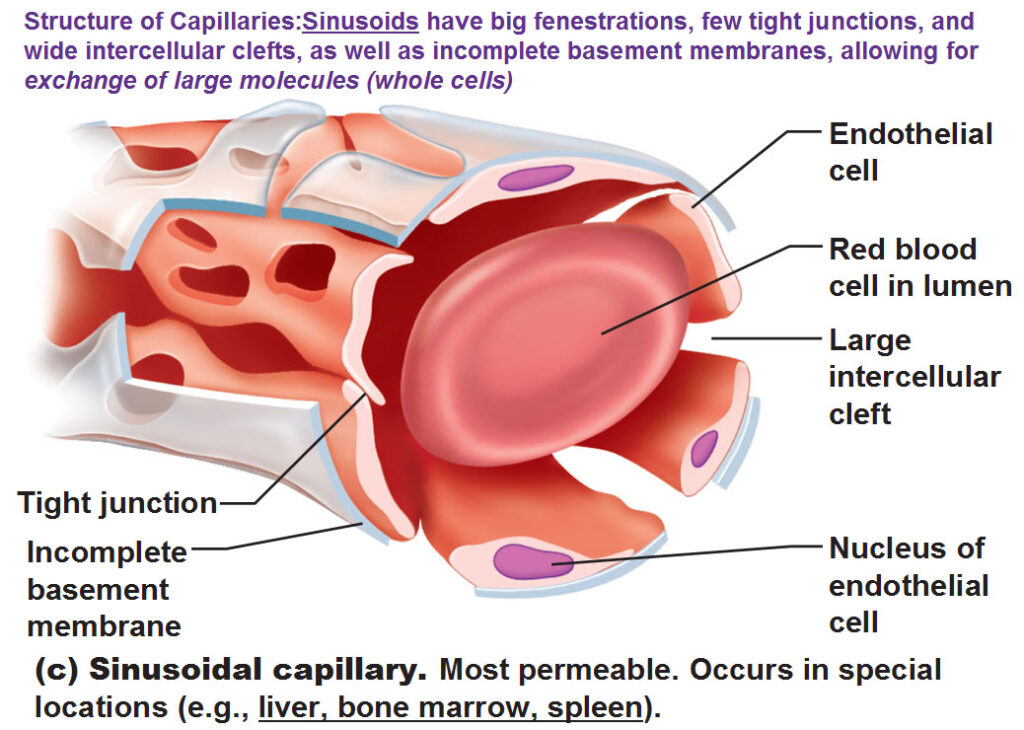
Which capillaries are the leakiest?
Sinusoidal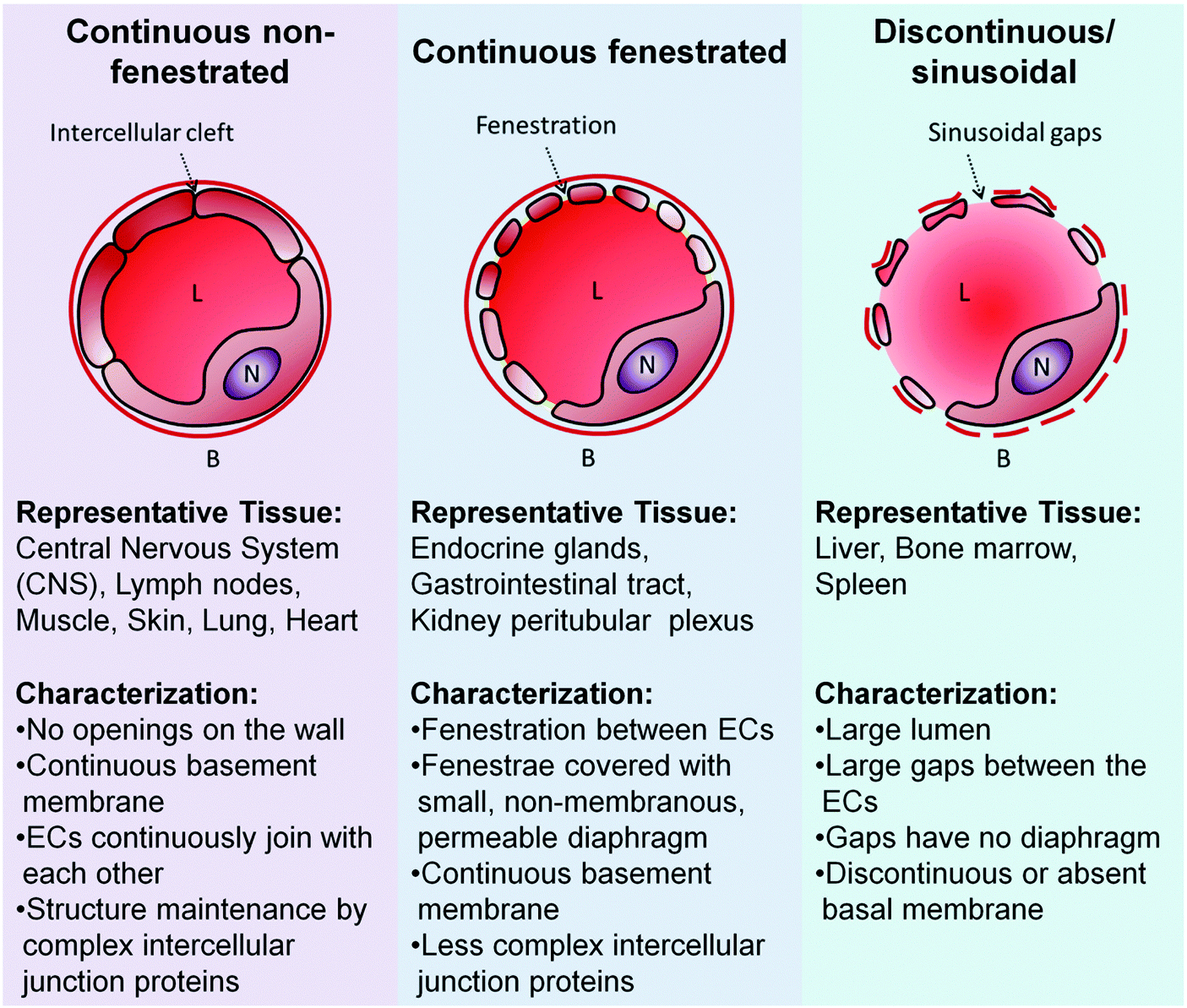
What are the major components of blood
1. Plasma
2. formed elements or "buffy coat"
Bonus: what are the 3 types of formed elements ?
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
..
RBCs, WBCs, platelets
EXTRA Bonus: other names for them? whats the percentage of each?
Whats the process of spinning a mixture liquid solution sample into its fluids based on their densities
Centrifuge
What is the normal systolic blood pressure?
120mmHg
What cells help form blood clots?
Platelets
Which organ removes old red blood cells?
Spleen

BONUS: Which pulp is this done at?
the plasma is composed of?
90% water, 9% proteins, 1% polar molecules
Which layer of a blood vessel controls vasodilation?
Tunica media
BONUS: what kind of tissue do we find here?
BONUSSx1:(many answers ) why would we need to vasodilate blood vessels?
BONUSSSx2: (also many answers) can you name a hormone that does this?
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
./
.
.
.
.
.
.
1) Many
To cool down the body (in heat)
To increase blood flow to active muscles (e.g. during exercise)
To lower blood pressure
In response to inflammation or injury
To allow nutrients and oxygen to reach tissues faster
2) Several are valid:
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) – causes vasodilation to reduce blood pressure
Nitric oxide (NO) – a gas released by endothelial cells that causes vasodilation
Histamine – dilates vessels during allergic reactions/inflammation
Bradykinin – another vasodilator in inflammation
Epinephrine – can cause vasodilation in some vessels (like skeletal muscles) and vasoconstriction in others (like skin/digestive organs)
What happens to blood flow if resistance increases?
Pressure decreases
BONUSSS: how does your body increase resistance ?
The inactive form of fibrin is called
Fibrinogen
What is the yellow pigment from heme breakdown?
Bilirubin:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/JaundiceGettyImages-155599928-697dfb02d14b438583f170f32cba5ccb.jpg)
BONUSSS: Whats the condition when bilirubin levels are too high?
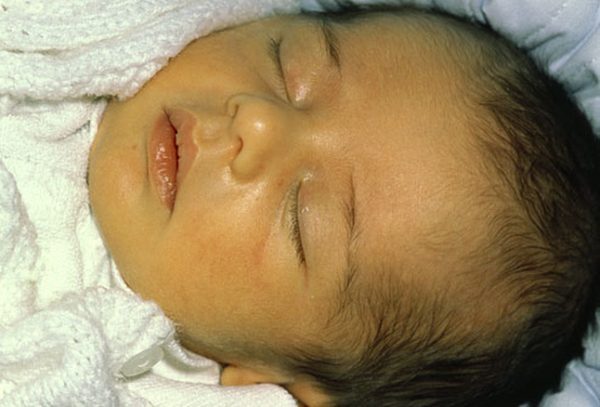
ANOTHER 1: Whats is that caused by?
What part of the conduction system causes the AV node delay?
Fibrous skeleton and fewer gap junctions
Smallest veins are called ?
Venules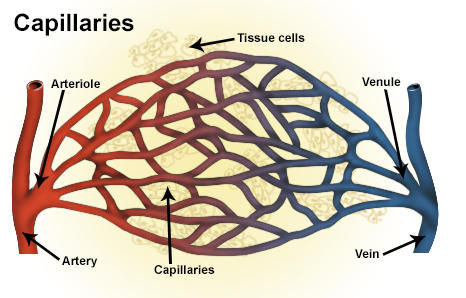
Which system regulates short-term BP changes?
Sympathetic nervous system
BONUS: what hormone does this?
.
.
.
.
.
..Epi/NE
Whats the vitamin needed for clotting factor production?
Vitamin K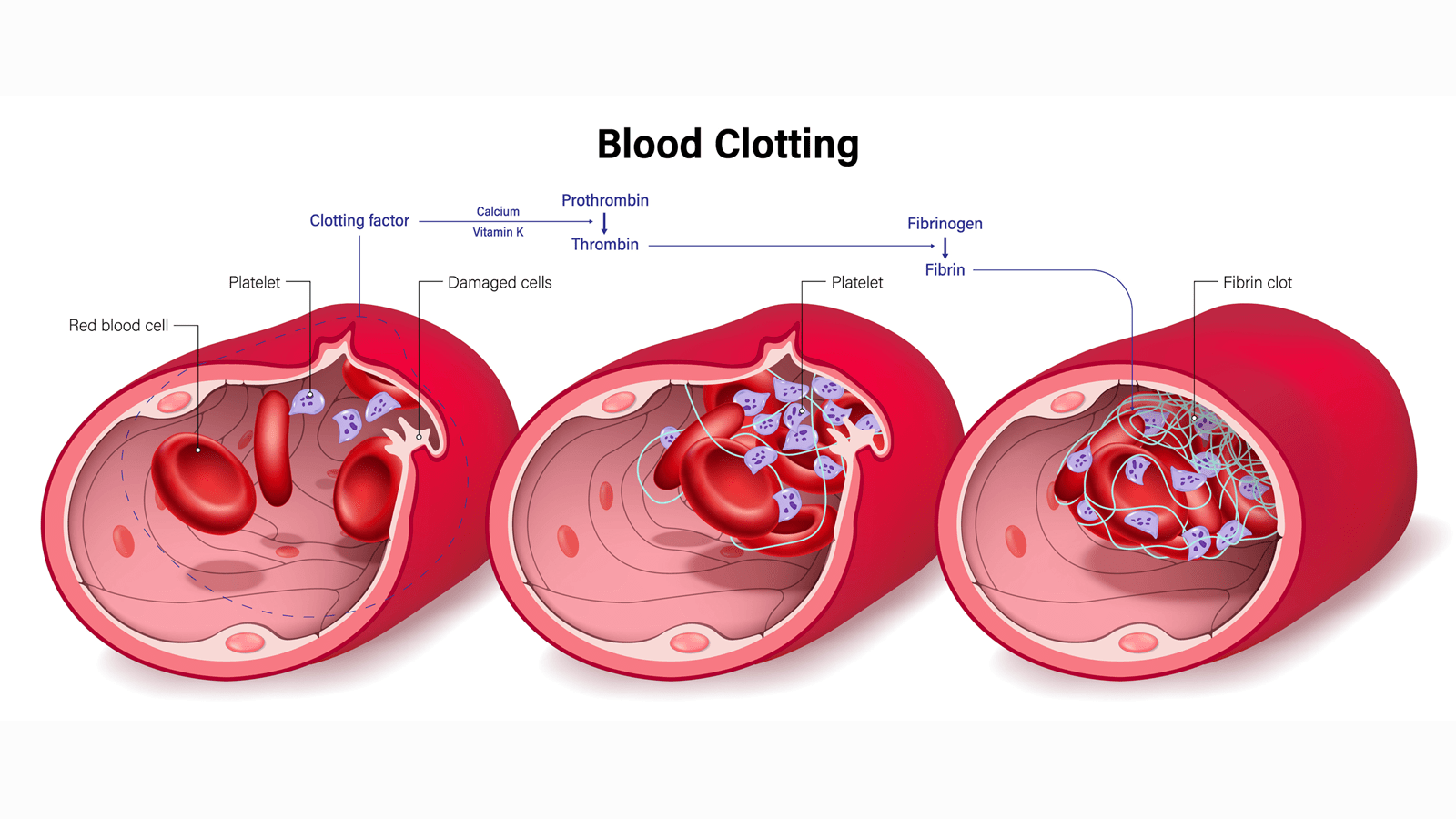
Which leukocytes fight parasitic worms?
Eosinophils
BONUS: most to least abundant Leuks: GO!
What is the name of the heart’s main pacemaker?
SA node
What structure prevents backflow in veins?
Venous valves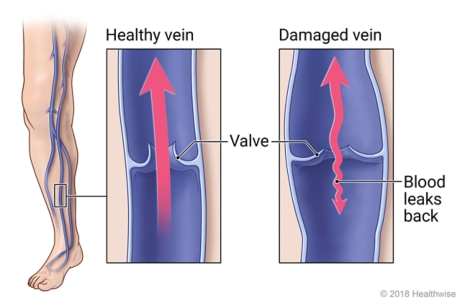
Which vessel type has the slowest blood flow?
Capillaries
BONUS: why?
What enzyme breaks down fibrin?
Plasmin
What causes sickle cells to get stuck in capillaries?
Abnormal hemoglobin (HbS) shape
hat hormone increases RBC production?
Erythropoietin (EPO)
The hole present in the interatrial septum of a fetal heart is called
foramen ovale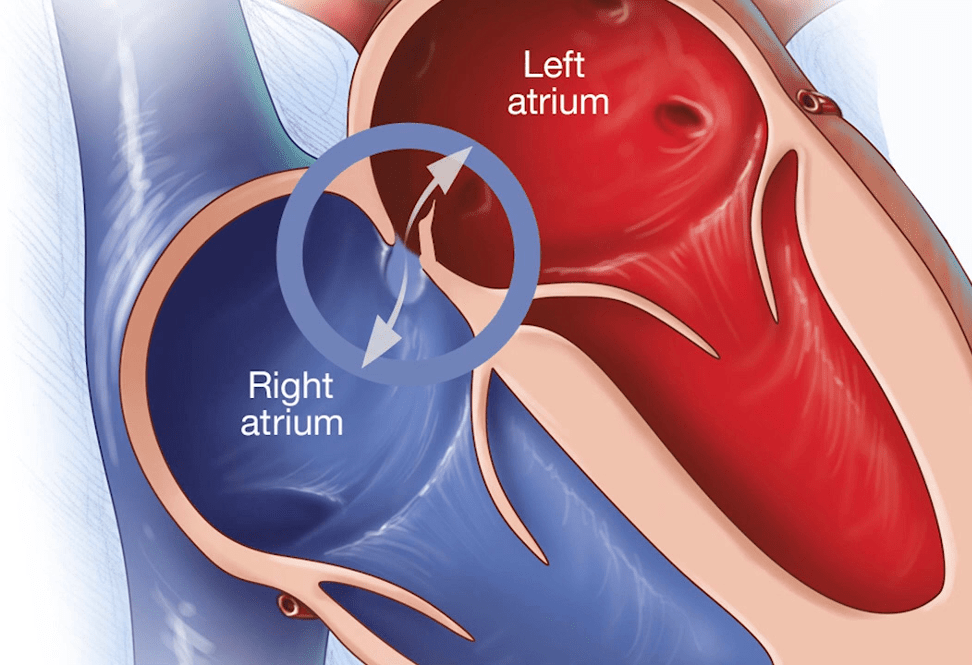
BONUS: why does this exist?
This hormone is released by the kidneys when blood pressure drops and leads to increased blood volume and vasoconstriction
Renin
BONUS:
x1: What hormone does renin help activate?
x2: What does angiotensin II trigger the release of?
x3: What does aldosterone do?
.
..
.
.
.
.

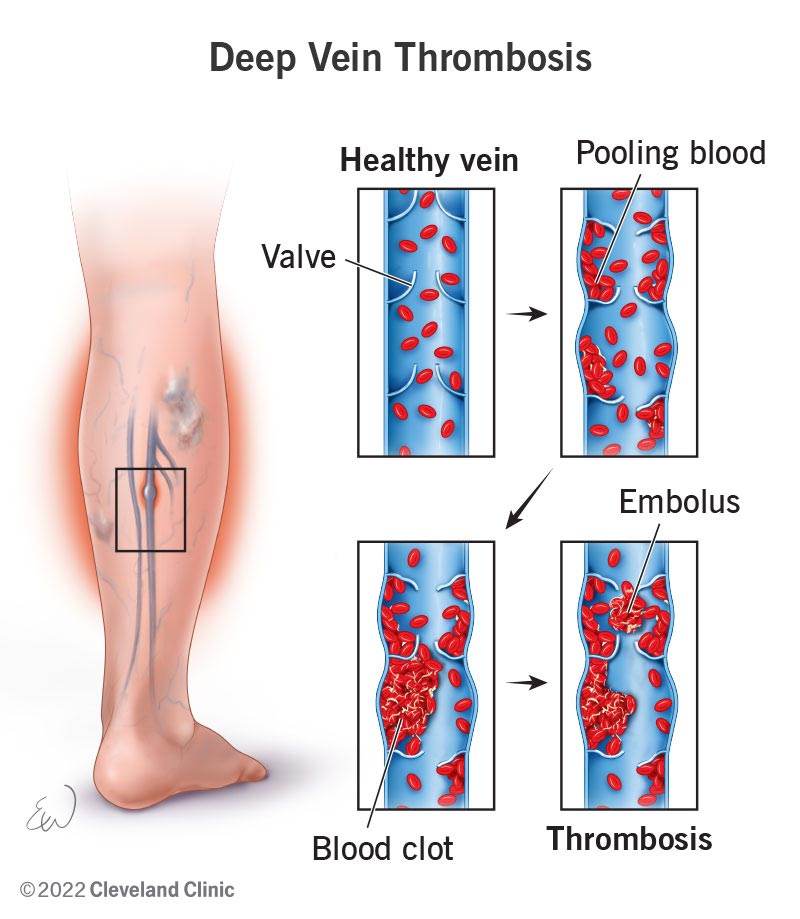
The condition that involves excessive clotting in deep veins?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)