Sunlight is an example of which type of light?
Incandescence: light produced when an object is heated
What does the refractive index describe?
How much slower light moves through that medium, compared to in a vacuum. Ie, how much the medium refracts light.
Which microscope structure is used to adjust the amount of light entering the slide?
The diaphragm
What is the function of the Golgi bodies?
Packaging proteins for transport in or out of the cell
What is the formula for hydrobromic acid?
HBr
Name all types of wavelengths, from lowest to highest frequency.
Radio; microwave; infrared; visible (RYGBCI); ultraviolet; x-rays; gamma
What happens to a light ray as it enters a denser medium?
It trends towards the normal.
What is the function of the stomach?
Chemical (HCl) and physical digestion (peristalsis) of the bolus before it enters the small intestine.
What is cellular differentiation?
Unspecialized cells (stem cells) specialize and take on their mature form and function.
Write the balanced decomposition reaction for sulphur pentoxide.
2SO5 --> 2S + 5O2
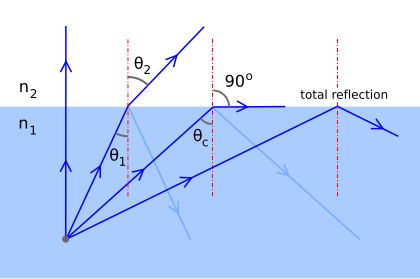
Describe what occurs with total internal reflection.
When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, the light is totally reflected back into the denser medium, and no refraction occurs.
Give the SALT characteristics for this image.

S: smaller (hi > ho)
A: upright (+hi)
L: in front of lens (di < do)
T: virtual
Compare the oesophagus to the trachea.
Oesophagus: smooth muscle tissue, part of digestive system
Trachea: cartilage (connective tissue), part of respiratory system
Both are tubes that connect the internal systems to the external environment.
What happens next after this phase of mitosis?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/meiosis_anaphase_1-56a09b4c5f9b58eba4b2052b.jpg)
Telophase: cytoplasm separates into two, nuclear membrane starts to reappear, spindle fibre breaks down
Write the balanced reaction equation for an incomplete combustion of any hydrocarbon.
ex. C2H6 + 3O2 --> CO2 + 3H2O + CO
(needs CO and/or C as products, and H2O)
Where will its image appear if an object is placed between a concave mirror and its focal point?
Behind the mirror (virtual)
Light is traveling from glass (n = 1.51) into zircon. If it makes an angle of incidence of 34o in glass and an angle of refraction of 26o in zircon, what is the index of refraction in zircon?
nzircon = 1.92
Name the blood vessels connected to the heart and explain what they are bringing where.
Pulmonary artery: brings deoxygenated blood to the lungs
Pulmonary vein: brings oxygenated blood to the heart
Aorta: brings oxygenated blood to the cells
Vena cava: brings deoxygenated blood to the heart
Give the chemical equation for cellular respiration.
O2 + glucose (sugar) --> CO2 + H2O + energy
Predict the products of this reaction: silver hydroxide reacts with sulphuric acid.
water + silver sulphate
AgOH + H2SO4 --> H2O + Ag2SO4
An inverted image is magnified by -2 when the object is placed 22.0cm in front of a converging mirror. Determine the di and f of the mirror.
M = -di/do --> di = 44cm
1/f = 1/do + 1/di --> f = 14.7cm
Draw a ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed at C (2f') of a converging lens, and describe its characteristics.

S: hi = ho; A: inverted (-hi); L: in front of lens (di = do); T: real
Trace the path of a CO2 molecule through the human body.
Exits tissue cells --> enters bloodstream through the capillaries --> venules --> veins --> vena cava --> right atrium --> right ventricle --> pulmonary artery --> arterioles --> capillaries --> exits bloodstream and enters alveoli --> bronchioles --> bronchi --> trachea --> exhale through mouth/nose
Name all types of animal tissues you have learned and a specific place you would find them.
epithelial: skin, organ lining
muscle: muscles, oesophagus, SI, blood vessels, heart
nervous: nerves, brain
connective: bone, fat, blood, cartilage
Write the balanced equation for the following reaction: Over time, the copper metal reacts with oxygen gas, carbon dioxide gas and water vapour in the air to form copper (II) carbonate solid and copper (II) hydroxide solution.
2Cu + O2 + CO2 + H2O --> CuCO3 + Cu(OH)2
