Creek
Primary contracture is mediated by _________ in the _________.
Secondary contracture is mediated by _________.
Primary contracture is mediated by elastin in the dermis.
Secondary contracture is mediated by myofibroblasts.
Random-pattern flaps must generally be limited to a __:__ length to width ratio to remain viable at the tip.
Random-pattern flaps must generally be limited to a 3:1 length to width ratio to remain viable at the tip.

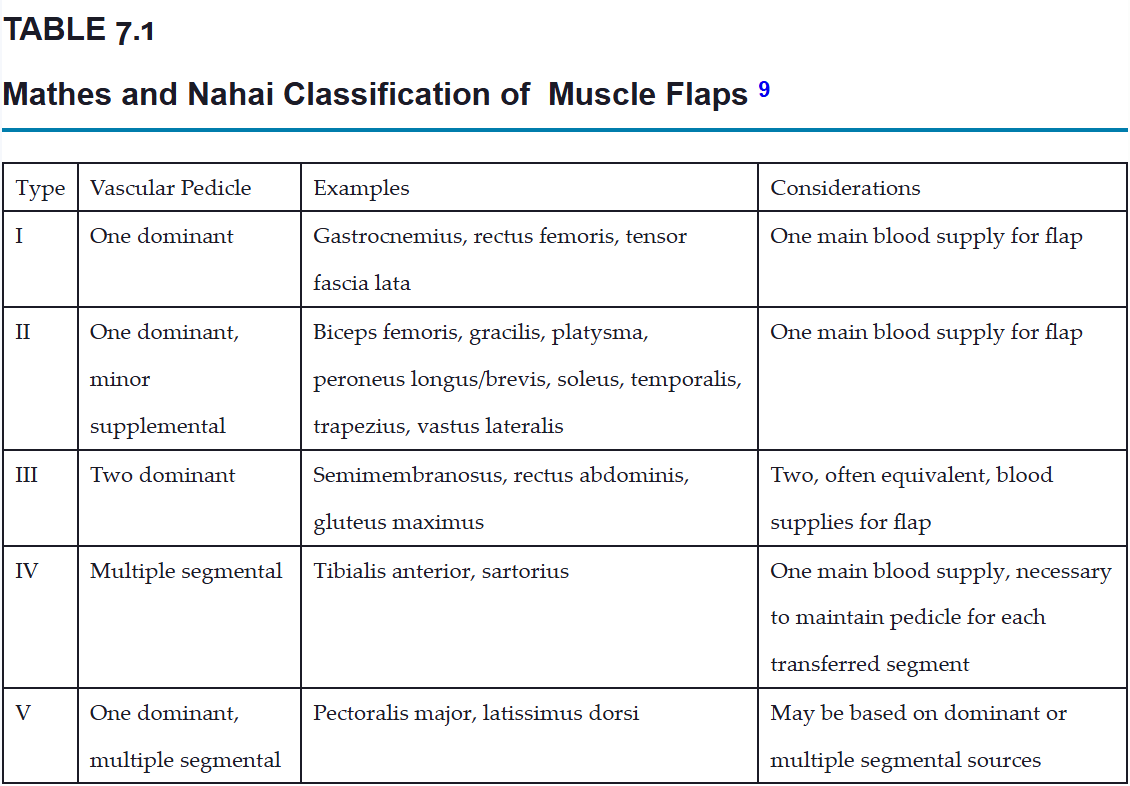
Describe the 5 types in the Mathes and Nahai classification.
Name the historical phases of engraftment AND their time frame.
Imbibition (0-48 hrs)
Inosculation (48-72 hrs)
Revascularization (> 96 hrs)
Name 5 causes of graft failure.
- Hematoma
- Seroma
- Infection
- Shear forces
- Poorly vascularized wound bed
- Patient medical co-morbidities: DM, PVD, hx radiation
__________ are the dominant cell type in the epidermis.
__________ are the dominant cell type in the dermis.
Keratinocytes are the dominant cell type in the epidermis.
Fibroblasts are the dominant cell type in the dermis.
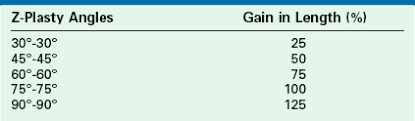
A Z-plasty angle of 75 degrees will create a gain in length of ___%.
A Z-plasty angle of 75 degrees will create a gain in length of 100%.
The gracilis is expected to run 2-3 cm posterior to the palpable adductor longus when a patient is in a frog leg position.

In 1984, Pruitt and Levine detained the attributes of an ideal skin substitute. Name 5 of these attributes.
- Little or no antigenicity
- Tissue compatibility
- Lack of toxicity, either local or systemic
- Permeability to water vapor just like normal skin
- Impenetrability to microorganisms
- Rapid and persistent adherence to a wound surface
- Porosity for ingrowth of fibrovascular tissue from the wound bed
- Malleability to conform to an irregular wound surface
- Elasticity for motion of underlying tissues
- Structural stability to resist linear and shear stresses
- A smooth surface to discourage bacterial proliferation
- Sufficient tensile strength to resist fragmentation
- Biodegradability
- Low cost
- Ease of storage
- Indefinite shelf life
What is the main bacteria of concern in leech therapy and what are 2 antibiotics that can be used for prophylaxis?
Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas caviae
Cephalosporins (e.g. cefazolin) and Ciprofloxacin
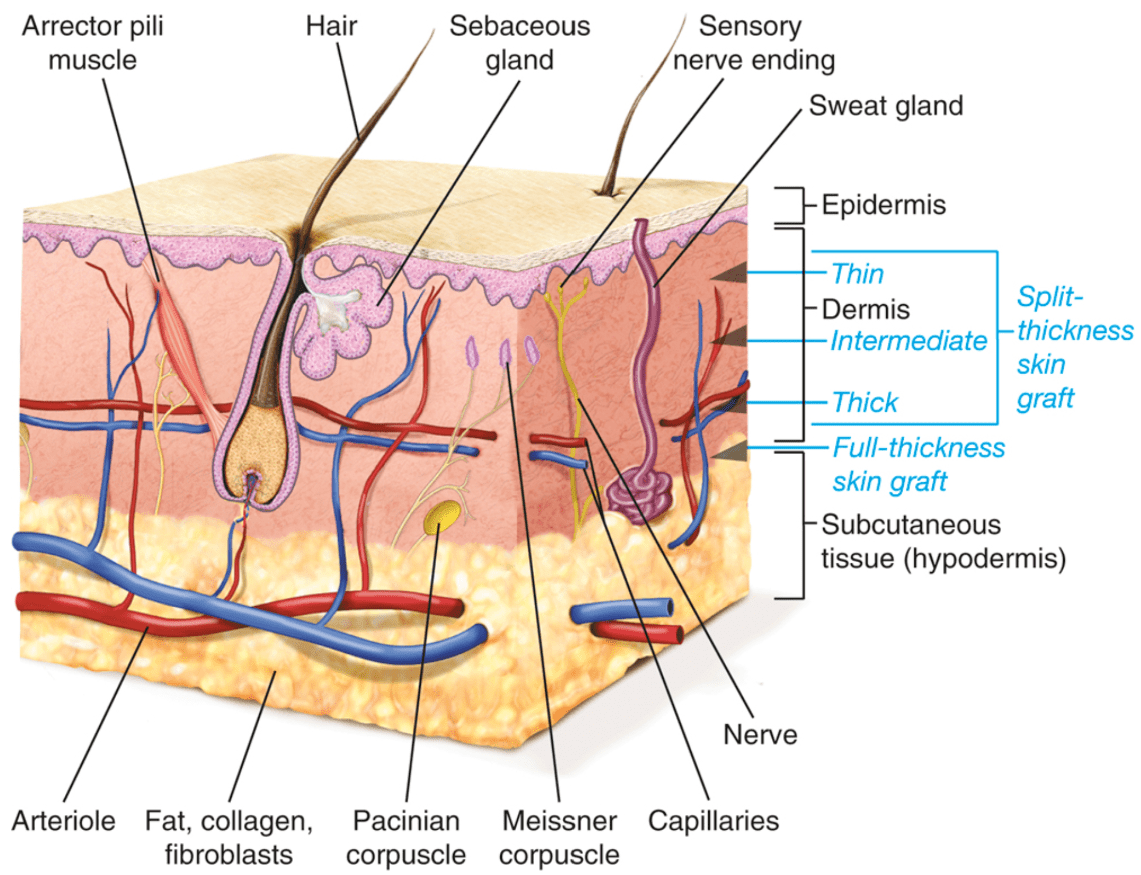
What are the layers of the epidermis (superficial to deep)?
Stratum corneum
Stratum lucidum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum basale
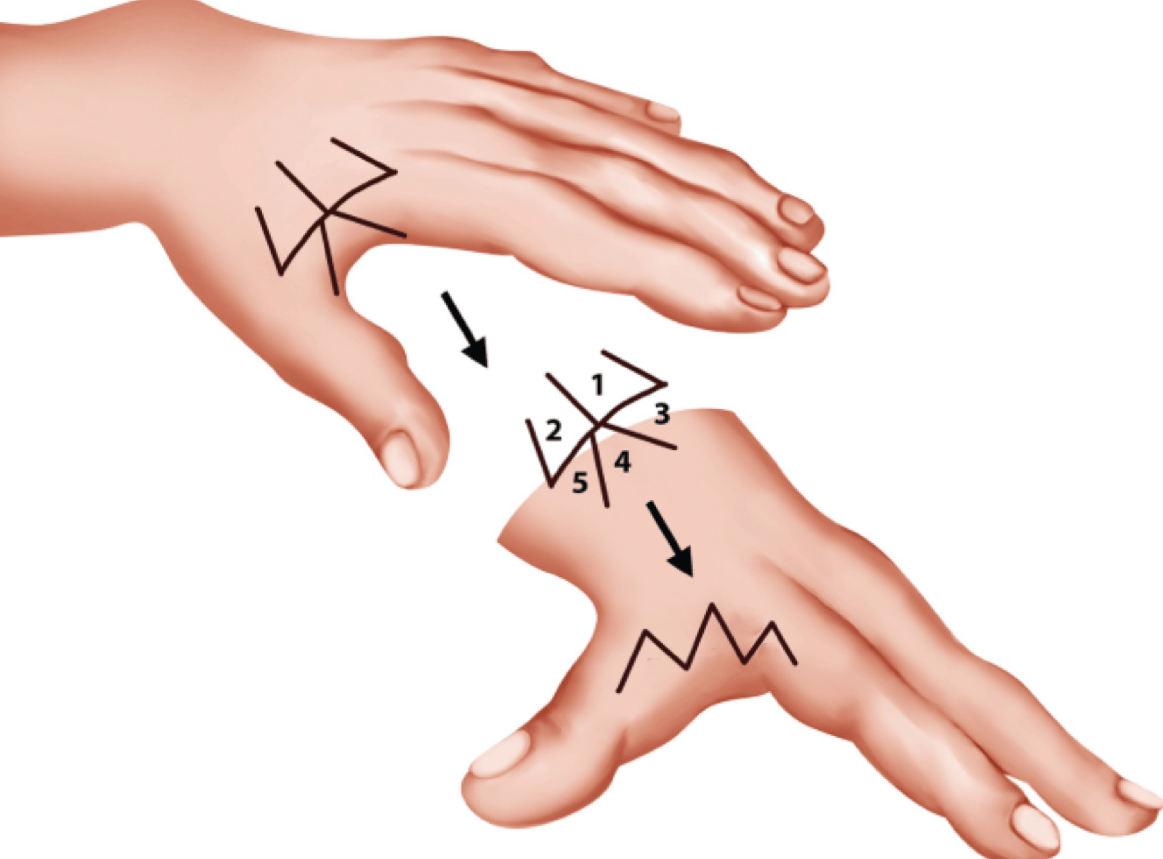
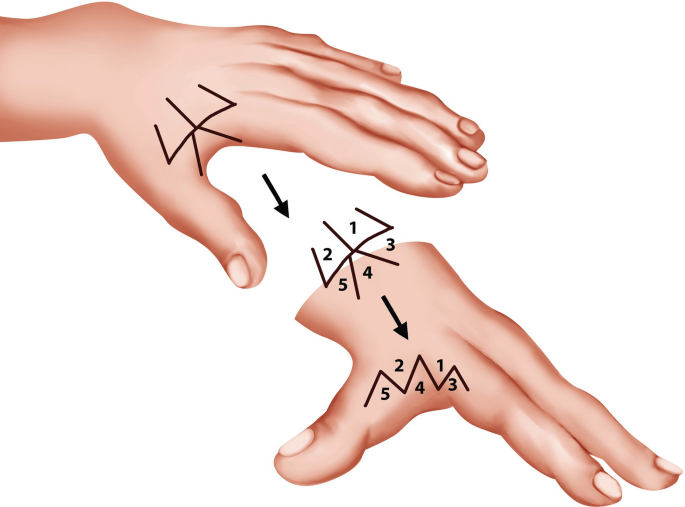
Describe the jumping man flap and to where the numbered flaps transpose.
Name 2 examples of type III muscle flaps and their blood supply.
Type III - 2 dominant branches
Semimembranosus - profunda femoris, popliteal artery
Rectus abdominis - superior and inferior epigastric arteries
Gluteus maximus - superior and inferior gluteal arteries
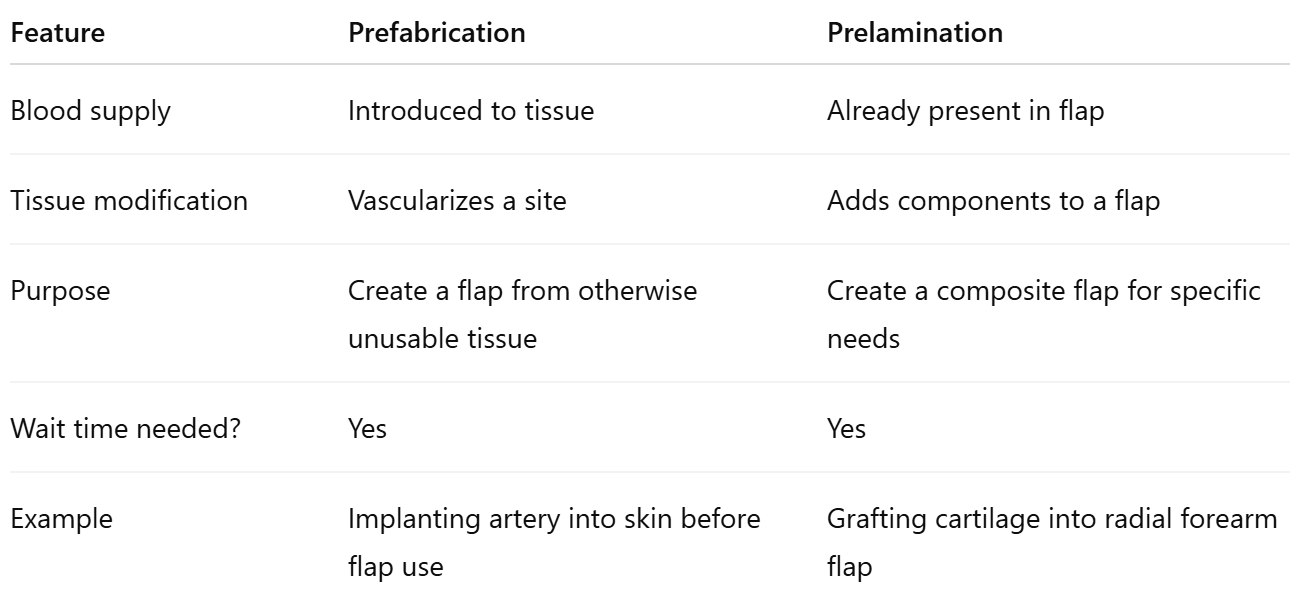
Describe the difference between prelamination and prefabrication.
Prelamination - Implantation of tissue (usually bone or cartilage) or an alloplastic device into a vascular territory prior to transfer. Mainly used for reconstruction of complex defects in the central third of the face.
Prefabrication - transferring a vascular pedicle into a desired block of tissue, then waiting 8 weeks for spontaneous neovascularization, thus creating a new vascular territory not previously found in nature. After maturation, the neovascularized tissue is transferred based on the implanted pedicle. This technique has been used to provide thin axial flaps and to transfer tissue with enhanced color and texture match.
What is a white blood clot composed of in free flap surgery?
Platelets and fibrin without a significant number of red blood cells
Name 4 characteristics of split thickness skin grafts when compared to full thickness grafts.
STSG:
- Less primary contracture
- More secondary contracture
- More pigment changes
- More susceptible to trauma
- Lower metabolic demand of the recipient site wound bed
What is the most common complication of local flaps in the nasal subunit?
Trapdoor deformity

Vascularized bone autografts are superior to non-vascularized bone graft in defects over __ cm.
5 cm
In regards to early incorporation, bone hypertrophy, mechanical strength, and osseous mass retention.
Name the pioneer of ReCell Autologous Cell Harvesting Device.
Dr. Fiona Wood

Name two systemic complications associated with dextran administration.
- Renal failure
- Pulmonary edema
- Congestive heart failure
Dextran has no effect on flap survival, but a 3.9-7.2-fold increase in systemic complications.
What percentage of original collagen in a skin graft is replaced within 5 months of grafting?
85%
Although STSG replace only half as much of their original collagen compared with FTSG of the same size.
When was the keystone flap first described and what local flap does it build from?
2003 by Behan
Two opposing V-Y flaps oriented parallel to the longitudinal axis of the defect
Name 5 examples of type II muscle flaps.
Type II - 1 dominant, minor supplemental
- Biceps femoris
- Gracilis
- Platysma
- Peroneus longus/brevis
- Soleus
- Temporalis
- Trapezius
- Vastus lateralis
The first documented skin graft was in _____ approximately _____ years ago.
The first documented skin graft was in India approximately 3000 years ago.
Full-thickness skin grafts were harvested from the gluteal region for nasal reconstruction after amputation (a common punishment for criminals).
What is steal syndrome in microsurgery?
When a side branch of the recipient artery is inadvertently included in the anastomosis, leading to blood flow being diverted away from the flap.