This is the idea that human wants are unlimited while resources are limited.
What is scarcity?
This is an example of a constant-opportunity cost production possibilities curve drawn on the whiteboard.
What is:

This is the benefit of specialization and trade according to comparative advantage.
What is the ability to consume beyond an economy's PPC?
This is a kind of cost that involves direct cash payments
What is an explicit cost?
This is the term for the additional benefit or utility gained from the consumption of one additional good
What is marginal utility/marginal benefit
This is an economic system characterized by government control of the allocation of resources.
What is a command economy?
This is an example of an increasing opportunity cost PPC drawn on the white board.
What is: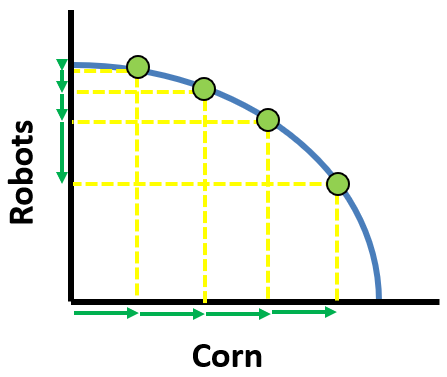
This is the country who has the comparative advantage in producing rice according to the table below:

Who is Vietnam (25/80 is less than 40/20)?
This is the definition of opportunity cost.
What is the value of the next best alternative that is forgone when a decision is made.
This is the total utility of a good when the marginal utility of the first unit is 200 and the consumer gains an additional 35 utils for the consumption of a second unit.
What is 235?
These are the 5 main factors of production.
What are natural resources (land), physical capital, human capital, labor, and entrepreneurship?
This is an example of an event that would cause the production possibilities curve to shift outward
What is increase in labor force/population/improvements in tech/improvements in education?
This is the person who has the comparative advantage in producing pie according to the table below
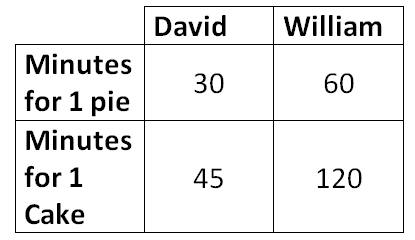
Who is William (60/120 is less than 30/45)?
This is John's total opportunity cost if he decides to take 4 hours off of his job that pays $20 per hour, and instead goes to spend $15 to see a movie with a friend.
What is $95 (Explicit cost of $15+Implicit cost of $80)
This is the marginal utility per $ of a good when the last unit consumed has a marginal utility of 15 and the price of the good is $3
5
This is an example of physical capital
What is (any example of machinery/tools/equipment)?
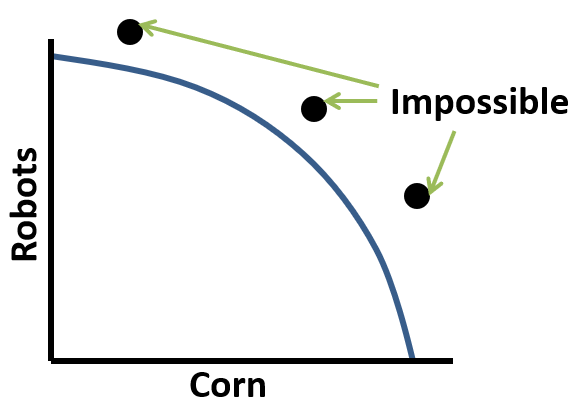
This is an example of a point on a PPC that is impossible under current conditions drawn on the white board.
What is:
This is the country that would export chocolate and import grapes according to the table below:

Who is Switzerland (OC for chocolates is 1, less than Brazil's 3; OC for Grapes is 1, more than Brazil's 0.33)
This is when a rational decision maker would choose to make a particular decision.
What happens when total benefit exceeds total costs?
This is the formula for utility maximization
MUx/Px=MUy/Py
This is an example of a non-rival, or not scarce, resource
What is established knowledge/air/solar power/anything that multiple people can consume at once
This is what happens to the opportunity cost of corn in the PPC depicted below.
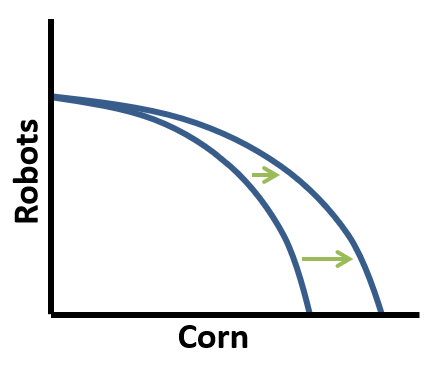
What is a decrease in opportunity cost?
This is an example of
This is an example of a trade ratio for 1 cake that would be mutually beneficial for David and William
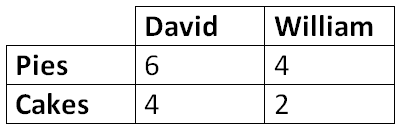
What is 1.75 pies (or any number between 1.5 & 2)?
This is the optimal units of activity to engage in based on the table below:

What is 3 (Total Net Benefit of 130, which is the largest TNB on the table)
This is the the optimal combination of pretzels and sundaes according to the table below, if pretzels cost $3 and sundaes cost $6, and the consumer wants to spend $30.
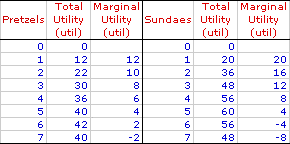
What is 4 pretzels (MU/P=2, $12 total)and 3 sundaes (MU/P=6, $18 total)