What is the difference between inversely proportional and directly proportional?
inversely: opposite directions together
directly: same direction together
The following are examples of which gas variable?
L, cm3, dm3, mL, m3
Volume
P1= A P2= D
V1= B V2= E
T1= C T2= ?
T2= (P2V2T1)/(P1V1)
Solve for P2, given the following information:
P1= 1.2 atm V1= 3.5 L T1= 32oC
P2= ? V2= 2.6 L T2=15oC
1.5 atm
Standard Temperature & Pressure
The following are examples of which gas variable?
K, oC, oF
Temperature
Graph B represents the relationship between which gas variables?
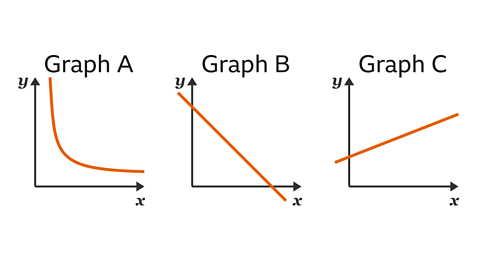
Pressure & Volume
Solve for pressure in torr, given the following information. Use appropriate sig figs (I expect you to memorize how many atm = torr)
P= ? V= 5.80 L T= 25.0oC n= 0.506 mol
1.62 x 103 torr
What type of relationship is present between temperature and volume?
Directly Proportional relationship
When temperature increases, volume increases
The following are examples of which gas variable?
torr, atm, mm Hg, kPa, barr, psi, Pa
Pressure
What is the ideal gas law with molar mass as a variable?
PV = (mRT)/M
Solve for mol of oxygen gas, given the following information. Use appropriate sig figs
P= 142 kPa V= 4.30L T= 23.0oC
0.248 mol O2
What type of relationship is present between pressure and temperature?
Directly Proportional relationship
When temperature increases, volume increases
Which R constant would you use if the given information has atmospheric pressure as a unit?
0.0821 (L*atm)/(mol*K)
What is the ideal gas law with density as a variable?
M= (DRT)/P
Find the mass of ammonia produced given the following information:
N2 + 3H2 --> 2NH3 at STP
6.05 L of N2
P= 85.5 kPa
T= 304K
6.97 g NH3
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT
Which R constant would you use if the given information has kPa as a unit?
What does m represent in the following manipulated, ideal gas law?
PV = (mRT)/M
mass in grams
The mercury is 25.0 mm higher in the atmospheric arm. Find the pressure in Pa and atm, if the atmospheric pressure is 120,000. Pa.
[1 mmHg = 133.322 Pa]
[1 atm = 101,325 Pa]
Pgas = Patm - PPa
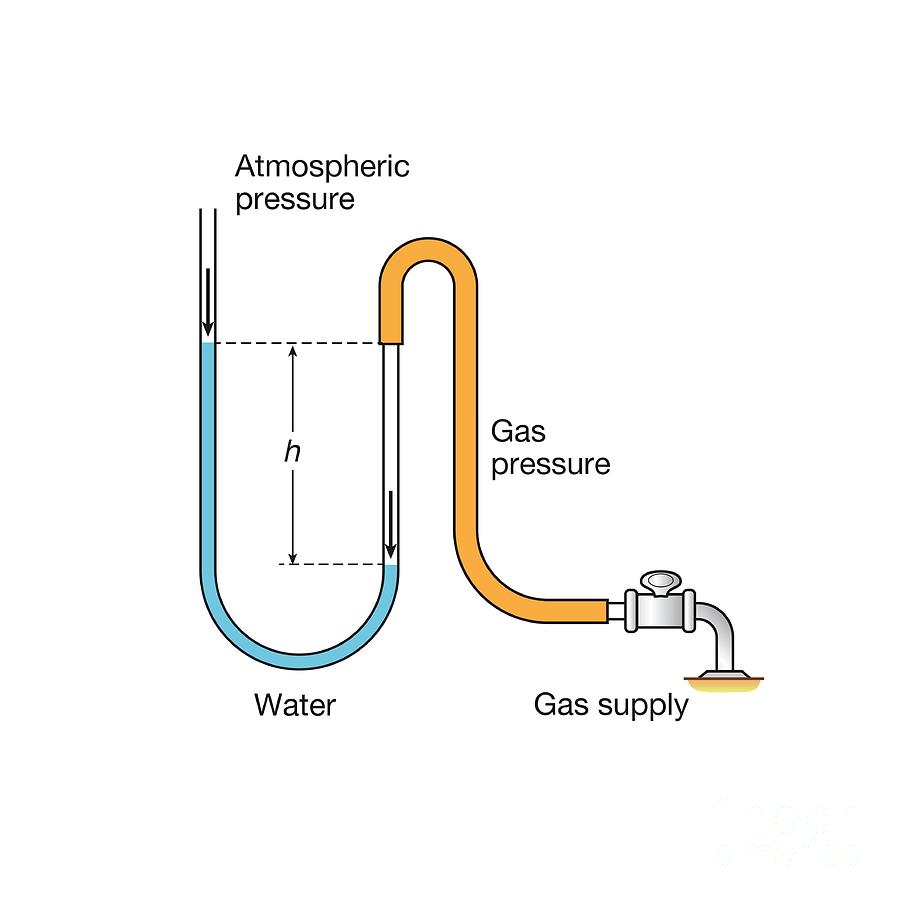
Pressure in Pa: 1.17 x 105 Pa
Pressure in atm: 1.15 atm