During the assessment of a 52-year-old female patient that is receiving oxygen via nasal cannula at 4 L/min, you hear the bubble humidifier making a whistling noise. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this finding?
A. There is an obstruction in the delivery tube
B. The patient’s ventilation has increased
C. There is a clogged system diffuser
D. The flowmeter pressure is set too high
There is an obstruction in the delivery tube
A 58-year-old female patient has arrived in the emergency department with an extremely deep and fast breathing rate. Which of the following best classifies this type of breathing?
A. Apneustic breathing
B. Kussmaul breathing
C. Biot’s breathing
D. Cheyne-Stokes breathing
Kussmaul breathing
A female patient who was in a motor vehicle accident arrives
to the emergency department with broken ribs. While
palpitating the patient’s neck, crepitations were felt. What is
most likely the cause of this finding?
A. The patient has a laryngeal tumor
B. The patient has a pneumothorax
C. Blood is in the back of the patient’s throat
D. The patient has aspirated a tooth
The patient has a pneumothorax
While reviewing the medical record of a 55-year-old female patient, you note that her FEV1/FVC ratio was reported as being severely decreased. Which of the following conditions would you expect to be present with this finding?
A. Pulmonary hypertension
B. Morbid obesity
C. Chronic asthma
D. Pneumonia
Chronic asthma
If you were to take the total of the maximum volume of air
that can be exhaled from the maximum inspiratory level, this
can be defined as which of the following?
A. Residual volume
B. Expiratory reserve volume
C. Vital capacity
D. Total lung capacity
Vital capacity
A BiPAP machine that was used in the emergency
department was just returned for cleaning. Which of the
following agents would you use for surface disinfection?
A. Ethylene oxide
B. 70% ethyl alcohol
C. Alkaline glutaraldehyde
D. Acetic acid
70% ethyl alcohol
After obtaining results from a transcutaneous blood gas
monitor, you are asked to validate the readings. You should
do which of the following?
A. Perform a two-point calibration of the monitor
B. Change the placement of the sensor every 2–6 hours
C. Compare the monitor’s readings to an ABG
D. Re-membrane the sensor and adjust its temperature
Compare the monitor’s readings to an ABG
You are called to assist with needle decompression for a
patient with a tension pneumothorax. Which of the following
is the correct placement for this procedure?
A. Second intercostal space in the anterior axillary line
B. Second intercostal space in the midclavicular line
C. Third intercostal space in the anterior axillary line
D. Third intercostal space in the midclavicular line
Second intercostal space in the midclavicular line
The husband of a comatose patient asks you to cancel a
previously approved DNR order. How should you proceed?
A. Record the request in the patient record
B. Explain that only her husband can cancel the order
C. Notify the charge nurse of the request
D. Notify the attending physician of the request
Notify the attending physician of the request
A 23-year-old male patient with a severe head cold is receiving oxygen via nasal cannula at 4 L/min. The pulse oximeter reveals an SpO2 of 85%. Which of the following would you recommend?
A. Increase the oxygen flow until the SpO2 equals or
exceeds 90%
B. Decrease the oxygen flow until the patient is more
comfortable
C. Switch to a simple mask
D. Recommend an ABG before considering any changes
C. Switch to a simple mask
A 71-year-old male patient is receiving ventilatory support and it was noted that his secretions are yellow and have gotten thicker over the past 24 hours. The patient has a white blood cell count of 17,000/mm3 and a temperature of 102 °F. Which of the following would you suggest?
A. Decrease the humidifier temperature
B. Administer an aerosolized bronchodilator
C. Schedule suctioning twice per hour
D. Obtain a sputum sample for culture and sensitivity
Obtain a sputum sample for culture and sensitivity
While performing a routine chest percussion, you noticed
that a 57-year-old male patient has a flat percussion note.
Which of the following does this finding indicate?
A. Pneumonia
B. Pneumothorax
83
C. COPD
D. Atelectasis
Atelectasis
A pre and post bronchodilator test was ordered on a 48-yearold
female patient. The forced expiratory measurement that
was obtained after the bronchodilator was given shows an
increase in the patient’s FEV1 from 60% to 80% of the
predicted value. This finding suggests which of the following?
A. A fixed airway obstruction
B. A reversible airway obstruction
C. A normal diffusion capacity
D. A restrictive process
A reversible airway obstruction
Other than obtaining the results from a vital capacity
maneuver, what else should be obtained and noted from the
patient?
A. The patient’s resting minute ventilation
B. The patient’s height, gender, and age
C. The patient’s heart rate before/after testing
D. The patient’s actual and predicted body weight
B. The patient’s height, gender, and age
A patient was admitted to the ICU with a severe case of
influenza. Before entering the patient’s rooms, in addition to
standard precautions, what else must be used?
A. Droplet precautions
B. Universal precautions
C. Contact precautions
D. Airborne precautions
Droplet precautions
You are needed to assess a 61-year-old male patient that is
conscious and appears to be in no apparent distress. You
note on the arterial pressure monitor that the pressure
waveform is absent and the alarm is sounding. What should
your first action be?
A. Call for the Rapid Response Team
B. Replace the broken monitor
C. Check the stopcock position
D. Confirm that the monitor is set to zero/cal
Check the stopcock position
After instructing a patient on how to perform diaphragmatic
breathing, which of the following can you observe to
recognize if they are performing it properly?
A. The use of pursed-lip breathing
B. The abdomen rising on exhalation
C. The abdomen rising on inspiration
D. The use of intercostal muscles during inspiration
The abdomen rising on inspiration
A 52-year-old female patient has been smoking 1.5 packs of
cigarettes per day for 30 years. Her smoking history would be
recorded as:
A. 15 pack-years
B. 30 pack-years
C. 45 pack-years
D. 60 pack-years
45 pack-years
A newly admitted adult patient with pneumonia has an
oxygen saturation of 87% on a nasal cannula at 2 L/min.
Which of the following is a potential cause of the patient’s
hypoxemia?
A. Fever and chills
B. Diffusion defect
C. Alveolar consolidation
D. Hypoventilation
Alveolar consolidation
While reviewing the chest x-ray of a 57-year-old male patient,
you note that there is blunting of the left costophrenic angle.
It’s also noted that the patient has a history of CHF. Which of
the following best describes this patient’s condition?
A. There is a pneumothorax on the left side
B. There is a pleural effusion on the left side
C. There is pulmonary edema in the left lung
D. There is pneumonia in the left lower lobe
B. There is a pleural effusion on the left side
A 59-year-old female patient has arrived to the emergency
department in respiratory distress due to severe hypoxemia.
She would most likely exhibit all of the following signs
except?
A. Diaphoresis
B. Cyanosis
C. Bradycardia
D. Tachypnea
Bradycardia
An adult patient has performed an FVC maneuver with the
following results: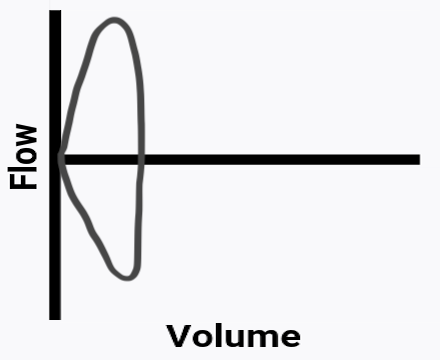
How would you interpret this flow-volume loop tracing?
A. Normal lungs
B. Small airway obstruction
C. Large airway obstruction
D. Restrictive disease
D. Restrictive disease
A 54-year-old female patient’s spirometry results show an
FEV1 that is calculated to be 80% of her forced vital capacity.
This finding suggests that the patient probably has which of
the following?
A. Chronic bronchitis
B. Emphysema
C. An obstructive lung disease
D. Clinically normal values
Clinically normal values
After auscultating a patient in the emergency department,
you noticed blood on the head of your stethoscope. How
should it be cleaned before use on another patient?
A. Sterilized with ethylene oxide
B. Wiped with a bleach solution
C. High-level disinfection with glutaraldehyde
D. Wiped with an alcohol solution
Wiped with a bleach solution
After collecting an ABG sample, you are about the analyze
the sample using a point-of-care analyzer. During the
process, the device flags the PaCO2 results. Which of the
following should you do at this time?
A. Send the sample to the central lab for analysis
B. Repeat the analysis using a fresh sample and the same
cartridge
C. Repeat analysis using a fresh sample and new cartridge
D. Repeat the analysis using the same sample and same
cartridge
A. Send the sample to the central lab for analysis
A 58-year-old male patient in the ICU just had a chest tube
inserted to drain the fluid from a pleural effusion. He is
receiving mechanical ventilation with basic settings and
displays the following vital signs:
Heart rate: 120/min
Blood pressure: 137/95
Set respiratory rate: 10/min
Total respiratory rate: 29/min
Body temperature: 99.2 F
113
Taking everything into consideration, you should
recommend which of the following?
A. Assess the patient for pain
B. Paralyze the patient
C. Ask the patient to relax
D. Reposition the chest tube
Assess the patient for pain
Which of the following is a major disadvantage of using a
pulse oximeter to monitor a patient’s oxygenation status?
A. Skin burns due to using incompatible probes
B. Erroneous results leading to inappropriate treatment
C. Electrical shocks at the measuring site
D. Pressure sores at the measuring site
Erroneous results leading to inappropriate treatment
An adult patient in the emergency room is unconscious with
an SpO2 of 95%. After re-checking with a CO-oximeter, it
reveals that the patient’s SaO2 is 67%. Which of the following
is the most likely cause of this discrepancy?
A. Opiate drug overdose
B. Diabetic ketoacidosis
C. Acute pulmonary edema
D. Carbon monoxide poisoning
Carbon monoxide poisoning
A 64-year old female patient was admitted and the physician
suspects that a pneumothorax is present. Which of the
following percussion notes would you expect to find in this
patient?
62
A. Increased resonance
B. Flat percussion note
C. Dull percussion note
D. Hyperresonant percussion note
Hyperresonant percussion note
After reviewing the chart of a 55-year-old female patient, you
note that she had an admission diagnosis of dehydration.
Which of the following findings would you expect for this
patient?
A. Pitting edema
B. Venous distension
C. Inspissated secretions
D. Crackles on auscultation
Inspissated secretions
A 56-year-old male patient has been admitted and
diagnosed with Guillain-Barré syndrome. In order to
determine the patient's need for ventilatory support, which
of the following values is the most critical to monitor?
A. Residual volume
B. Inspiratory capacity
C. Peak inspiratory flow
D. Expiratory reserve volume
B. Inspiratory capacity
A 29-year-old female patient with suspected asthma needs
to undergo pulmonary function testing to confirm the
diagnosis. Which of the following tests would be the least
helpful in this situation?
A. Lung diffusion study
B. Flow-volume loop
C. Bronchoprovocation testing
D. Pre- and post-bronchodilator testing
Lung diffusion study
All spirometry values obtained under ambient conditions
should be converted to which of the following?
A. Standard temperature and pressure, dry (STPD)
B. Ambient temperature and pressure, dry (ATPD)
C. Ambient temperature and pressure, saturated (ATPS)
D. Body temperature, ambient pressure, saturated (BTPS)
Body temperature, ambient pressure, saturated (BTPS)
After drawing an ABG sample, you notice that the blood
appears to be darker in color. You suspect that obtained
sample is actually venous blood. Which of the following
would be the best way to confirm this suspicion?
A. Get a second opinion from the attending physician
B. Compute the alveolar-arterial O2 gradient
C. Compute the patient’s P/F ratio
D. Cross-check the results against the patient’s SpO2
Cross-check the results against the patient’s SpO2
Which of the following EKG leads should be placed in the 5th
intercostal space at the midclavicular line?
A. V1
B. V2
C. V3
D. V4
V4
The physician requests a humidifier device that can
condition the inspired gas to 100% body humidity. Which of
the following would you recommend?
A. Bubble humidifier
B. Pneumatic nebulizer
C. Heated wick humidifier
D. Heat and moister exchanger
Heated wick humidifier
You are called to administer 70/30 heliox on an 11-year-old girl
in the emergency department. Which of the following would
you use to deliver the therapy?
A. Aerosol mask
B. Venturi mask
C. Nonrebreathing mask
D. Binasal cannula
C. Nonrebreathing mask
You are called for the assessment of a child in the
emergency department. It has been noted that the child has
stridor. Which of the following conditions would you expect?
A. Croup
B. Asthma
C. Pneumonia
D. Cystic fibrosis
Croup
You are called for the assessment of a chest radiograph for a
patient suffering from advanced stages of emphysema.
Upon observation, which of the following would you expect
to see?
A. An increased C/T ratio
B. Increased vascular markings
C. Decreased radiolucency
D. Flattening of the diaphragm
Flattening of the diaphragm
A 56-year-old female patient’s bedside spirometry results are
as follows:
FVC is decreased
FEV1 is normal
FEV1% is increased
What is the most likely problem?
A. Normal results
B. An obstructive disease
C. Poor patient effort
D. A restrictive disease
A restrictive disease
You are about to perform a pulmonary function test on a 65-
year-old male patient after providing a bronchodilator
breathing treatment. It is suspected that the patient has
COPD. His results are as follows:
FEV1/FVC ratio = 64%
FEV1 = 86% predicted
How would you would characterize this patient?
A. Normal
B. Mild COPD
C. Moderate COPD
D. Severe COPD
Mild COPD
Which of the following infection control procedures is to be
used when drawing an arterial blood gas?
A. Hand washing and gloves only
B. Gown and protective eyewear
C. Mask and protective eyewear
D. All CDC standard precautions
All CDC standard precautions
You are called to provide a STAT bronchodilator treatment
for a male patient that is having a severe asthma attack.
While confirming the physician’s written order, you are not
sure if the note says “5 mL of Albuterol” or “0.5 mL of
Albuterol.” The prescribing doctor is busy overseeing a code
and is unable to respond. What action should you take?
A. Have the nurse review the note and clarify the order
B. Cross out the prohibited notations and initial and date
the changes
C. Wait until the physician is done with the code so that you
can clarify the improper notation and the correct order
D. Administer the treatment using the standard albuterol
dosage of 0.5 mL and clarify the order as soon as possible
thereafter
Administer the treatment using the standard albuterol
dosage of 0.5 mL and clarify the order as soon as possible
thereafter
A 61-year-old male patient is scheduled to undergo
cardiopulmonary exercise testing. In which of the following
would you recommend extra precautions before the
performing the test?
A. A patient with a resting systolic BP > 200 mm Hg
B. A patient being evaluated for coronary artery disease
C. A patient recommended for cardiac rehabilitation
D. A patient being assessed for a cardiopulmonary disability
A patient with a resting systolic BP > 200 mm Hg
A 56-year-old male patient with pneumonia has a moderate
amount of oral secretions. Which of the following would you
recommend for suctioning at the patient’s bedside?
A. Lukens trap
B. Coude catheter
C. Yankauer
D. Bulb suction
Yankauer