an example of passive transport
simple diffusion OR facilitated diffusion OR osmosis
what the enzyme acts upon
Substrate
a pairs with
t
the chloroplast soup is called
the stroma
the mitochondrial soup is called
the matrix
main requirement for active transport
energy or ATP
where the enzyme meets the substrate
active site
c pairs with which base and how many bonds?
g, 3 H bonds
stacks of thylakoids are called
grana
type of cell that would contain lots of mitochondria
liver, immune, muscle
hydrophobic part of the cell membrane
lipid tails or fatty acid tails
an enzyme is a biological...
catalyst
the backbone of DNA
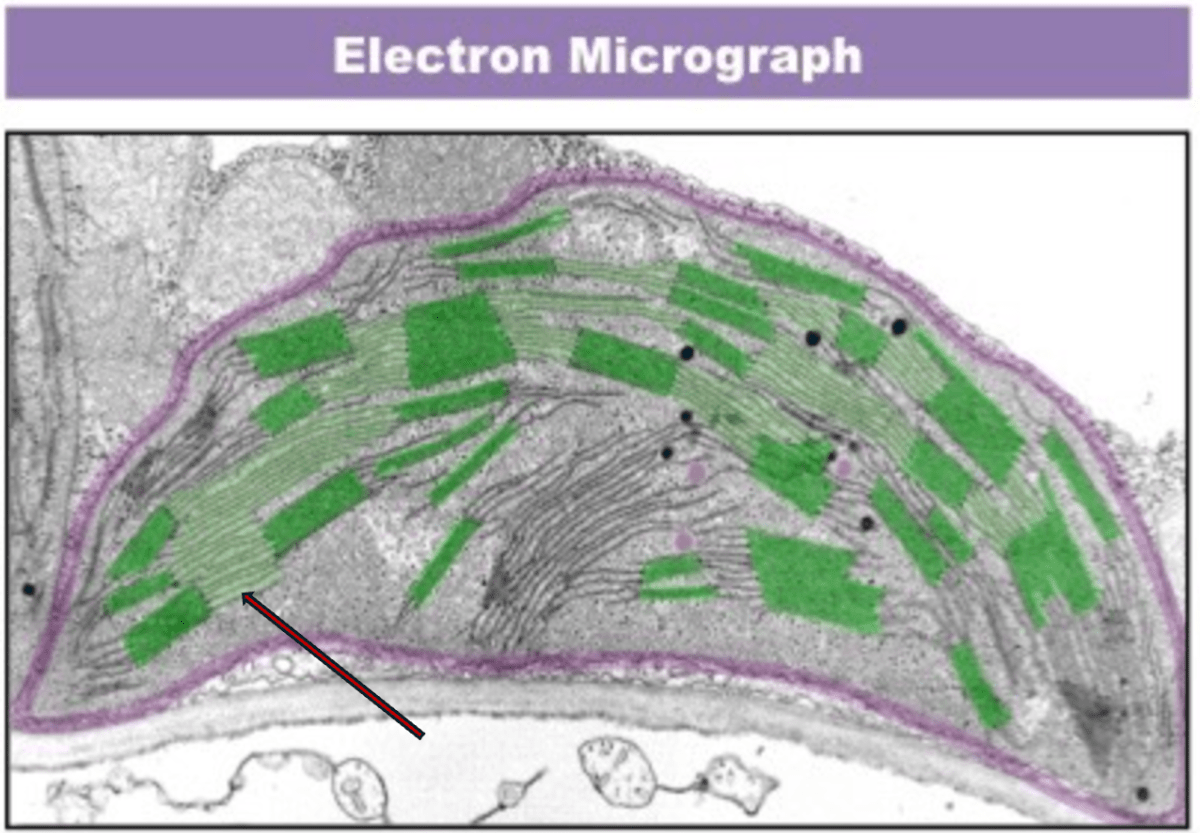
What is the arrow pointing at?
Lamella
site of aerobic respiration
mitochondria
hydrophilic part of the cell membrane
phospho heads or phospholipid heads
what happens with mechanical stress, non-optimal pH and high temperatures to enzymes?
denaturation
sugar, phosphate, base together are called
nucleotide
what the light-independent reaction builds
glucose
What is the respiration equation for aerobic respiration?
Glucose + oxygen -> 36 ATP + carbon dioxide + water
the name for the structure of the cell membrane
phospholipid bilayer
During a metabolic reaction if an enzyme is present, it speeds up the process and is used up.
TRUE OR FALSE.
IF FALSE EDIT IT TO BE TRUE.
FALSE.
During a metabolic reaction if an enzyme is present, it speeds up the process and is not used up. Enzymes get released and are able to be used again.
okazaki fragments are glued together by
ligase
the pigment in chloroplasts
chlorophyll
reaction in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
glycolysis