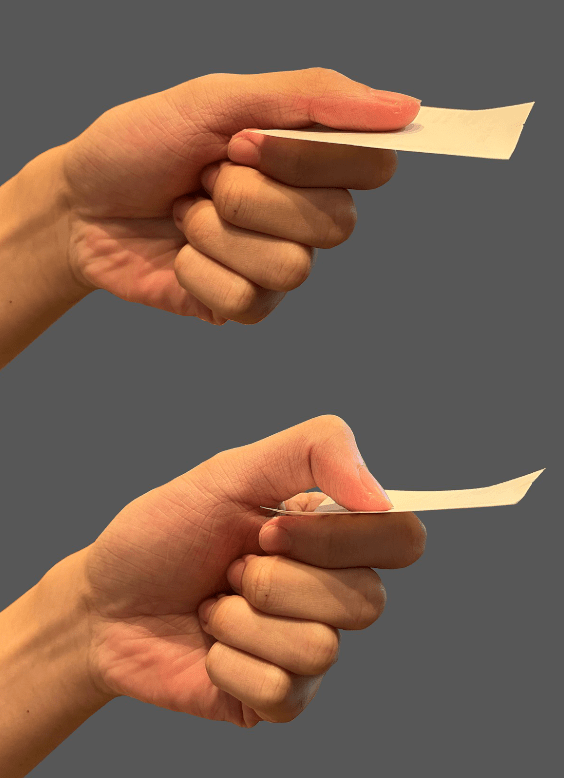
Nerve lesion of the ulnar nerve demonstrates inability to hold piece of paper with thumb and index finger with pure thumb adduction (adductor pollicis) weakness.
Leads to using median nerve innervated flexor pollicis longus to flex the interphalangeal (IP) jointInheritance: X linked recessive
Gene locus: Xp21