What is DKA?
uncontrolled glucose levels rise and breaks down fat rapidly causing a build up of ketones (acid) in the body and can be life threatening
What are the three main signs that someone is having difficulty breathing and what added sign points to ARDS?
agitation, restlessness, confusion
ARDS- low O2 despite oxygenation
What are the five main meds for sedation in intubated patients?
midazolam, fentanyl, propofol, rocuronium, succinylcholine
A patient is found to have a blood glucose of 375 mg/dL, positive ketones in the urine, and blood pH of 7.25. Which condition is this?
DKA
Which of the following is NOT a medical treatment for DKA and HHNS?
- A. IV regular insulin
- B. Isotonic fluids
- C. Bicarbonate
- D. IV potassium Solution
C. Bicarb
what is the difference betweek DKA and HHNS? (one major thing)
ketones are only present in DKA
What is ARF?
it is a symptom of a condition that causes the lungs to be unable to maintain Oxygenation or eliminate CO2
What supplies should ALWAYS be with a chest tube in case of dislodgement?
petroleum gause, 4x4 gauze, transparent dressing, clamp, sterile water/saline
Which diagnostic test will provide the nurse with the most specific information to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions for a patient with ventilatory failure?
a. Chest x-ray
b. O2 saturation
c. Arterial blood gas analysis
d. Central venous pressure monitoring
C. arterial blood gas analysis
Your patient is being supported with mechanical ventilation. The high pressure
alarm in a mechanical ventilator sounds. An appropriate first nursing action would
be to:
A. check the ventilator connections
B. measure the endotracheal cuff for a leak.
C. call respiratory therapy
D. assess the patient’s respiratory status
D. assess the patient's respiratory status
always check the patient first!
Why is kussmaul breathing common in DKA?
Kussmaul respirations happen when the body tries to remove carbon dioxide, an acid, from the body by quickly breathing it out.
When should you notify a provider about drainage?
if it is greater than 100 mL/hr or is increasing
for mediastinal chest tubes- if it is over 250 mL in first hr, or 800 mL in 4 hrs.
A 27-year-old client has a tracheostomy and is currently in the hospital using a mechanical ventilator. The nurse is preparing to suction the client. Prior to starting the suction procedure, which of the following should the nurse do first?
- Hyperoxygenate the client
- Remove the cap on the tube and insert the suction catheter
- Administer 2 mL of normal saline into the trach tube
- Remove the trach dressing
hyperoxygenate the client
A patient with a chest tube has no fluctuation of water in the water seal chamber. What could be the cause of this?
- A. This is an expected finding.
- B. The lung may have re-expanded or there is a kink in the system.
- C. The system is broken and needs to be replaced.
- D. There is an air leak in the tubing.
B. the lung may have re-expanded or there is a kink in the system
What are some s/s of HHNS?
symptoms slow onset, severe dehydration, dry mucous membranes, hypotension, tachycardia, diaphoresis, tachypnea, polyuria, polydipsia, altered LOC, Polyphagia, Lethargy and fatigue, Vision changes, Rapid onset of lethargy, Stupor and coma, Neurologic changes
What are treatments for ARDS?
Correct the cause!
Respiratory support—may need
intubation and ventilation
Antibiotics and steroids, O2, Diuretics, Prone positioning, Hydration, Nutrition
What are some assessments you would perform after intubation to verify success?
end tidal CO2 level--first, lung sounds, temporarily secure ET tube until after CXR, vital signs, SpO2, mark and document placement of tube, CXR, ABG, ventilator changes as per ABG and provider
Which of the following is not a sign or symptom of Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
- A. Positive Ketones in the urine
- B. Polydipsia
- C. Oliguria
- D. Abdominal Pain
C. Oliguria
A patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and acute kidney injury has several drugs prescribed. Which drug should the nurse discuss with the health care provider before giving?
a. Gentamicin 60 mg IV
b. Pantoprazole (Protonix) 40 mg IV
c. Sucralfate (Carafate) 1 gram per NG tube
d. Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) 60 mg IV
A. gentamicin; because it can be nephrotoxic (aminoglycoside antibiotics)
What can cause DKA?
stress, surgery, illness, infection, new onset of DM1, inadequate insulin. missed or reduced dose of insulin
What does ARDS look like chemically? (thing ABGs)
Tachypnea causes alkalosis as CO2 levels decrease.
The lack of oxygen also forces the body into anaerobic metabolism and adds to the acidosis.
Unless gas exchange is restored and this process is reversed, acidosis worsens until all organ systems are affected and fail.
What are the three ventilation modes and how do they work?
volume controlled- delivers a set amount of volume to patient
controlled volume- machine is doing all the breathing, lungs inflated to set pressure
high frequency oscillating ventilation- very low tidal volume, deliver 300-900 breaths/ min usually used for ARDS, neonates or very abnormal breathing pattern
When admitting a patient with possible respiratory failure and a high PaCO2, which assessment information should be immediately reported to the health care provider?
a. The patient appears somnolent.
b. The patient reports feeling weak.
c. The patient’s blood pressure is 164/98.
d. The patient’s oxygen saturation is 90%.
A. the patient appears somnolent. (sleepy or drowsy)
While helping a patient with a chest tube reposition in the bed, the chest tube becomes dislodged. What is your immediate nursing intervention?
- A. Stay with the patient and monitor their vital signs while another nurse notifies the physician.
- B. Place a sterile dressing over the site and tape it on three sides and notify the physician.
- C. Attempt to re-insert the tube.
- D. Keep the site open to air and notify the physician.
B. place a sterile dressing over the site and tape it on three sides and notify the physician
How do you treat DKA?
correct fluid deficits
IV REGULAR insulin continuous
replace K+
treat precipitating factors (specific event or trigger to the onset of the current problem)
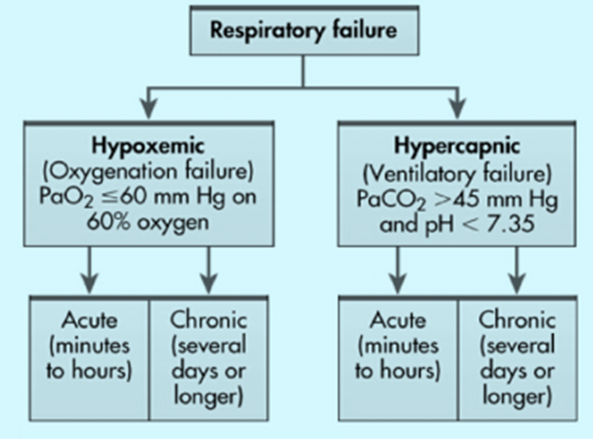
What are the two types of respiratory failure and what is failing?
If tubing disconnects from a chest tube, what should you do?
Clamp, insert end of ct in sterile water then unclamp, prepare new sterile drainage unit, clamp CT, clean Ct, reattach new tubing
A patient has been admitted with bilateral pulmonary contusions received in a
motor cycle collision. He is being supported with mechanical ventilation on
Pressure Control Volume regulated Ventilation mode, FiO2 50%, and 8 cm
PEEP. Based on this information, the nurse would plan to:
A. Measure urinary output every hour
B. Evaluate bilateral breath sounds every four hours
C. Monitor mean airway pressures and compliance ratios
D. Suction the endotracheal tube at least every two hours
C monitor mean airway pressures and compliance ratios
The nurse assesses vital signs for a patient admitted 2 days ago with gram-negative sepsis: temperature of 101.2° F, blood pressure of 90/56 mm Hg, pulse of 92 beats/min, and respirations of 34 breaths/min. Which action should the nurse take next?
a. Give the scheduled IV antibiotic.
b. Give the PRN acetaminophen (Tylenol).
c. Obtain oxygen saturation using pulse oximetry.
d. Notify the health care provider of the patient’s vital signs.
C. obtain oxygen saturation using pulse oximetry
The patient’s increased respiratory rate in combination with the admission diagnosis of gram-negative sepsis indicates that acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) may be developing. The nurse should check for hypoxemia, a hallmark of ARDS.
continue insulin, test glucose more frequently, and early recognition of DKA
What can cause Ards and why does it happen?
trauma, stomach contents, noxious gases, surgery, near drowning
It happens when the aveoli become hard due to inflammation and fluid filling of the capillaries making it impossible to exchange CO2 and O2
When monitoring ABG with a patient on a ventilator, what could it indicate?
PaO2- oxygenation issue which would be fixed through adjusting PEEP and FiO2
PaCO2 or pH- ventilation issue which would be fixed through adjusting rate and tidal volume
A patient with respiratory failure has a respiratory rate of 6 breaths/min and an oxygen saturation (SpO2) of 78%. The patient is increasingly lethargic. Which intervention will the nurse anticipate?
a. Administration of 100% O2 by non-rebreather mask
b. Endotracheal intubation and positive pressure ventilation
c. Insertion of a mini-tracheostomy with frequent suctioning
d. Initiation of continuous positive pressure ventilation (CPAP)
B. endotracheal intubation and positive pressure ventilation
You are providing care to a patient with a chest tube. On assessment of the drainage system, you note continuous bubbling in the water seal chamber and oscillation. Which of the following is the CORRECT nursing intervention for this type of finding?
- A. Reposition the patient because the tubing is kinked.
- B. Continue to monitor the drainage system.
- C. Increase the suction to the drainage system until the bubbling stops.
- D. Check the drainage system for an air leak.
D. check the drainage system for an air leak
what are at least 5 S/S of DKA?
Polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia
Altered LOC, Weakness/fatigue, Blurry vision, Nausea/vomiting, Fruity breath, Confusion, Kussmaul breathing, Metabolic acidosis with elevated anion gap, Ketonuria and ketonemia, Hyperglycemia
What s/s will you see in a hypercapnic patient that are not seen in a hypoxemic patient??
headache, confusion, and increased somnolence (also may or may not be hypertensive)
If a chest tube is knocked over, what do you do?
immediately sit it up right- check water seal- check drainage level(tip to the right to refill chambers)
You are providing care to a patient experiencing diabetic ketoacidosis. The patient is on an insulin drip and their current glucose level is 300. In addition, to the insulin drip the patient also has 5% Dextrose 0.45% NS infusing in the right antecubital vein. Which of the following patient signs/symptoms causes concern?
- A. Patient has a potassium level of 2.3
- B. Patient complains of thirst.
- C. Patient is nauseous.
- D. Patient's skin and mucous membranes are dry.
A. potassium level of 2.3
After receiving change-of-shift report on a medical unit, which patient should the nurse assess first?
a. A patient with cystic fibrosis who has thick, green-colored sputum.
b. A patient with pneumonia who has crackles bilaterally in the lung bases.
c. A patient with emphysema who has an oxygen saturation of 90% to 92%.
d. A patient with septicemia who has intercostal and suprasternal retractions.
D. A patient with septicemia who has intercostal and suprasternal retractions.
This patient’s history of septicemia and labored breathing suggest the onset of ARDS, which will require rapid interventions such as administration of O2 and use of positive-pressure ventilation. The other patients should also be assessed, but their assessment data are typical of their disease processes and do not suggest deterioration in their status.
What labs are drawn for HHNS and DKA?
ABG, CMO, lactic acid, anion gap
What can cause hypercapnic failure? CO2 is higher than 50 and ph is less than 7.35 and O2 may be abnormal
COPD exacerbation, aspiration pneumonia, obesity, pneumonia, atelectasis, PE, sleep apnea, CNS depression
What are the 4 settings on a vent and what do they do?
FiO2- Fraction of inspired oxygen or how much O2 patient is getting (0.3-1.0/30%-100% (room air 0.21/21%))-use the minimum amount needed to maintain adequate O2 levels avoid oxygen toxicity
PEEP- positive end expiratory pressure, increased paO2 levels, between 5-25 cm H2O
Respiratory Rate- based on ABG and focuses on ventilation, not oxygenation
Tidal Volume- volume of air in lungs with inspiration (5-8 mL/kg; normal 350 mL, yawn 1200 mL)
To promote safety for a client receiving mechanical ventilation, which of the
following is a priority nursing action?
A. maintaining an oral airway in place at all times.
B. restraints on upper limbs at all times.
C. preset the pressure alarms on highest value
D. ensure that an Ambu bag is at the bedside at all times.
D. ensure that an ambu bag is at the bedside at all time
In case of dislodgement
A patient is about to have their chest tube removed by the physician. As the nurse assisting with the removal, which of the following actions will you perform? Select-all-that-apply:
- A. Educate the patient how to take a deep breath out and inhale rapidly while the tube in being removed.
- B. Gather supplies needed which will include a petroleum gauze dressing per physician preference.
- C. Place the patient in Semi-Fowler's position.
- D. Have the patient take a deep breath, exhale, and bear down during removal of the tube.
- E. Pre-medicate prior to removal as ordered by the physician.
- F. Place the patient is prone position after removal.
B. Gather supplies needed which will include a petroleum gauze dressing per physician preference.
C. Place the patient in Semi-Fowler's position.
D. Have the patient take a deep breath, exhale, and bear down during removal of the tube.
E. Pre-medicate prior to removal as ordered by the physician.
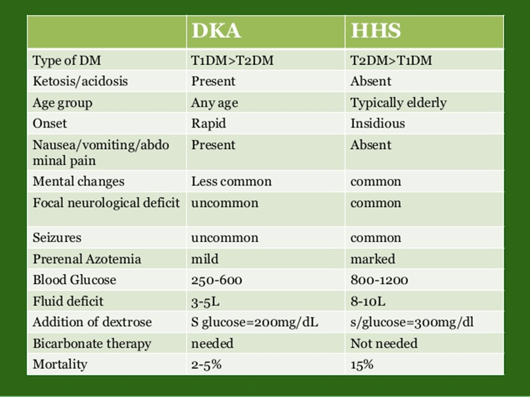
What are the differences between DKA and HHS?
What is the difference between hypoxemic and hypercapnic respiratory failure?
Type 1 respiratory failure occurs when the respiratory system cannot adequately provide oxygen to the body, leading to hypoxemia. Type 2 respiratory failure occurs when the respiratory system cannot sufficiently remove carbon dioxide from the body, leading to hypercapnia.
If chest tube is pulled out of patient, what do you do? KNOW THIS!!!!!!!!
Immediately cover site, if patient can, cough and exhale as long as able, sterile occlusive dressing in 3 border seal, petroleum gauze 4x4-transparent dressing- call provider-need CXR- prepare for reinsertion
A patient develops increasing dyspnea and hypoxemia 2 days after heart surgery. What procedure should the nurse anticipate assisting with to determine whether the patient has acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or pulmonary edema caused by heart failure?
a. Obtaining a ventilation-perfusion scan
b. Drawing blood for arterial blood gases
c. Positioning the patient for a chest x-ray
d. Insertion of a pulmonary artery catheter
D. insertion of a pulmonary artery catheter
The patient in room 2569 calls on the call light to tell you something is wrong with his chest tube. When you arrive to the room you note that the drainage system has fallen on its side and is leaking drainage onto the floor from a crack in the system. What is your next PRIORITY?
- A. Place the patient in supine position and clamp the tubing.
- B. Notify the physician immediately.
- C. Disconnect the drainage system and get a new one.
- D. Disconnect the tubing from the drainage system and insert the tubing 1 inch into a bottle of sterile water and obtain a new system.
D. disconnect the tubing from the drainage system and insert the tubing 1 inch into a bottle of sterile water and obtain a new system.