Silver+ Tin powdered metal BEFORE mixed with liguid Mercury is ______ ______.
Amalgam Alloy
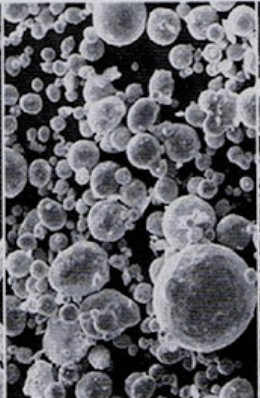
Speherical alloy
1st stone to use in Amalgam Polishing
use _____ stone.
Green Stone
What is the purpose of amalgam polishing:
To produce a restoration that can be easily cleaned by the patient and more compatible with oral health
Name 1-2 types of Abrasives:
1. Emery- like (nail file)
2. Silex-quartz -powder form
3. Tin Oxide-Powder form
4. Aluminum Oxide- bonded to disk and strips
5. Cuttle-
6. Garnet
7. Chalk-mineral form of calcite, can polish teeth, gold, amalgam restorations, and plastic materials.
8. Pumice- used on enamel, gold foil, amalgam, and acrylic denture bases in the laboratory.
9. Sand- form of mineral quartz, bonded to a disk for grinding metals and plastics.
A combination of several metal elements.
Dental Alloy
This metal is added to improve the clinical performance of an Amalgam, to increase strength, reduce corrosion, and break down.
Copper (Cu)
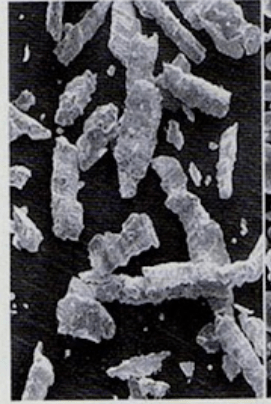
Lathe-cut alloy, irregular alloy
_____ Stone.
White stone, on slow speed to define occlusal anatomy.
List a benefit of amalgam polishing:
-Smooth and flash cavosurface margins
-Re-creation of defined anatomy
-Decreased plaque retention
-Healthier surrounding tissue
-Higher resistance to tarnish and corrosion
-Increased longevity of the restoration
-Improved esthetics
List 1-2 factors that influence the rate of abrasion:
•Hardness
•Size
•Shape
•Pressure
•Speed
•Lubrication
The RESULT of mixing approximately equal parts by weight of powdered alloy and liquid mercury is called _______ ______?
Dental Amalgam
The mixture phase of dental amalgam that is the weakest and most corrosion prone is _____.
Tin+Mercury phase
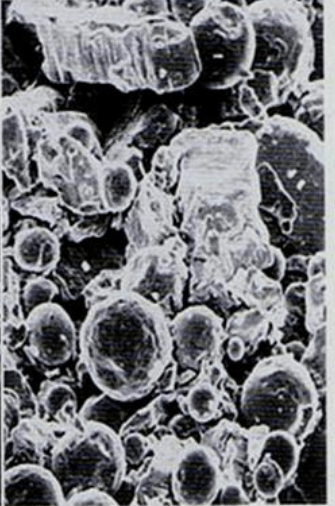
Admixed or blended alloys
3rd stone to use in amalgam polishing is to use
_____ point.
Brown Point, to minimize scratches.
Fill in stone for composite polishing:
1. Dura-___ silicone carbide stones for adjusting
2. Dura-____aluminum oxide stones for finishing
3. CompoSite silicone _____is impregnated with aluminum oxide for polishing
1. Green-for adjusting
2. White-for finishing
3. CompoSite Silicone Points for polishing
1. The process of producing the final shape and contour of a restoration _____.
2. Removing materials by shearing off process using dental burs, chisel, spoon, excavator, hoe, hatchet is called _____.
3. A material is considered ____ when it "wearing away" at a surface. Using disk, stones, wheels, strips, paste...
4. ___ wearing away a surface by grinding producing small scratches.
1. Finishing
2. Cutting
3. Abrasive
4. Abrasion
Amalgamation or Trituration
Using an Amalgamator or a Triturator
Two kinds of corrosion that leads to recurrent decay are _____ and _____ corrosion.
1. Surface- discolors that lead to pitting
2. Internal- Interior of restoration, leading to arginal brad down, and sometimes fracture.
What GV classification is this gold filling?
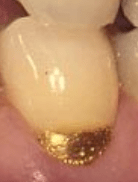
Class V
4ths stone to use when polishing amalgam is to use
_____ point.
Greenie Point to further polish.
____ is produced when using hand piece at high speed with firm pressure.
HEAT, use low speed and light, intermittent pressure when polishing.
___ polishing is to polish only the teeth that are stained.
Selective Polishing,
**follow manufacturer's recommendations.
**Enamel is in a constant state of "mineralization flux". Demineralizing at times and remineralizing.
**If a microscopic layer of enamel is removed from polishing, it will be remineralized by saliva minerals and fluoride exposure. esp if pt gets fluroide tx after polishing.
The kind of retention amalgam restoration is held together by _____
Small change in shape when an object is under continuous compression is called _____.
Creep
Gold foil restoration is also called :
2. Cohesive Gold
Due to cost and aesthetics, direct gold is rarely used.
Result of poor carving of Amalgam: Name A: B. C
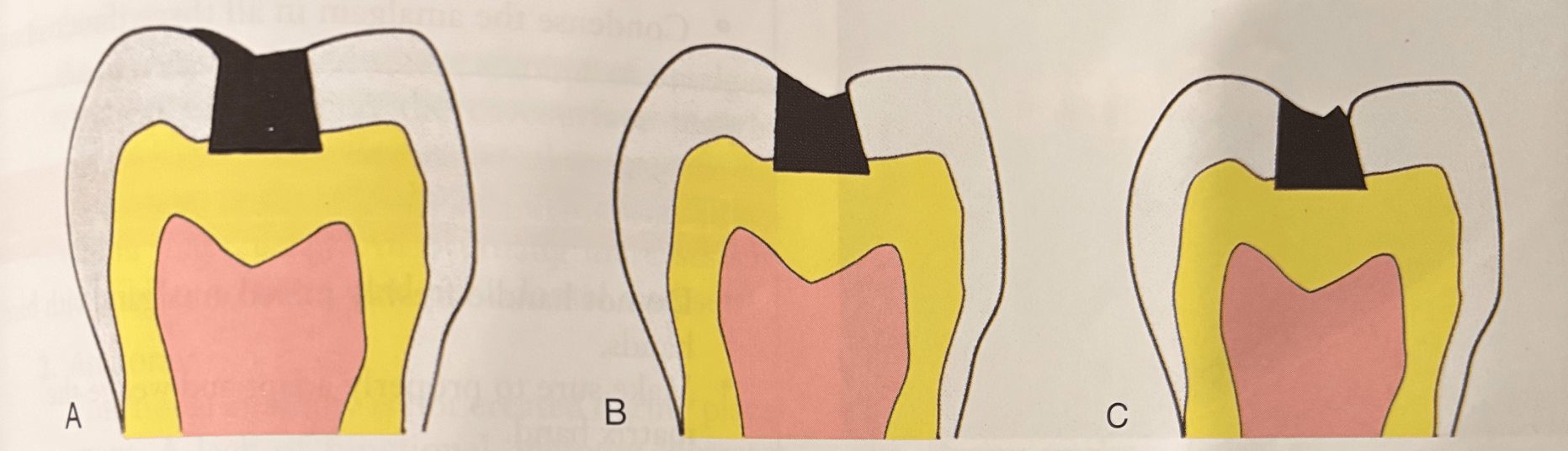
A. Overextension/Flash- extending beyond cavosurface.
B. Submarginal
C. Openmargin
___ is the process of abrading a surface to reduce the size of scratches until the surface appears shiny.
POLISHING
List some Air Polishing Powders :
1. Sodium Bicarbonate (special processed), uses kinetic energy to propel powder polishingthe tooth surface ideal for heavy stains. (contraindicated for high-blood- pressure, renal disease)
2. Aluminum trihydroxide- alt to Sodium Bicarbonate
3. Glycine powder
4. Calcium Carbonate
5. Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate
6. Erythritol