Geologic Timeline
Geologic Timeline
Superposition
Fossils
During what era and period did the Age of Mammals begin?
The Law of Superposition states that the oldest rock layers are always on the __________, and the layers that formed on top of those layers are _______________
bottom, younger
What type of rock are fossils most likely to be found in?
Sedimentary
Describe the relative age of Layer A5 using only rock layers from Outcrop A.
Layer A5 is younger than Layer A___ but older than Layer A___
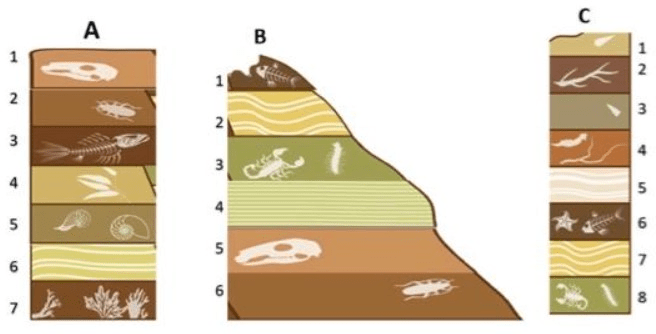
Layer A5 is...
younger than Layer A6 & A7
older than Layers A1, A2, A3, A4
What is the name of the type of fossil that include footprints, trails, animal holes, and even feces.
Trace Fossil
Which era was ended with a mass extinction that caused most marine invertebrates as well as amphibians to disappear?
Paleozoic Era
The law of superposition gives us the ... of rock layers.
A. Absolute age
B. Relative age
B. Relative age
Do Index Fossils give us the relative age or absolute age of rock layers?
A. Relative Age
B. Absolute Age
A. Relative Age
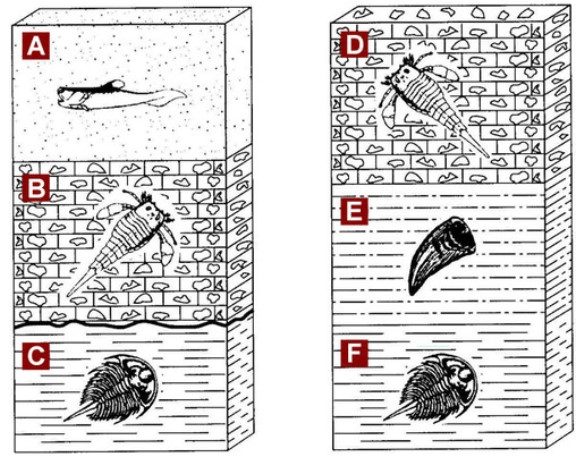
4 layers match up to be the same age based on the fossils found. For example, Layer B1 matches C6.
Name the other 3 matchups.
Layer A1 & Layer B5
Layer A2 & Layer B6
Layer B3 & Layer C8
Minerals replace the dead cells of an organism and slowly turn it into a rocklike fossil.
Petrified Fossil
If we read the Geologic Timeline like the law of superposition, what is the oldest period shown, and what is the most recent (current) period shown?
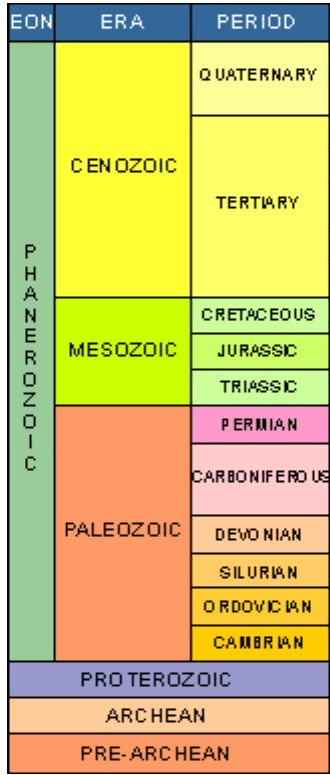
Oldest = Cambrian
Most recent = Quaternary
What is the relative age of Layer E?
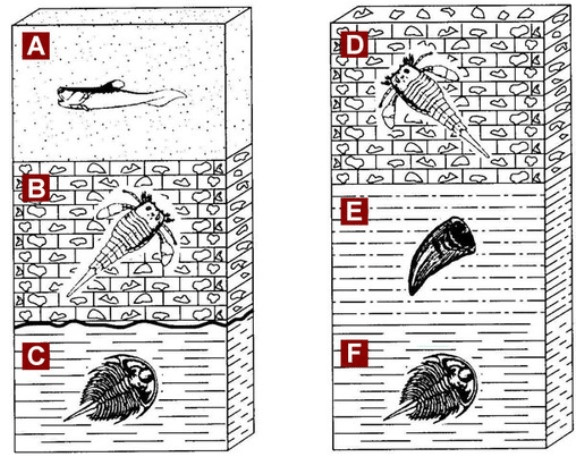
Layer E is younger than Layer F but older than Layer D
What are the 2 characteristics a fossil needs to be considered an index fossil?
1. Lived over a short period of time
2. Lived in many places on the planet
1. Of all the rock layers in the picture, what is the oldest layer of rock?
2. Of all the rock layers in the picture, what is the youngest layer of rock?
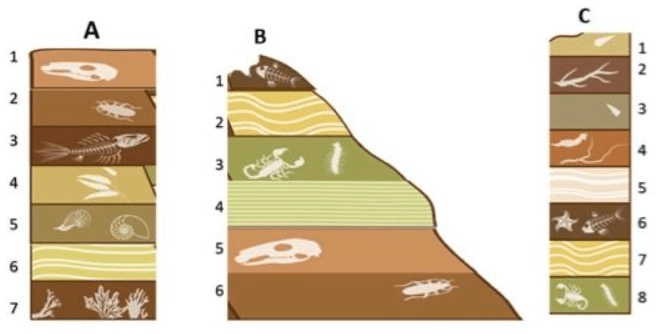
1. Oldest = A7
2. Youngest = C1
What theory explains why you can find similar fossils on different continents?
Plate Tectonics
List the units of time in the geologic time scale from longest amount to shortest amount. (There are four units of time).
Eon, Era, Period, Epoch
Put all the layers in order from youngest to oldest based on the fossils within each layer.
Youngest
A
B & D
E
C & F
Oldest
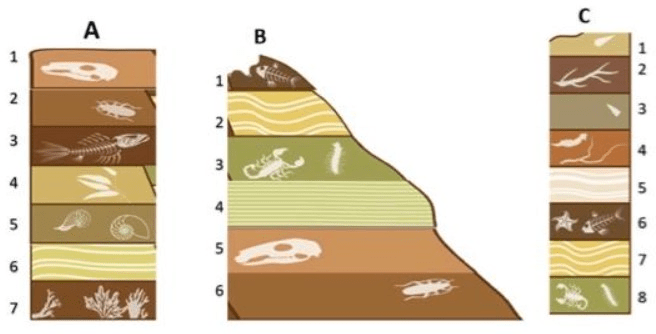
Looking at Layer C1 & Layer C2, which has a shorter relative age range? Explain how you know.
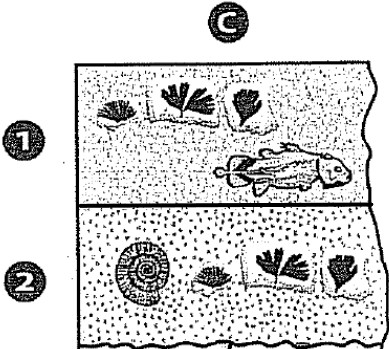
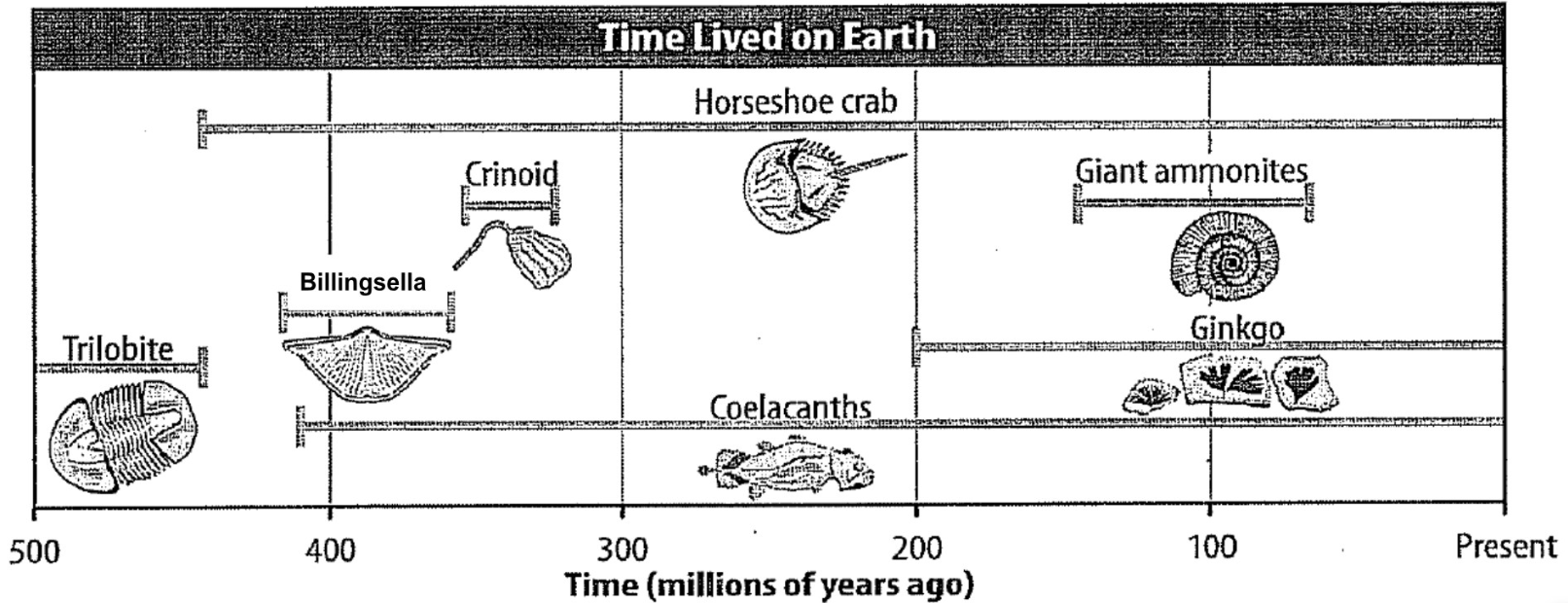
Layer C2 because both layers contain Ginkgo fossils, but Layer C2 contains an ammonite fossil that lived for a much shorter time period than the Coelacanths that was found in Layer C1
Relative Age Range for C1 = 200 myo - present
Relative Age Range for C2 = ~150 myo - ~75myo
If Layer B3 is 10myo and Layer B5 is 14myo describe the relative ages for Layers B4.
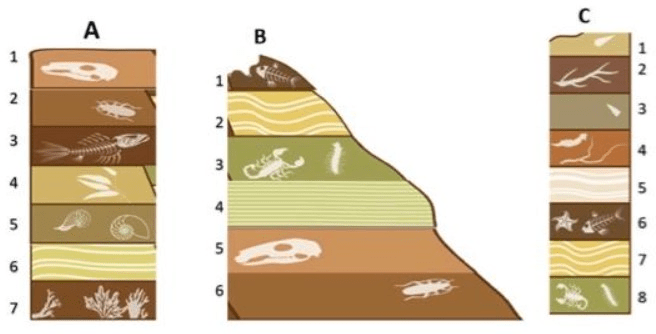
Layer B4 is older than 10myo but younger than 14myo
Name the two ways that rock layers can be disturbed that we went over.
Intrusions and Faults
Which period in the Mesozoic Era lasted the longest in geologic history?
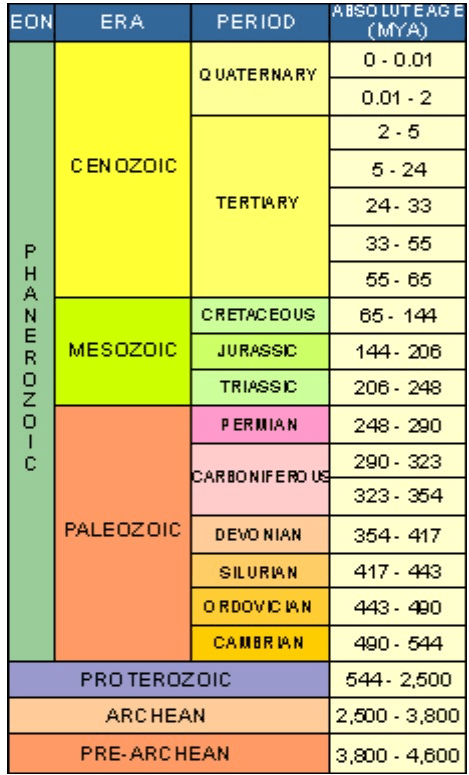
Cretaceous = 79 million years
Jurassic = 62 million years
Triassic = 42 million years
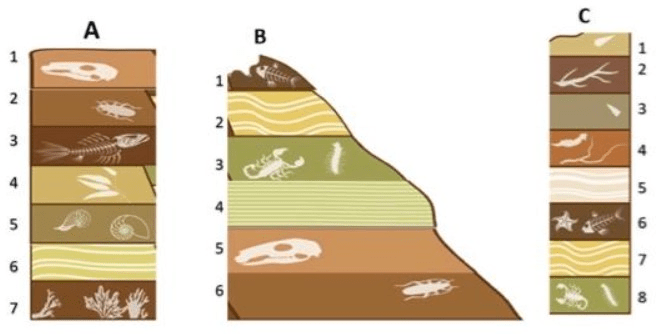
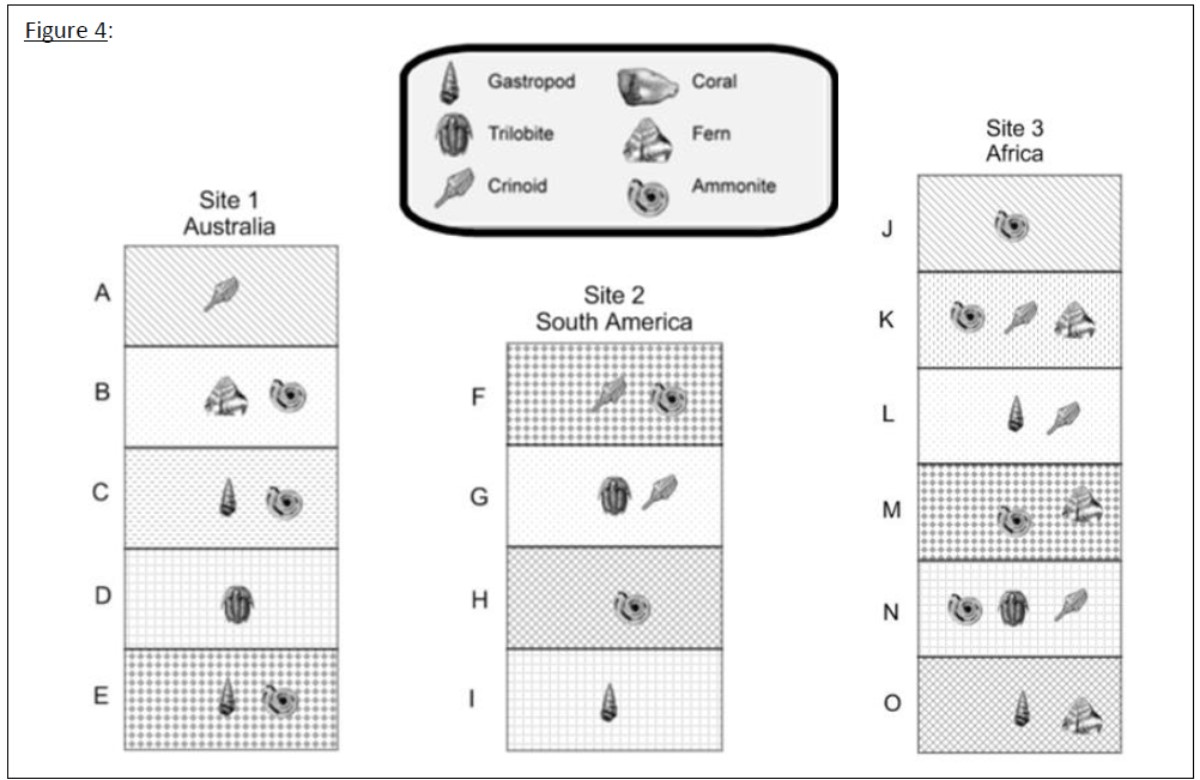
Put the layers in order from youngest to oldest based on the matching fossil layers and stone layer patterns.
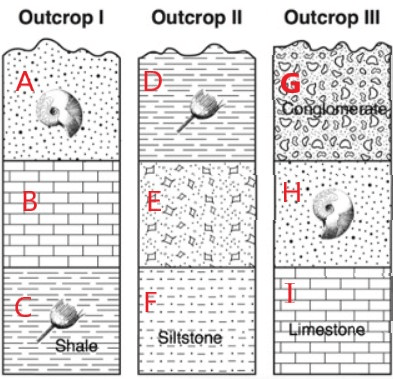
youngest
G
A & H
B & I
C & D
E
F
oldest
Looking at these 3 rock layer outcrops, what is the best index fossil? When deciding, pay attention to the three characteristics that make up a good index fossil to help you.
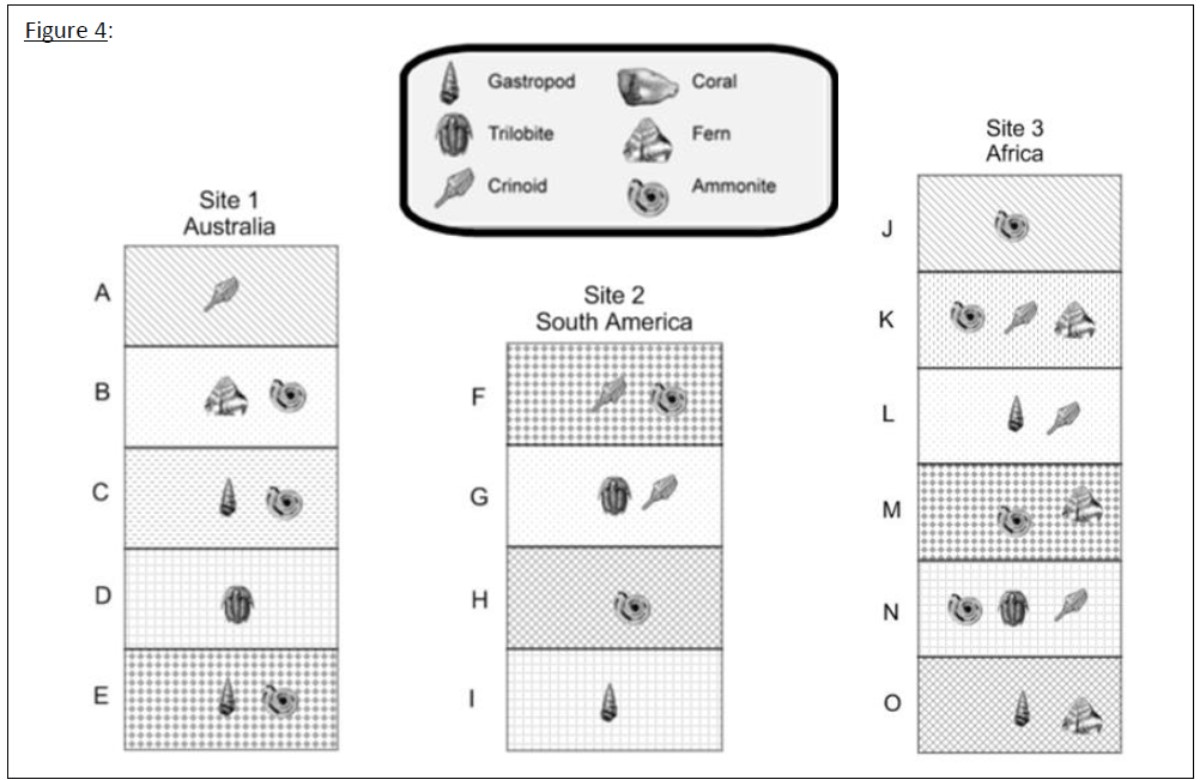
The Trilobite
If Layer B3 is 10myo and Layer B5 is 14myo describe the relative ages for Layer A2 & Layer C6.
Layer A2 is older than 14myo but younger than Layer A3
Layer C6 is older than Layer C7 but younger than 10myo
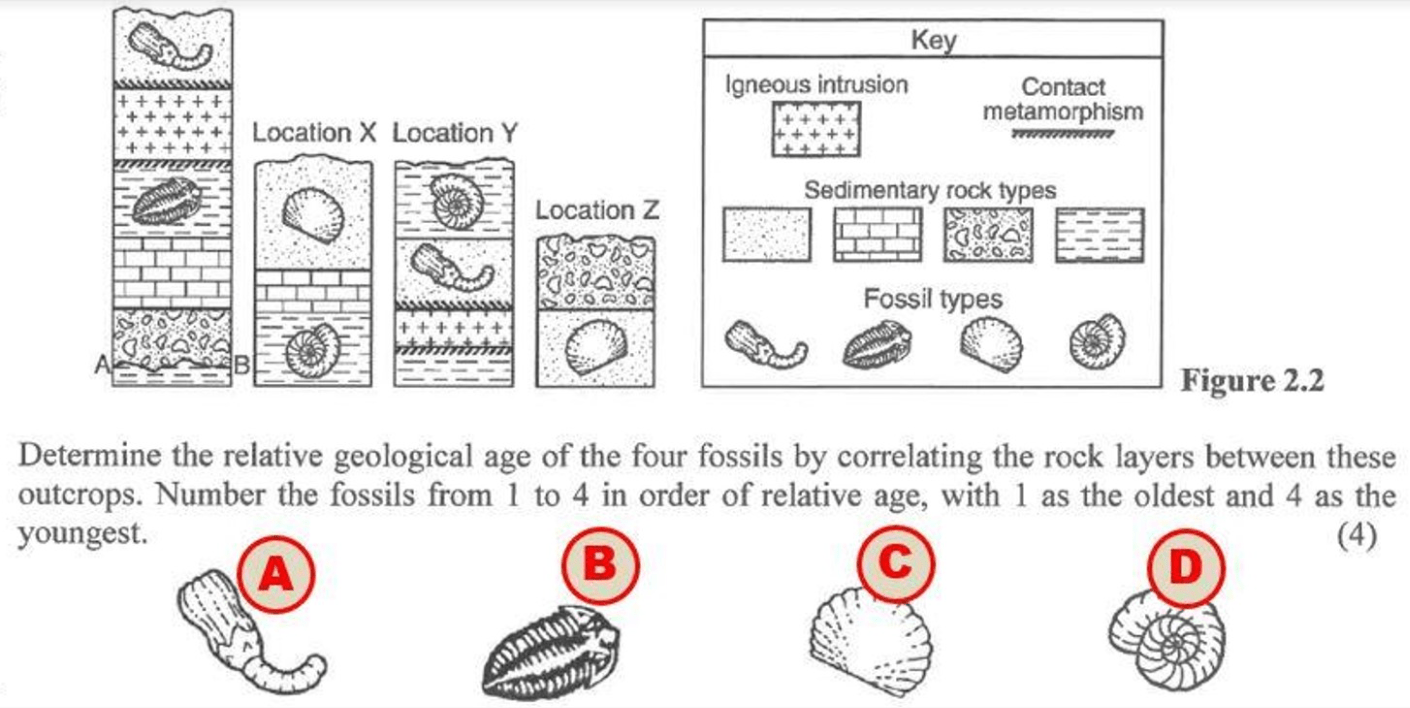
Youngest
C
D
A
B
Oldest