The movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
What is diffusion/passive transport?
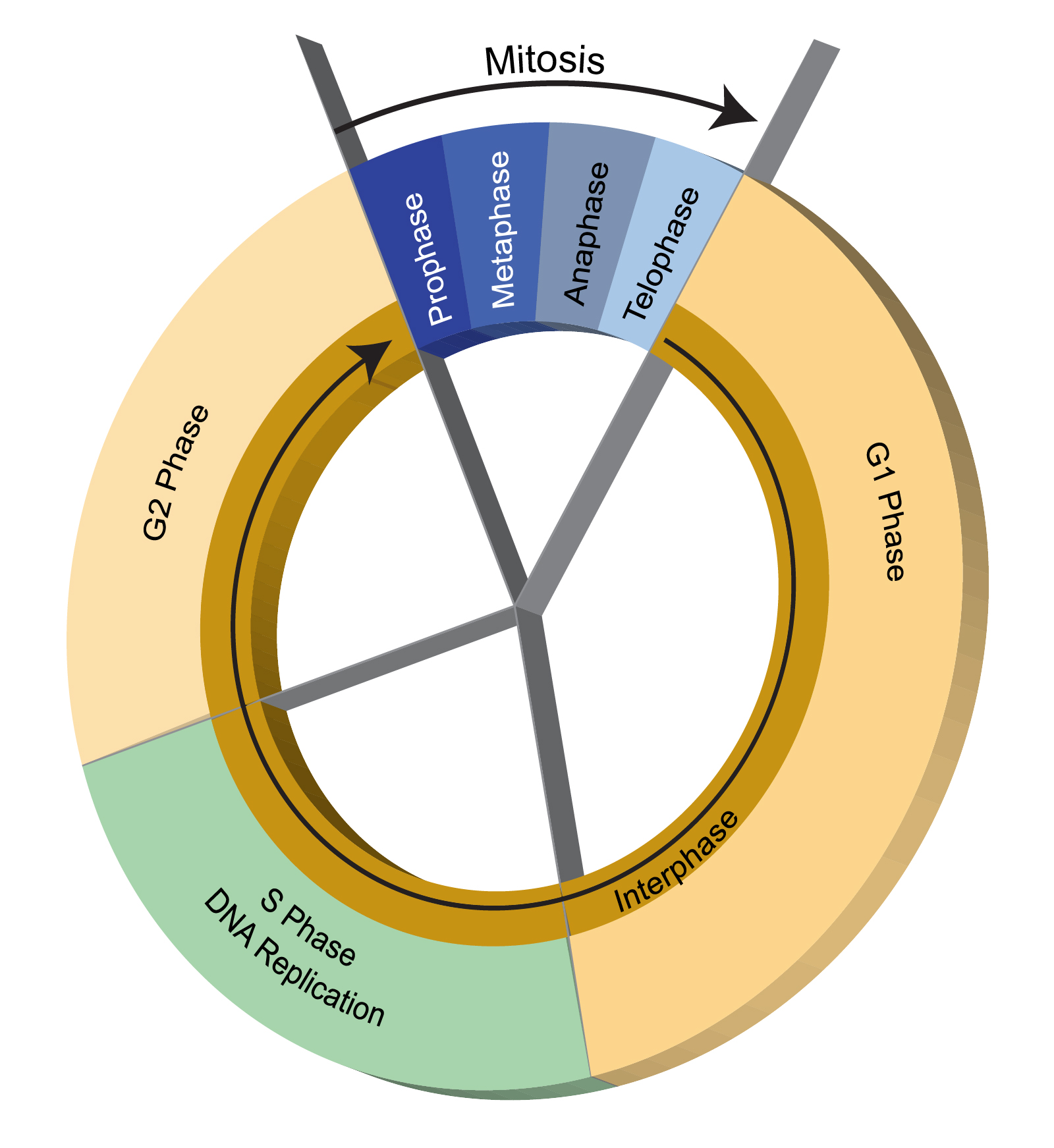 The longest part of the cell cycle, where most cell activity takes place.
The longest part of the cell cycle, where most cell activity takes place.
What is interphase?
First phase of mitosis, chromosomes condensed.
What is prophase?
DNA/chromosomes are located in the _____________ of the cell.
What is the nucleus?
Diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion.
What is passive transport?
 The phase where cell growth occurs.
The phase where cell growth occurs.
What is G1?

Second phase of mitosis, chromosomes line up in middle of cell.
What is metaphase?
Long-term energy storage (think polar bear hibernating), also makes up cell membranes.
What are lipids?
Protein pumps, endocytosis, exocytosis.
What is active transport?
 The phase where DNA is replicated (synthesized)..
The phase where DNA is replicated (synthesized)..
What is S phase?

Third phase of mitosis, chromosomes separate, move away from each other towards poles of cells.
What is Anaphase?
Made up of long chains of amino acids.
What are proteins?
_______________ transport does not use energy.
_______________ transport requires energy.
What is passive, active?
 The phase where more cell growth and preparation for mitosis occurs, .
The phase where more cell growth and preparation for mitosis occurs, .
What is G2 phase?

Fourth phase of mitosis, nuclear envelope starts forming, cytoplasm starts dividing.
What is Telophase?
Stores genetic information.
What are nucleic acids?
Phospholipid bilayer.
What is a cell/plasma membrane?
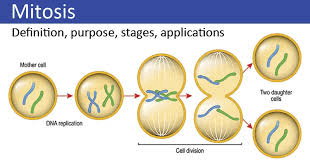
 The phase where cell division occurs.
The phase where cell division occurs.
What is mitosis?

Occurs after mitosis, cells divide.
What is Cytokinesis?
Short-term, immediate energy.
What are carbohydrates?
The energy molecule used in active transport.
What is ATP?
The phase after cell division (mitosis/meiosis/cytokinesis).
What is interphase?
Mitosis creates _______________ cells with the _____________ number of chromosomes.
What is 2/identical, same/diploid?
DNA replication is called a _____________________ process because new DNA consists of one old strand and one new strand.
What is a semi-conservative?