100 points: Why did Peruvian fishermen call the event “El Niño”?
Answer: Because it occurred near Christmastime.
100 points: What causes wind to form?
Answer: Cooler dense air moves into low-pressure areas.
100 points: What is the zone near the equator called?
Answer: The tropical zone.

100 points: Define elevation?
Answer: The distance above sea level.
100 points: Since the late 1800s, how much has Earth’s temperature increased?
Answer: About one degree.
200 points: How often do El Niño events typically occur?
Answer: Every two to seven years.
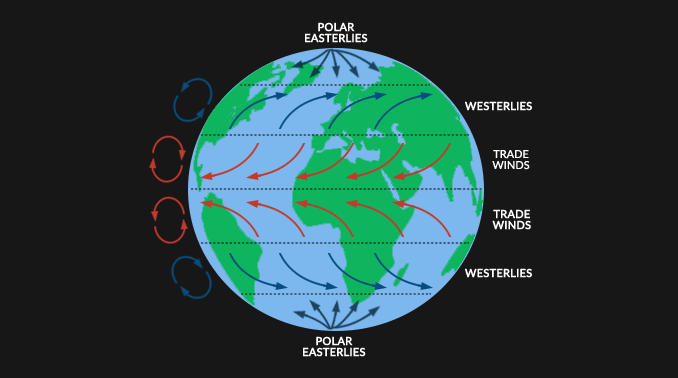
200 points: What is the name of the effect that bends winds because of Earth’s rotation?
Answer: The Coriolis effect.
200 points: How are lands in tropical zones characterized?
Answer: Hot all year long.
200 points: How much does temperature drop as you climb 1,000 feet?
Answer: About 3.5°F per 1,000 feet.
200 points: What is the greenhouse effect?
Answer: Solar energy trapped by gases in the atmosphere.
300 points: During El Niño, which direction does the warm water move?
Answer: Eastward toward the Americas.
300 points: From which direction does a north wind blow?
Answer: From north to south.
300 points: What are the middle-latitude zones called?
Answer: Temperate zones.
300 points: What is the climate like above 12,000 feet?
Answer: Similar to Arctic areas, with snow and ice.
300 points: What might happen if global warming continues?
Answer: Ice caps could melt, flooding coastal areas.
400 points: What happens in Australia and Asia during El Niño?
Answer: They experience droughts.
This shift means that less warm water and moisture reach Asia and Australia.
Because rainfall depends on that moisture, these areas receive much less rain, leading to drought conditions.
400 points: How do winds and ocean currents affect Europe’s climate?
Answer: They help keep Europe’s temperature moderate.
Even though Europe is far north, the combination of warm ocean currents and winds makes its climate more moderate and livable than other regions at similar latitudes.
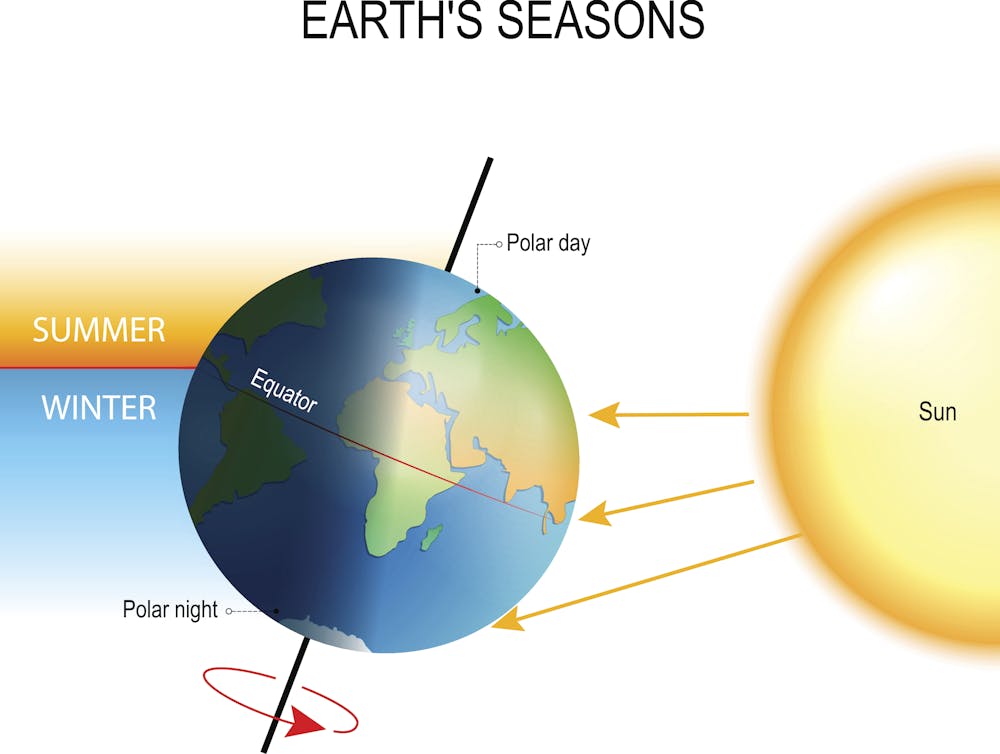
400 points: Why are summers warmer than winters in temperate zones?
Answer: Solar heating is greater in summer. The tilt of the Earth at 23.5 degrees.
400 points: How does topography affect rainfall on mountains?
Answer: Moisture-laden winds rise, cool, release rain or snow, then dry and warm on the leeward side.

400 points: What is one natural cause of climate changes over time?
Answer: Ice ages and solar cycles.
500 points (harder): How does La Niña affect rainfall along the Pacific coasts of the Americas and in India?
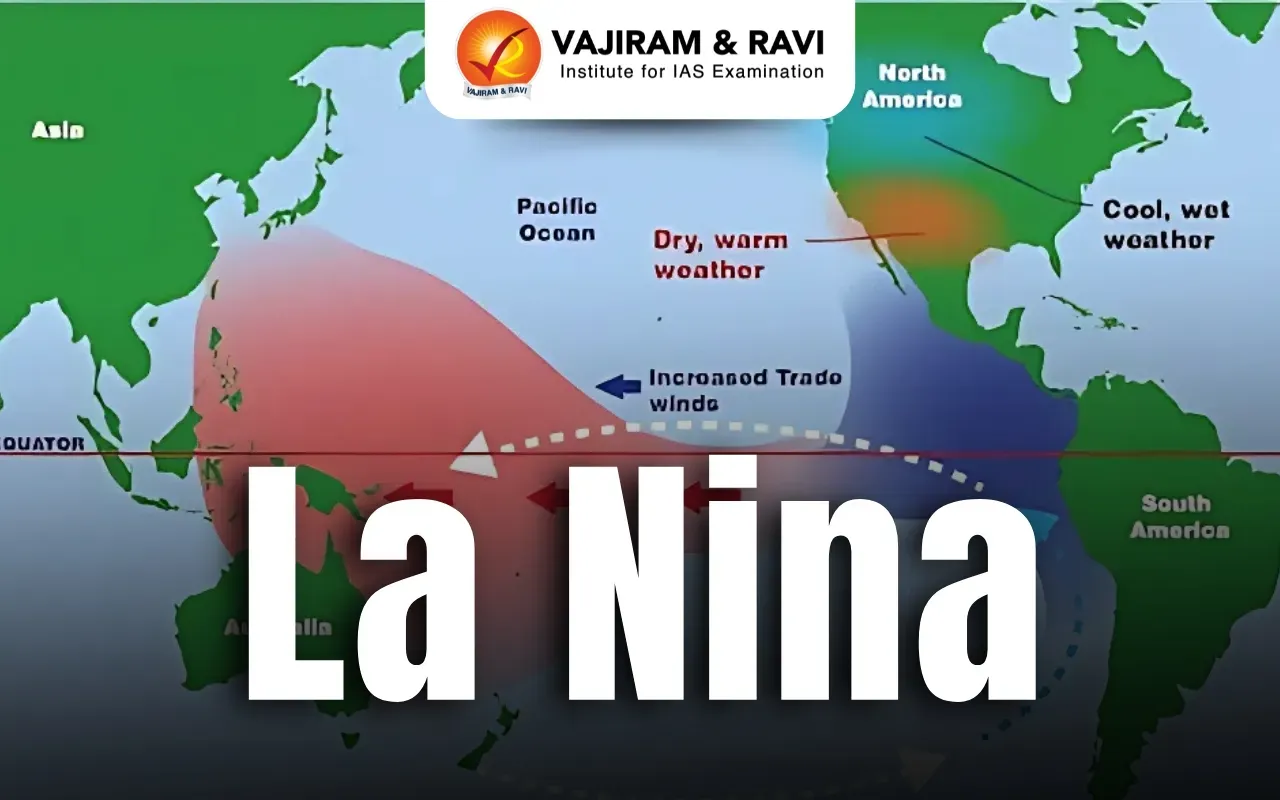 Answer: Causes dryness along the Pacific coasts of the Americas and increases precipitation in India.
Answer: Causes dryness along the Pacific coasts of the Americas and increases precipitation in India.
500 points (harder): How do cold ocean currents influence coastal climates?
Answer: They chill the air and reduce precipitation, sometimes creating deserts.

500 points (harder): How do climates change as latitude increases and what role does elevation play?
Answer: Higher latitudes are colder; higher elevation reduces the number of climate zones and lowers temperatures.

500 points (harder): Why do deserts like the Atacama form near cold ocean currents?

Answer: Cold currents chill the air, preventing precipitation.
500 points (harder): How do human activities contribute to global warming?
Answer: Burning fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases, trapping solar energy and increasing temperatures.
![]()