What are carbohydrates good for?
Short term energy along with structural support for animals like bugs to make an exoskeleton
What do prokaryotes and eukaryotes have in common?
both contain DNA
both use ribosomes to make proteins
both are living
The lack the ability to reproduce by themselves. they have no nucleus to hold their dna and no ribosomes to create proteins. They also cannot respond to their environment
What does Homeostasis mean?
The state of internal balance in spite of external change
What gives the enzyme its ability to do its function?
It's form
What are lipids used for?
They are good for long term energy storage along with making up the cell membrane and as hormones
How are prokaryotes and eukaryotes different?
Eukaryotes have a true nucleus, have membrane bound organelles, enclose their dna in the nucleus
Prokaryotes dont have a nucleus, lacks complexity, has free floating dna
Which type of cycle is associated with the quick onset of symptoms
Lytic cycle
A freshwater fish was placed into a tank with high tonicity. The fish began to shrivel and die. What did the fishes cells experience and what direction was the water moving?
The cells was shriveling because the water was rushing out of the cells
How do enzymes effect chemical reactions? What happens to the enzymes afterwards
They lower the activation energy of a reaction allowing the reaction to happen faster. The enzyme is the reused for another reaction
What are proteins for?
They serve a variety of functions based on their shape and they can act as enzymes
If you compare the plant cell to an animal cell, you will notice that the plant cell has cellulose. What is the purpose of that molecule?
It makes up the cell wall and provides the cell with rigidity and protection
If scientist wanted to create a medication to stop a virus from infecting targeted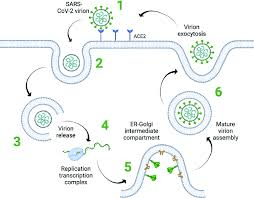 cells, which step should they focus on?
cells, which step should they focus on?
Step one, when the virus binds to the receptors
A student has a semi-permeable bag that contains water with 1.01 g/mol of a salt concentration. What amount of salt concentration should the student place the bag in if the wants to maintain a isotonic environment and reach homeostasis?
Place the bag in a 1.01g/mol salt concentration solution.
Someone catches the cold and it results in the development of a fever, which raises your body temperature. How will this change in temperature effect the activity of the active site?
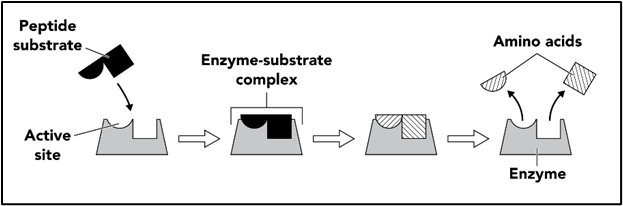
The substrate will be broken down more slowly
What are nucleic acids used for?
Carry genetic information and is used as energy in the form of ATP
A person discovers a new organism and finds that is is heterotrophic, has a nucleus and has gametes. What can be determined by these traits? also, is it uni or multicellular
It is a eukaryote and multicellular
Medical researchers isolated a new virus, virus A, that causes flu-like symptoms. They identified and characterized the main surface protein of virus A. This information enabled them to develop a vaccine. Several months later, the researchers isolated a new strain of virus A. This strain spread rapidly and became the most common variant of virus A.
The diagram shows the surface proteins in the two variants of the virus.
Will the people who are already vaccinated need to have an updated vaccine?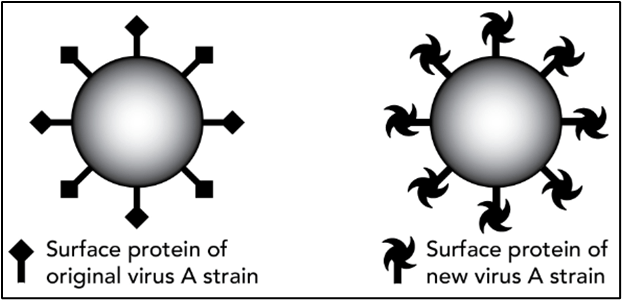
Yes because the surface proteins of the original virus are different from the mutated one
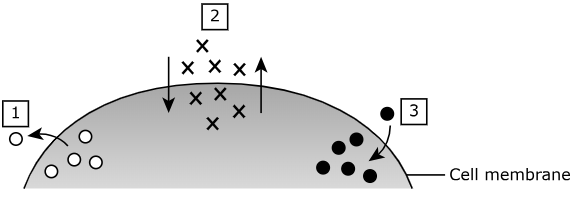
This diagram shows the movement of 3 substances. Which one would require energy to move across the membrane?
What is it called when the enzyme binds with the substrate
The enzyme substate complex
What biomolecule is responsible for making up the cell wall
Cellulose, which is a carbohydrate
Which applies to cells only, which applies to viruses only and which applies to both:
- Genetic information is in a capsid
- Only reproduces within a host cell
- Evolves over time
- Can cause diseases
- Is alive
- Genome consists of one or several RNA molecules
Viruses: 1, 2, 6; Cells: 5; Both viruses and cells: 3, 4
A biotechnology company is developing a type of medication that interferes with the infection cycle of the COVID-19 virus. The medication blocks an important enzyme that the COVID-19 virus requires in order to make functional virus particles.
Where should this process take place based on the infection cycle?
Inside the host cell because virus only reproduce in the host
What type of transport is the Na+/K+ pump and how does it move the ions?
It is active transport using energy to move ions against their concentration gradient.
What is a retrovirus?
A type of virus that uses the host's machinery to turn its RNA into DNA
Whats the difference between lipids and carbs
lipids is for long term energy while carbs are for short term energy
A student is making models of cells and uses the following materials:
- dried peas to represent ribosomes
- shelled peanuts to represent mitochondria
- uncooked noodles to represent DNA
- shoestrings to represent the cell membrane
Which material would be used in a model of a eukaryotic cell but NOT a prokaryotic cell?
What makes a virus specific to the cell it attaches to
The receptors on the virus matching the receptors on the cell
How is glucose moved in the cell?
It is moved through facilitated diffusion
Where does the virus keep its genetic material?
In its capsid