answers may vary.
What is kinetic energy?
the energy of motion/movement.
What is density?
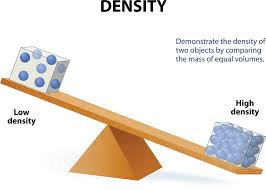
It refers to how tightly packed a substance is. It is found by mass divided by volume.
List three physical properties that describe a metal.
Answers may include lustrous, malleable, ductile, good conductors of thermal and electrical energy, high melting/boiling point etc.
How is a metalloid different from a metal or nonmetal?
Metalloids are shiny like metals, but brittle like nonmetals.
Which state of matter does not have a definate/fixed shape or volume and has molecules with high kinetic energy?
gas
Which state of matter has the highest kinetic energy?
gas
Which liquid has the highest density?

Honey
List three physical properties of a nonmetal.
brittle, poor conductor, dull, low melting point, can be in gaseous form at room temperature, etc.
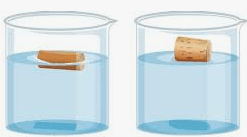
Both of these objects are floating on water. Which object is the least dense. How do you know.
The object on the right is the least dense because it is floating higher in the water.
Which state of matter has a definite/fixed shape and volume and a molecules that have a low kinetic energy?
solid
which state of matter has the lowest kinetic energy
solid
Which item is the least dense?
ping pong ball
Would the following be a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid?
This elemnt has a low melting point, it is brittle, and it does not conduct electicity or heat.
nonmetal
What happens to the kinetic energy of a liquid as it is heated and evaporates?
The kinetic energy increases.
Which state of matter has a definite/fixed volume but not a definite shape?
liquid
What happens to the kinetic energy of molecules when thermal energy is added?
The kinetic energy increases.
If water has a density of 1 g/mL and honey has a density of 1.42 g/mL, which of the following will likely be more dense than water but less dense than honey?
A. Ping pong ball: 0.25 g/cm3
B. Bottle cap: 0.92 g/cm3
C. Cherry Tomato: 1.12 g/cm3
D. Bolt: 7.9 g/cm3
C. Cherry Tomato: 1.02 g/cm3
Which of the following is likely to maleable, dutile, and a good conductor of eletricity?
A. Carbon (C) B. Boron (B) C. Calcium (Ca) D. Argon (Ar)
C. Calcium (Ca)
 Which of the following is likely to be a gas at room temperature.
Which of the following is likely to be a gas at room temperature.
A. Boron (B) B. Lithium (Li) C. Sulfur (S) D. Helium (He)
D. Helium (He)
Give an example of an object that changes its state of matter.
Answers may very: An object is a solid, if it changes its state it will turn into a liquid and melt. Ex: butter melting when heated.
Describe how the kinetic energy of the molecules in ice differ from the kinetic energy of the molecules in water vapor.
The KE in ice (solid) is low and the KE in water vapor (gas) is high. The molecule sin a solid just vibrate and the molecules in a gas move fast and freely.
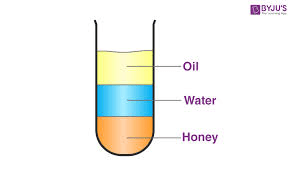
If oil has a density of 0.92 g/mL, water has a density of 1.0 g/mL and honey has a density of 1.42 g/mL. Where would an object with a density of 1.23 g/cm3 be located if placed in this test tube?
In the water, floating above the honey

According to the location of the elements on the period table, how does the physical properties of Iron (Fe) compare to the physical properties of Silicon (Si)?
Iron is a metal so it is shiny, malleable, ductile, and a good conductor. Silicon is a metalloid so it is shiny like a metal, but brittle like a nonmetal. It does not conduct as well as iron.
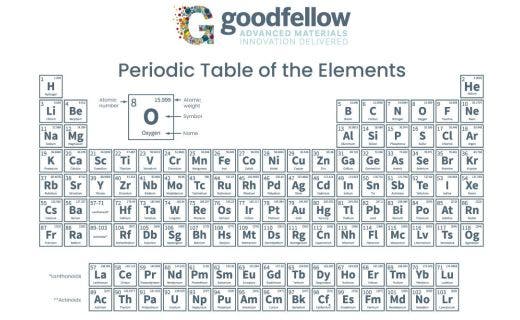
 Indicate where the metals, metalloids, nonmetals, and rare earth metals are located on this periodic table.
Indicate where the metals, metalloids, nonmetals, and rare earth metals are located on this periodic table.
The metals are on the right side. The metalloids are along the staircase. The nonmetals are on the right side except for Hydrogen (H), the rare earth elements include the top line on the bottom as well as Sc and Y.
