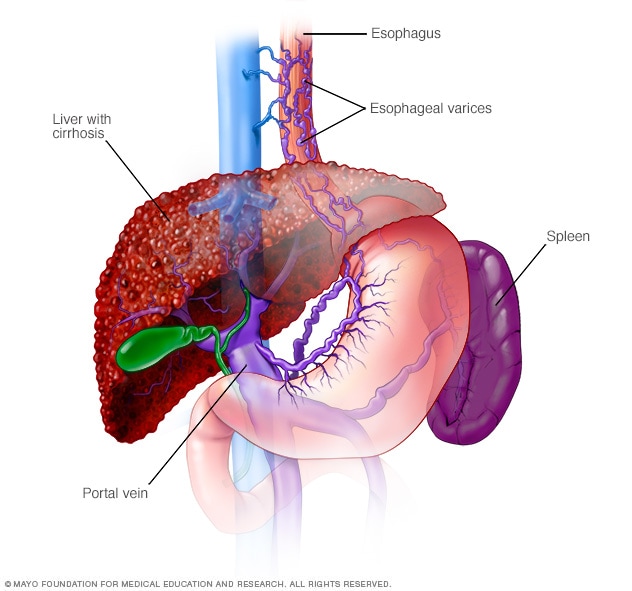
Vomiting blood or passing black, tarry stool in a cirrhotic is often due to these dilated veins?
What are esophageal/gastric varices
A positive Castell's sign indicates what condition?
What is splenomegaly?
The most common CBC clue to portal hypertension from hypersplenism.
What is thrombocytopenia?
This score (based on bilirubin, INR, creatinine and sodium) helps determine mortality risk and transplant priority.
What is MELD-Na?
This common cause of abdominal distension in portal HTN results from fluid in the peritoneal cavity.
What is ascites?
Traube's space.
What is the space between the 6th rib, costal margin and mid-axillary?
Low albumin, elevated INR and elevated bilirubin suggest this underlying cause of portal hypertension.
What is impaired hepatic synthetic function?
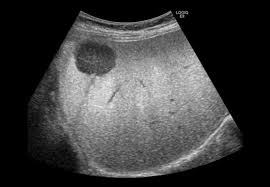
Cirrhosis and a liver lesion on screening ultrasound raises concerns for this complication.
What is Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)?
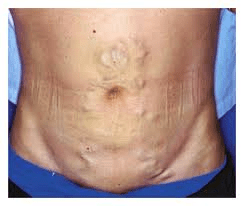
This exam finding - dilated superficial abdominal veins - can look like "a head of snakes" or the "hair of a mad woman".
What is caput medusae?
This skin finding (spider like lesions) points toward chronic liver disease, often underlying portal HTN but a sign of hyperestrogenemia.
What are spider angiomata?
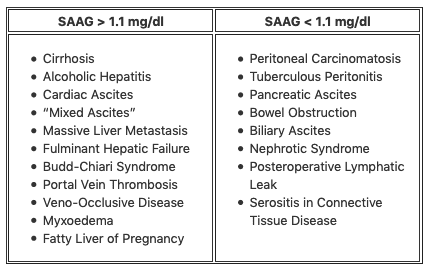
In portal HTN, this ascitic fluid pattern suggests portal HTN physiology (not infection or malignancy).
What is a high SAAG (serum-ascites albumin gradient)?
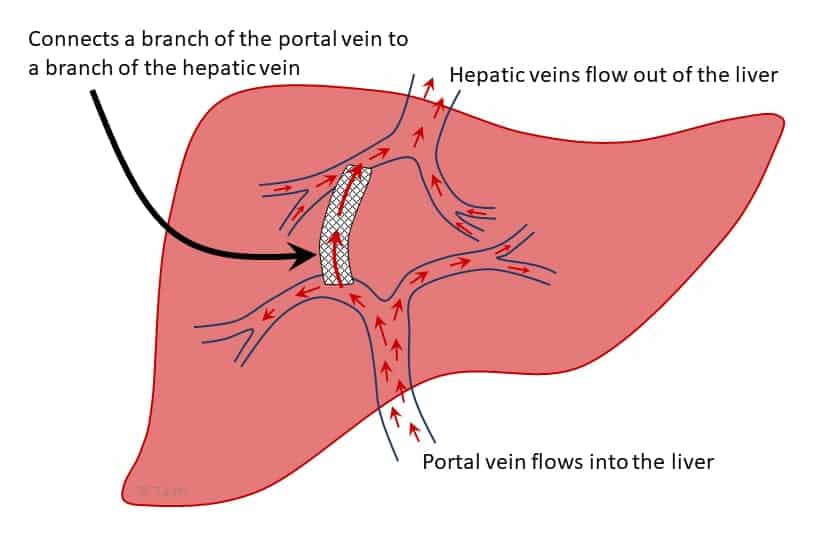
This procedure creates a channel between the portal vein and this hepatic vessel to lower portal pressure.
What is the TIPS procedure?
Confusion and sleep-wake reversal in advanced liver disease suggests this complication often associated with portal HTN.
What is hepatic encephalopathy?
Straight arms, hands open and acting like a stop sign with the eyes closed. Boom...a flap.
What is asterixis?
This electrolyte abnormality is common in advanced cirrhosis and ascites and often signals worse disease severity.
What is hyponatremia?
Indication for TIPS procedure when ascites persists despite sodium restriction and maximal diuretics and/or frequent large-volume paracenteses.
What is refractory ascites?
This GI bleed can be subtle and present as fatigue and low hemoglobin rather than hematemesis.
What is occult blood loss from portal hypertensive gastropathy?

A bruit over the epigastrium in portal HTN can indicate increased flow through this collateral pathway.

What is a portosystemic collateral/shunt (eg: recanalized umbilical vein)?
Fever, abdominal pain, and worsening encephalopathy in a patient with ascites suggests this diagnosis.
What is spontaneous bacterial peritonitis?
Acute kidney injury after large-volume paracentesis without adequate expansion can be prevented with this.
What is albumin?
1.5g/kg day 1 then 1g/kg day 3