What is the more basic cell? Prokaryotes or Eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes
Pro = No membrane bound organelles (including nucleus)
Eu = YOU are complex
What organelle and function?
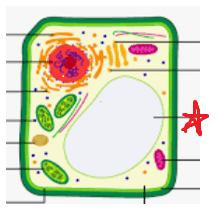
Vacuole
Storage of water
Leaves and stems have lots of them
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Gatekeeper
What can go in and out of the cell
Which phase of interphase does most growth occur?
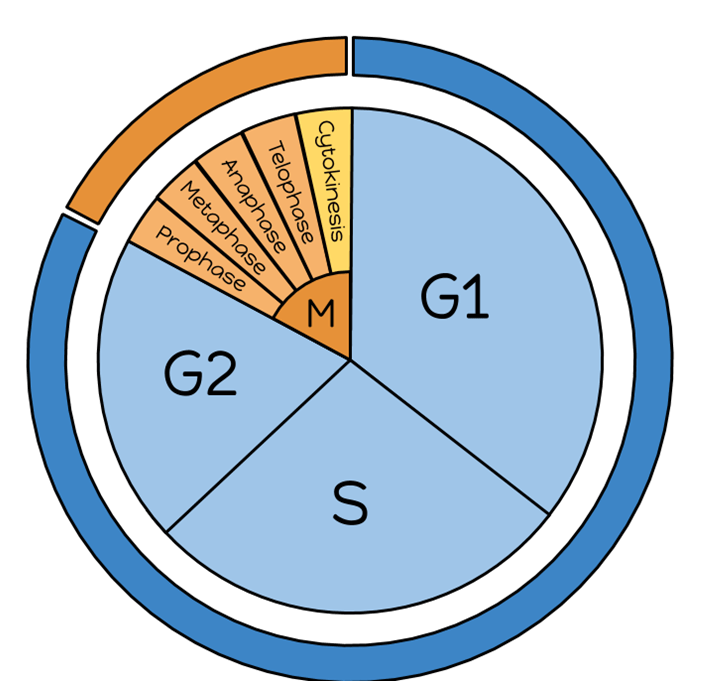
G1
Remember interphase is the phase cells spend most of their life, but in interphase it's G1
What stage of mitosis is this?
Prophase
Notice the dotted lines, this means the nuclear membrane is disappearing
What 3 things are in all cells?
DNA
Ribosomes
Cell Membrane
Which organelle and the function
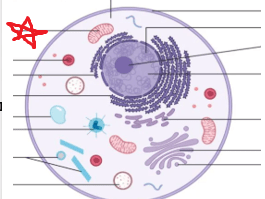
Mitochondria
Makes and stores energy
Muscle cells have lots of these
What will happen to the cell and why type of solution is this?
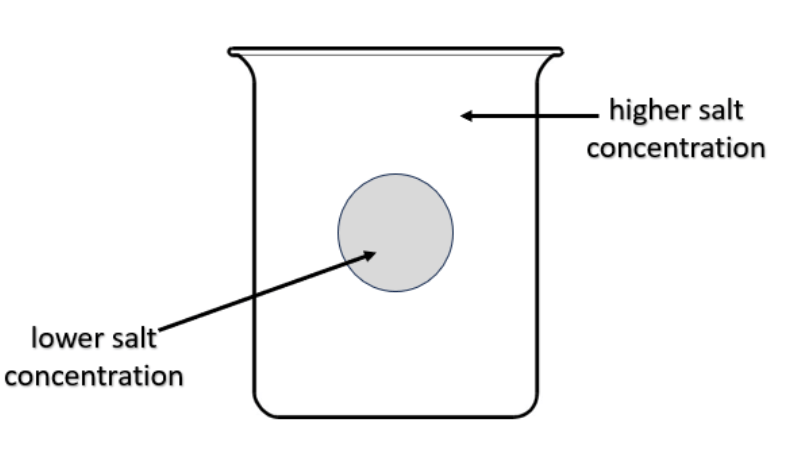
Cell will shrink
Hypertonic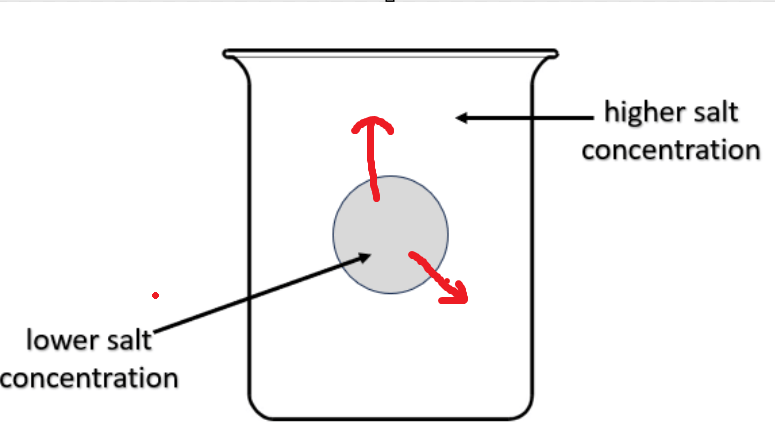
What form of DNA is found during interphase?
Chromatin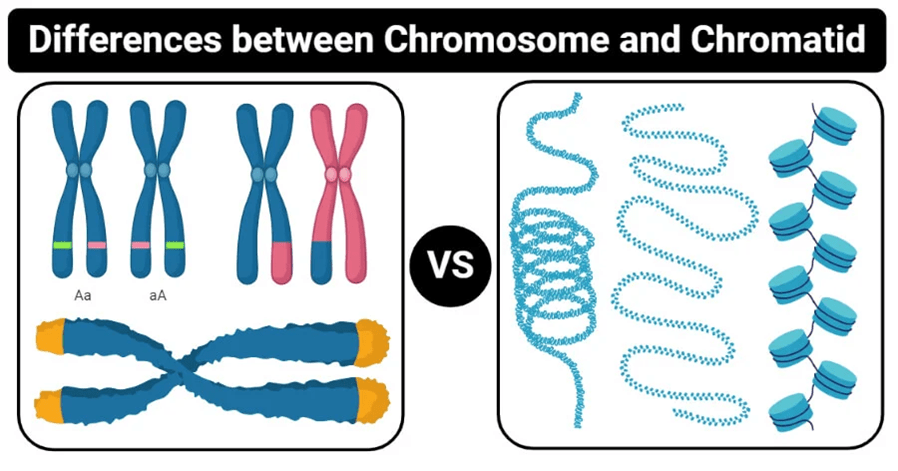
What phase of mitosis is this?
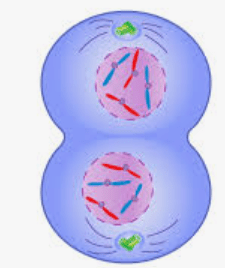
Telophase
Dotted lines represent the nuclear membrane forming.
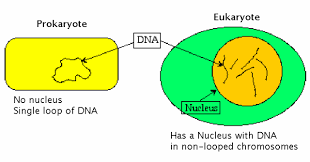
Where is the DNA located in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Which organelle and what is the function?
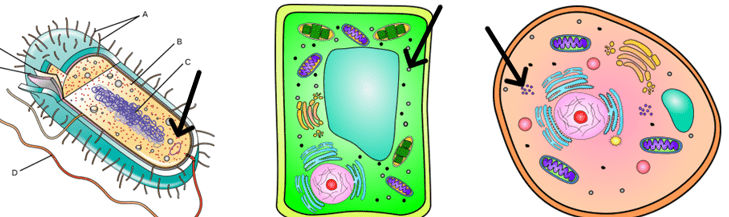
Ribosomes
Makes Proteins
If cell is low in protein, ribosome problem
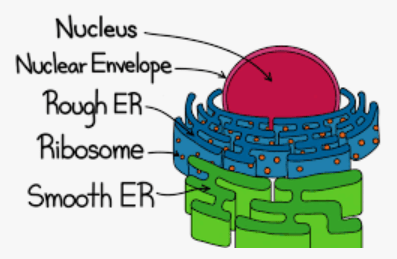
What is this an example of and is it passive or active?
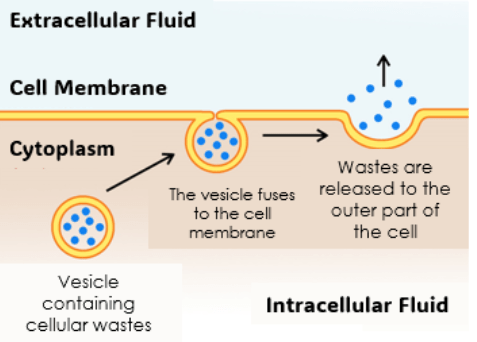
Exocytosis (exiting the cell)
Active
What happens in the S phase?

DNA replicates (makes a copy)
Still considered chromatin, condenses during mitosis
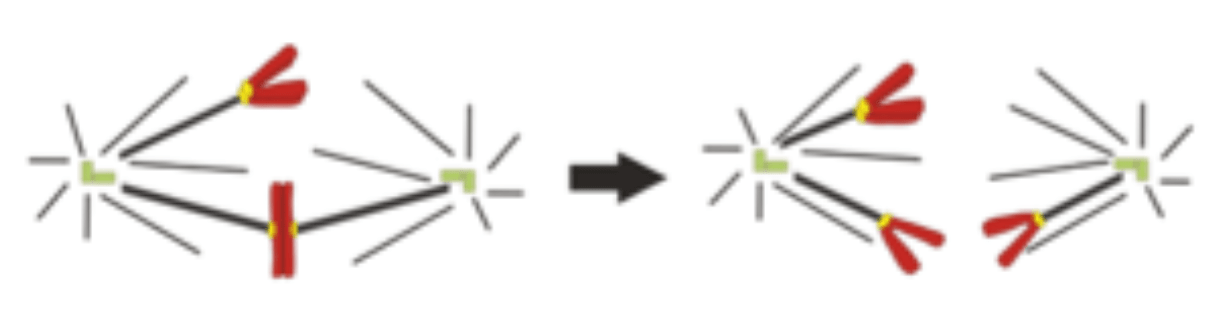
What would most likely be produced when a parent cell with 6 chromosomes undergoes mitosis?
_____ daughter cells with ______ chromosomes each
2 daughter cells with 6 chromosomes each
What are 3 organelles only found in plant cells?
Cell wall
Chloroplast
Large vacuole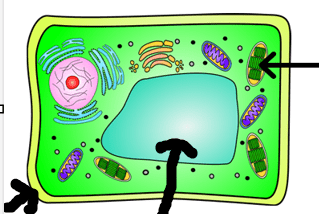
What organelle and the function (notice dots inside)
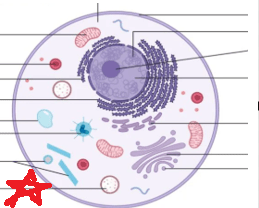
Lysosome
Removes trash
White blood cells destroy and remove bacteria
What are the 3 passive forms of membrane transport?
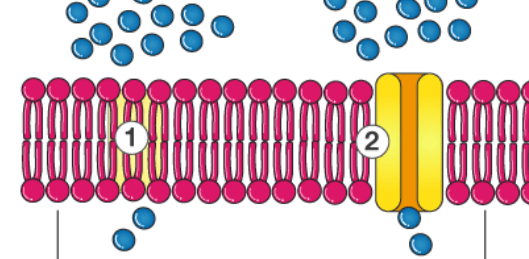
Diffusion (high to low)
Facilitated Diffusion (protein help)
Osmosis (water high to low)
Why does the cell cycle have check points?
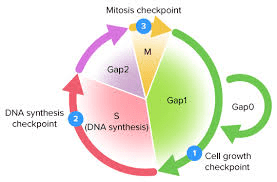
To be sure the cell is ready for the next step
Inhibits cancer / tumor growth
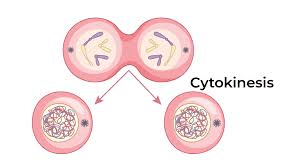
The process where the cytoplasm divides.
Cytokinesis
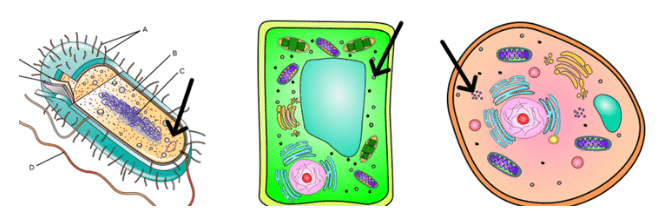
Draw an example of a eukaryotic AND prokaryotic cell.
Which organelle and what function
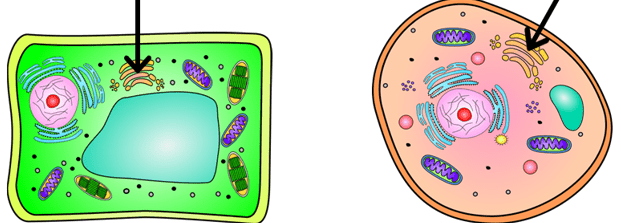
Golgi Body
Packages and sorts material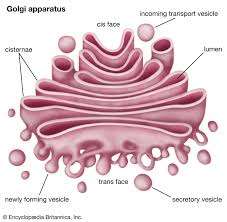
Label these
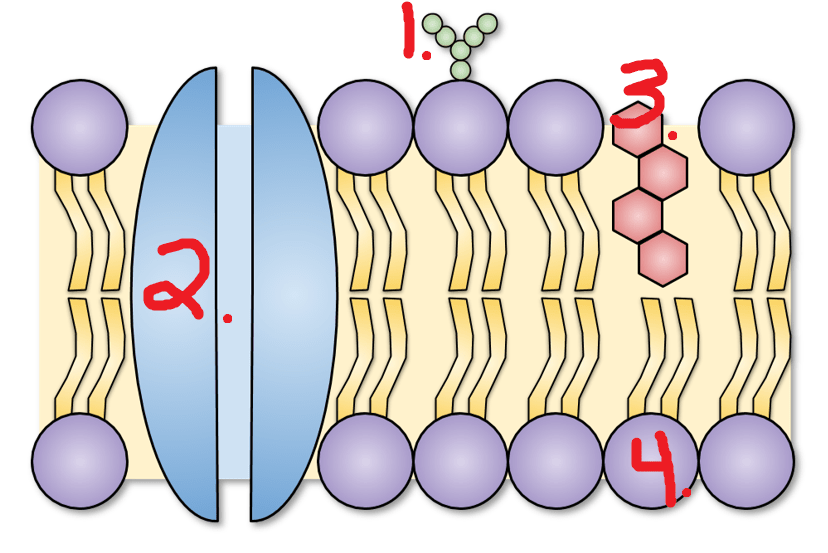
1. Carbohydrate (cell ID)
2. Protein channel
3. Cholesterol (stability)
4. Phospholipid (purple hydrophilic / yellow hydrophobic)
Difference between stem cells and differentiated cells.
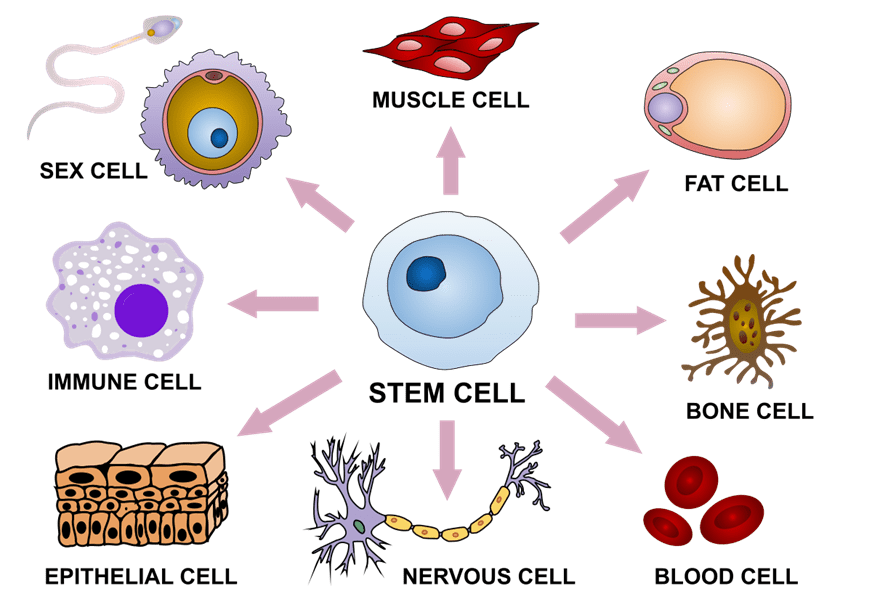
Stem cells divide into other stem cells OR become a differentiated cell.
Differentiated cells are specific cells (like skin cell or blood cell)
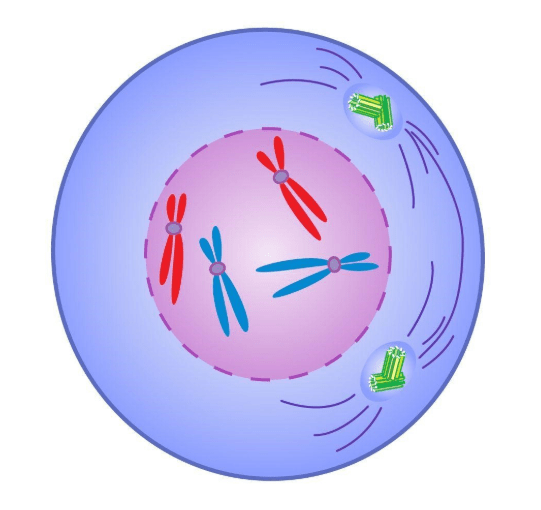
What went wrong?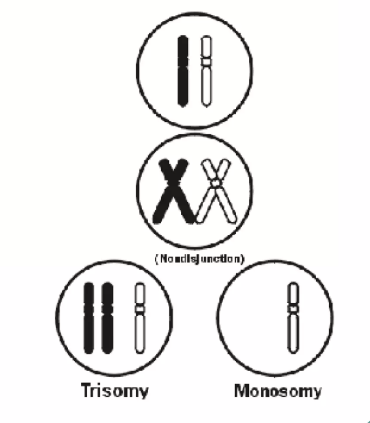
Spindle fibers did not pull sister chromatids apart