This scientist studied pea plants and proposed that traits are passed as discrete units.
Who is Gregor Mendel
The repeating subunit (monomer) that makes up DNA.
What is a nucleotide?
The phase of the cell cycle when DNA is copied.
What is the S phase?
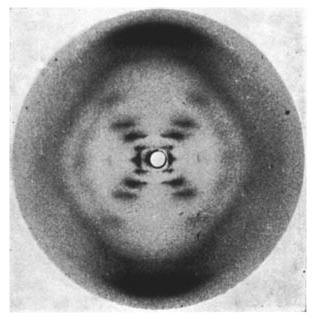 Theis scientist was able to use image crystallography to capture the first image of the Double helix
Theis scientist was able to use image crystallography to capture the first image of the Double helix
who is Rosalind Franklin?
This scientist discovered the “transforming principle” using smooth and rough bacteria in mice.
FWho is Fredrick Griffith
The three parts of a DNA nucleotide.
What are a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base?
The enzyme that “unzips” DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds.
What is helicase?
An organism that infects bacteria
What is a Bacteriophage?
This scientist provided evidence that DNA—not protein—was the transforming principle.
Who is Oswald Avery
These two bases always pair together using double bond in DNA.
What are adenine and thymine?
The enzyme that adds new DNA nucleotides to the growing strand.
What is DNA polymerase?
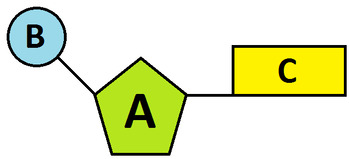 What is structure C
What is structure C
What is a nitrogen base?
These two scientists used radioactive sulfur and phosphorus to prove DNA enters bacterial cells.
Who are Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase?
The type of bond that holds complementary bases together in the center of the DNA molecule.
What are hydrogen bonds?
The type of replication where each new DNA molecule contains one old strand and one new strand.
What is semiconservative replication?

What isa double helix?
This scientist produced X-ray images that showed DNA had a helical shape.
Who is Rosalind Franklin?
The shape of DNA described as a twisted ladder.
What is a double helix?
This strand of DNA that is copied in short fragments discontinuously.
What is the lagging strand?
 What is the blue structure
What is the blue structure
What is Helicase?