What is a universal protocol that must be completed before every surgery?
Time Out
What is the best way to help prevent atelectasis in a postoperative patient?
Incentive spirometry/early ambulation
What do you call the amount of stimulus a patient is willing to accept?
Pain tolerance
True or False: Medications used to treat nociceptive pain can also be used to treat neuropathic pain.
False
Name two of the common pain scales, one for adults and one for children.
Adults - Numeric Rating Scale, Visual Analog Scale, Nonverbal Pain Scale
Children - Wong-Baker FACES Pain Rating Scale, FLACC Scale, CRIES (neonates)
A nurse is conducting a preoperative assessment. The patient states that he frequently uses chewing tobacco. The nurse knows that the patient is at risk for which complication(s)?
Blood clots, myocardial infarction, death
A nurse in PACU have just received a patient. Upon assessment the patient develops shortness of breath, hypoxia, and blue discoloration around the lips. What is the possible post-op complication?
Pulmonary Embolism
True or False: Every client has the right to pain management as a basic human right.
True.
If a patient is going to have a painful procedure, when should you offer pain medication?
About 30-40 minutes before the procedure
What is this postoperative complication?
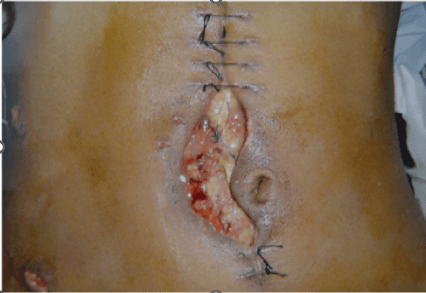
Dehiscence
What condition is a patient more at risk for if a family member has suffered from the same complication?
Malignant Hyperthermia
The nurse has just received a patient from PACU after the patient received a two liters of fluid. The nurse assesses the following: Crackles, JVD, and pitting edema in the legs. Which complication does the patient have?
Hypervolemia
What are the three categories of factors that form the experience of pain?
Biological factors, psychological factors, and social factors
What does the mnemonic PQRST stand for?
Precipitating Cause
Quality
Region
Severity
Timing
How often should the nurse educate a postoperative patient to use the incentive spirometer?
10 times per hour or every commercial break.
Hypovolemia
A nurse in PACU administers morphine to a patient. 15 minutes later the nurse assesses the patient to find that he is breathing 6 times per minute. What is the complication/adverse effect?
Respiratory depression
Pain is associated with actual or potential ________________ .
tissue damage
What are two examples of non-pharmacological interventions for pain?
Positioning, cold, heat, massage, distraction, therapeutic touch, relieve bony prominences, or splint post-op incision with a pillow
The FLACC is used with children ages 2 months to 7 years, and clients who are cognitively disabled. What does FLACC stand for?
Face
Legs
Activity
Cry
Consolability
What signs symptoms might alert the nurse that the patient has developed an ileus? All or nothing!
Distended abdomen, hypoactive/no bowel sounds
A nurse knows that a patient with a history of smoking is at higher risk for which complication(s)?
Difficulty with anesthesia, breathing, and DVT
What is the difference between acute pain and chronic pain?
Acute pain - anticipated or predictable end; lasts less than 6 months
Chronic pain - constant or recurring; lasts longer than 6 months
_________ pain can be described as aching or throbbing, whereas, ________ pain can be described as intense, shooting, or burning.
1. Nociceptive pain
2. Neuropathic pain
Name at least 3 things that are included in the preoperative assessment? All or nothing!
Patient Education, Head-to-Toe Assessment, Ensuring Informed Consent, Medical History Review, Lab Results Review, Diagnostic Test Review, Proper Identification, Allergies, Medications, Reactions to Anesthesia, Tobacco & Alcohol Use, Spiritual/Cultural Needs, Pain