What is the ultimate source of energy in most ecosystems, used in the first stage of photosynthesis?
What is sunlight?
This gas is fixed during the Calvin cycle to form glucose.
What is CO2?
Glycolysis breaks down one molecule of glucose into two molecules of this 3-carbon compound.
What is pyruvate?
The Krebs cycle occurs in this part of the mitochondrion.
What is the mitochondrial matrix?
The main output of oxidative phosphorylation is this molecule:

What is ATP?
This pigment in chloroplasts absorbs sunlight to power the light reactions of photosynthesis.
What is chlorophyll?
What is this molecule, the main output of the Dark Reactions/Calvin Cycle?
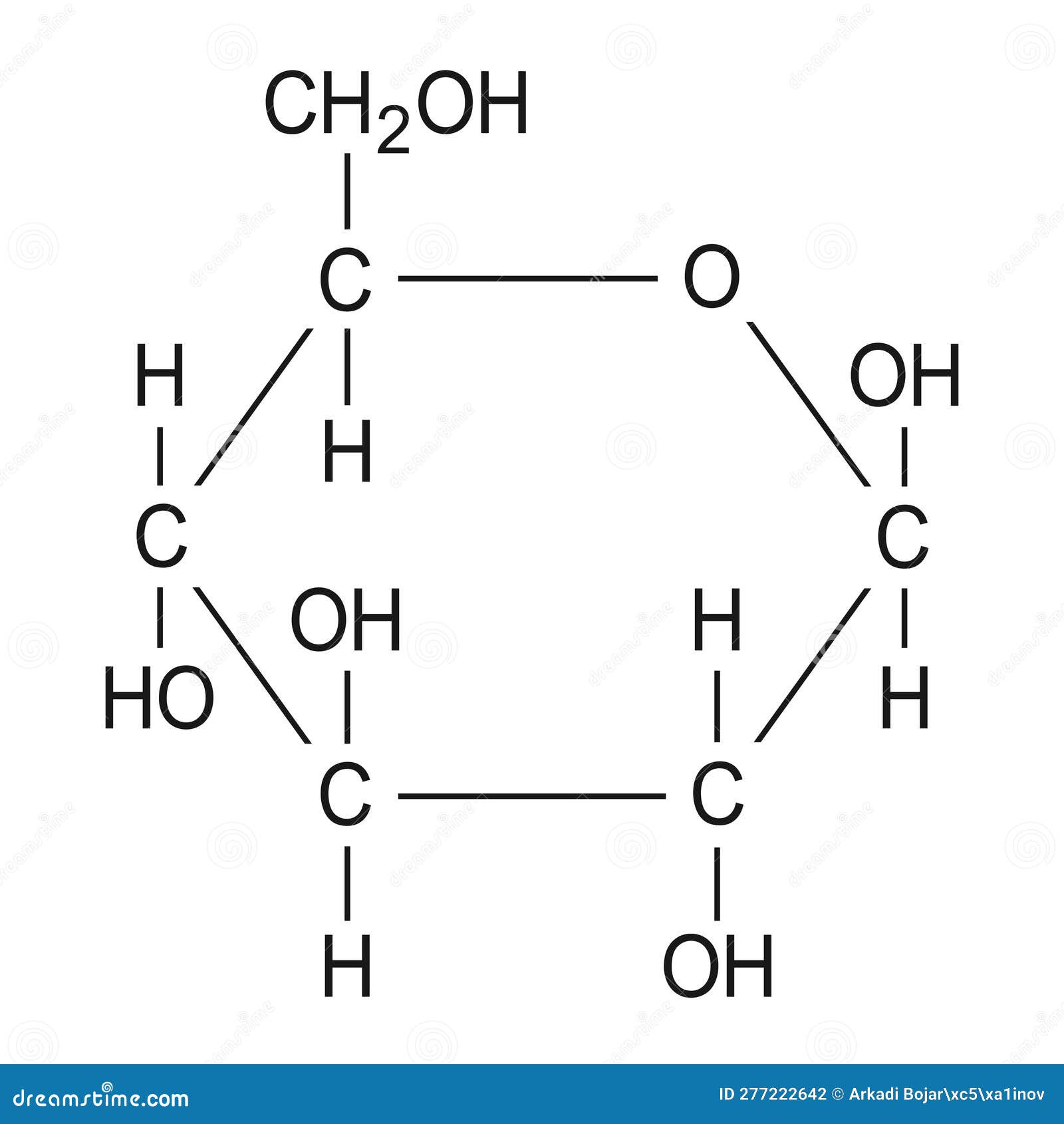
What is Glucose?
Glycolysis occurs in this part of the cell.
What is the cytoplasm?
This gas is released as a waste product during the Krebs cycle.
What is carbon dioxide (CO₂)?
This molecule is the final electron acceptor at the end of the electron transport chain.
What is oxygen?
The primary purpose of the light reactions is to produce these two molecules used in the Calvin cycle.
What are ATP and NADPH?
What is the 3-carbon precursor molecule used to make one molecule of Glucose?
What is G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate)?
The products of Glycolysis are ________, ________, and _______.
What are ATP, NADPH, H+
At the end of the Citric Acid Cycle, _____________ has been completely broken down.
What is glucose?
____________ is the precursor molecule to ATP, the energy molecule of the cell.
What is ADP + Pi?
This molecule is split during the light reactions, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
What is water?
Organisms that make their own food through photosynthesis are called_________________; Organisms that cannot make their own food are called _____________________.
What are autotrophs; heterotrophs?
The electron carrier NAD+ is reduced to ______________ during glycolysis and carries electrons to later stages.
What is NADPH?
These high-energy electron carriers are produced in the Krebs cycle and used in oxidative phosphorylation.
What are NADH and FADH₂?
The use of high energy electrons are required to generate a __________ gradient in order to make ATP.
What is a proton (H+) gradient?
Which two particles result from the splitting of water?
Electrons (carried on NADPH), and H+ (protons).
Explain how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are energy transformations.
What is: photosynthesis is transforming sunlight energy into chemical energy (Glucose), and cellular respiration is the transformation of chemical energy (glucose) into chemical energy (ATP)?
This step must happen to pyruvate before it can enter the Krebs cycle.
What is conversion to Acetyl-CoA?
The outputs of the Citric Acid Cycle are _______
What are FADH2, NADH, ATP, CO2?
How does the poison cyanide work?
What is by displacing oxygen at the end of the electron transport chain, grinding cellular functions to a halt.