the variable that you are testing/manipulating
what is
Independent variable
water is considered a ____________ molecule because it has both a negative and positive end
what is
polar
Which macromolecule is used as the primary source of energy
what is
carbohydrates
Which organelle is involved
A rare blood disorder causes red blood cells to burst easily because water rushes into them too quickly.
What is
plasma membrane
the majority of the plasma membrane is made of what two components
what is
phospholipids and proteins
type of transport that does not use energy
what is
passive transport
what does hypertonic mean
what is
more salt than water
variable that responds to the changes you made
what is
dependent variable
property that allows water to stick to itself
what is
cohesion
Which macromolecule makes up the majority of our plasma membrane?
what is
lipids (phospholipids)
Which organelle am I
A child is diagnosed with Diamond-Blackfan anemia, a condition where the body cannot make enough red blood cells. Doctors discover that the patient’s cells struggle to build proteins needed for blood cell production.
what is
ribosomes
What part of the plasma membrane is responsible for cell to cell recognition or communication
what is
carbohydrates / oligosaccharide
movement across the membrane from H-L
what is
osmosis
If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution what will happen to the cell?
what is
it will shrink
variables that stay the same
what is
constant / control
property that allows a tree to pull water from the roots to the leaves
what is
capillary action
Which macromolecule does this monomer belong to?
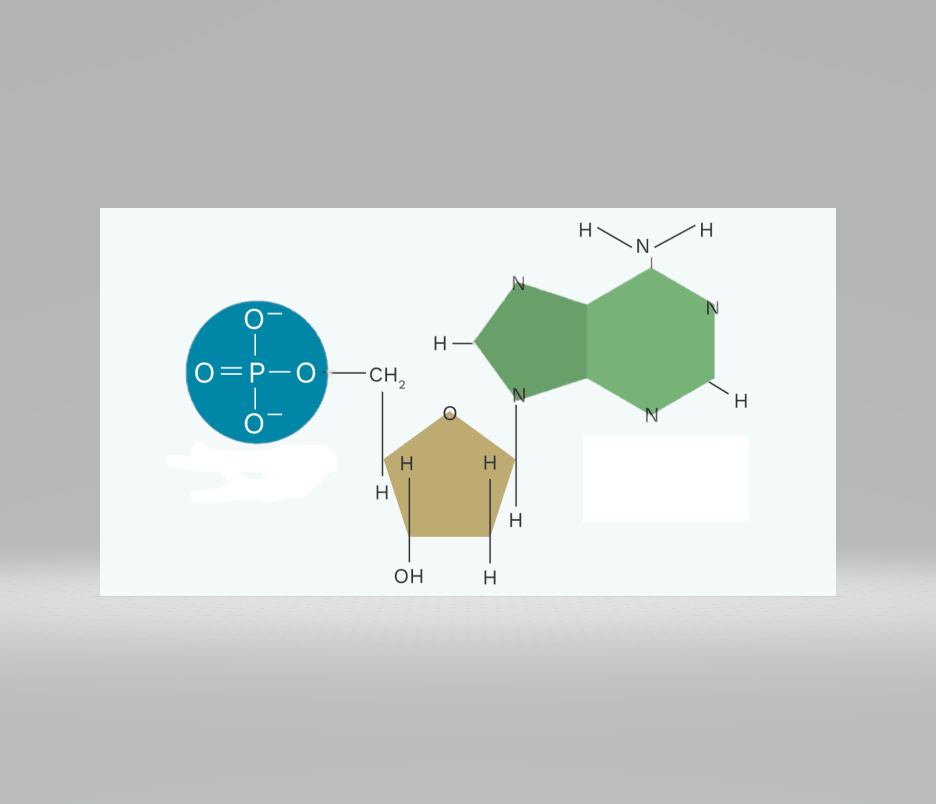
what is
nucleotide
Which organelle is malfunctioning?
A muscle cell disorder prevents calcium from being released at the right time during contraction, making movement difficult.
what is
smooth ER
component of the membrane that helps control the fluidity of the membrane
what is
cholesterol
movement of bulk materials out of the cell
what is
exocytosis
A cell placed in an isotonic solution will:
what is
stay the same
how does the type of fertilizer change the growth of a plant
What is the independent variable
what is
type of fertilizer
When water sticks to another substance
what is
adhesion

Which macromolecule does this monomer belong to?
what is
proteins
Which organelle is affected?
A newborn has I-cell disease, where enzymes meant to digest waste are released outside the cell instead of staying where they belong. Waste materials build up inside the cell.
what is
lysosomes
type of transport that moves bulk substances into the cell
what is
endocytosis
how does CO2 and O2 move across the membrane
what is
simple diffusion
a cell that is placed in hypotonic solution will
what is
swell
How many variables can be tested at one time
what is
one variable
Bond that allows water molecules to stick to each other
what is
hydrogen bonds
macromolecules are put together by which process?
how does it happen (2 words)
what is
dehydration synthesis
removing water
A rare disorder causes cells to build up waste because lysosomes do not receive the enzymes they need. The enzymes are made but never delivered.
Which organelle is responsible for this problem?
what is
Golgi body
Type of transport that brings liquids into the cell (be specific)
what is
pinocytosis
What type of transport will move large and polar substances across the membrane
What is
facilitated diffusion
a cell that has 30% solute is placed in a solution that has 60% solute
What will happen to the cell
what is
it will shrink
the group that is given the independent variable
what is
experimental group
property that allows water to regulate the Earth's climate
what is
specific heat
Macromolecules are broken down by which process
How does it happen (2 words)
what is
hydrolysis
adding water
Which organelle normally performs this function?
A person has high levels of toxins in their bloodstream because their cells cannot neutralize harmful chemicals.
what is
smooth ER
bringing large food particles into the cell
be specific
what is
phagocytosis
Type of transport that pumps 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell
What is
active,
sodium potassium pump
primary active transport
A cell is placed in a solution that is 50% water and 50% salt, the cell has a water concentration of 80%
What will happen to the cell
What is
it will shrink