What is a major drawback of longitudinal studies?
Attrition
What are the "factors" in factorial design?
The independent variables
What is one major benefit of correlational designs over factorial designs?
The results are much easier to interpret
Require fewer participants
Easier to conduct
How many factors does a two-way between-subjects factorial design have?
2
A research team finds that people report higher levels of happiness when they are eating more tacos each week. What type of correlation is being described here?
Positive
Because correlational analyses only include two variables it is always possible (and even likely) that there is some other factor that may change the relationship or change how we understand it. This concept is known as…
What is one of the major benefits of using a pre-post quasi experimental design relative to other quasi-experimental designs?
They allow researchers to see existing trends in the data
In the context of factorial designs, what do we mean when we talk about “levels”?
The number of groups or conditions within each IV
A team of researchers predicts that happiness and shoe size are positively correlated. They test this hypothesis with a correlational study. Their analysis results were r(50) = 0.16, p = .062. What should the team conclude about their hypothesis?
Fail to reject the null
Why to researchers tend to avoid higher-order designs?
They require huge samples (i.e., more power) and are difficult to interpret.
What type of correlation is depicted in the scatterplot?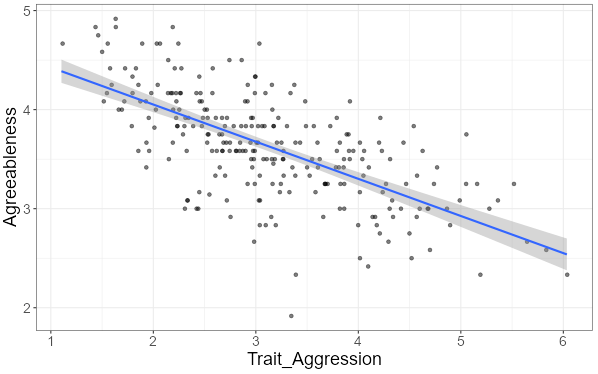
Negative association
On a scatter plot in which there were no correlation between the two variables, what would the trend line (i.e., the linear slope of X and Y) look like?
horizontal (flat, running left to right)
When developmental studies use a cross-sectional approach they could introduce a threat to validity due to the comparison of groups from different generations. What is this called?
Cohort effects
What does "higher-order design" mean?
Any factorial design with 3 or more factors
Interpret the following correlation: r = .35, p = .012
Positive, moderate strength, significant correlation
What is one major concern regarding within-subjects factors in a factorial design?
They can introduce order effects (e.g., carryover effects).
What is a major drawback of longitudinal studies?
Attrition
What is the major difference between quasi-experimental and non-experimental studies?
Quasi-experiments attempt to control as much as possible, non-experiments do not use controls
If you were designing a study that was aimed at understanding how certain personality traits develop over the life course (i.e., through adolescents and adulthood), which study design would provide the strongest evidence?
A longitudinal study
A research team used a between-subjects factorial design for testing the effects of social rejection and relationship type on aggression. Their study had two levels of the social rejection IV: acceptance vs. rejection and three levels of the relationship IV: stranger, friend, and relative. What is the total number of unique/independent conditions possible in this study?
6
How does external validity differ between true experiments and correlational designs?
Correlational studies have higher external validity
When a factorial design is going to require more participants than the research can afford to pay, what is one step a researcher can take to remedy this issue?
Alter the design to include one of more within-subjects factors
In a factorial design using a between-subjects factor and a within-subjects factor participants are exposed to the between-subjects levels using __________________ and are exposed to the within-subjects levels using __________________.
Random assignment
Counterbalancing
Smaller effects, like those common to interactions in factorial designs, require ____________ power.
more
A pretest-posttest nonequivalent control group design is a type of quasi-experiment that measures two independent (i.e., between-subjects) groups at two different times (e.g., before treatment and after treatment). What could this design also be called?
A mixed-methods design
A research team used a mixed-methods factorial design for testing the effects of work stress (within-subjects factor) and relationship satisfaction (between-subjects factor) on aggression.
Their study had two levels of the work stress IV: high vs. low and two levels of the relationship satisfaction IV: high and low. What is the total number of unique/independent conditions possible in this study?
2
A descriptive study design where two or more samples of respondents answer the same questions at different points in time. Each sample is only asked these questions once (e.g., Surveying all students enrolled VSU in spring 2018, spring 2028 & spring 2038).
Successive independent samples design
In a 3 x 3 x 3 factorial design, a researcher can examine how many main effects, 2-way interactions, and 3-way interactions?
Three main effects
Three 2-way interactions
One 3-way interaction
One of the major drawbacks of a correlational analysis is that it only allows us to detect linear relationships. Sometimes there are relationships between variables that are not linear. One form of a non-linear relationship that correlation cannot detect is called…
Curvilinear
Some researchers compared average values between men and women on depression symptoms using a nationally available database containing records dating back to 1991.
What type of research strategy is being used here?
Archival and non-experimental