This type of insulin releases slowly and steadily - does not have a specific timeframe when it starts to lower blood sugar
What is long-acting insulin (e.g., insulin glargine)?
This type of insulin does not have a specific time when it is most active - it releases steadily throughout the day.
What is long-acting insulin (i.e. insulin glargine)?

This type of insulin lasts 24 hours.
What is long-acting insulin (i.e. insulin glargine)?

The purpose/benefit of mixing different insulins in one syringe
What is to minimize the amount of injections a patient has to receive?

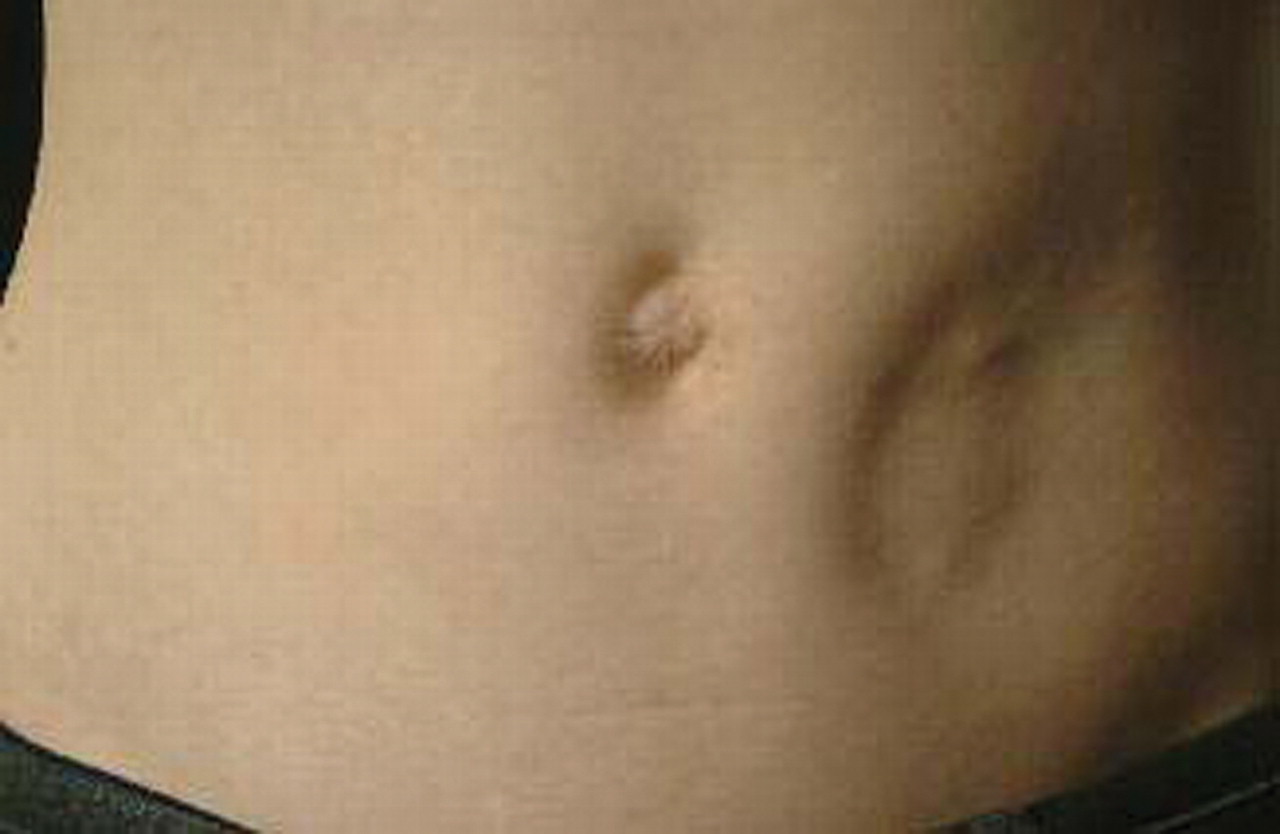
This adverse effect can occur if the injection site of insulin is not rotated
What is lipodystrophy?
This is the best time to give rapid acting insulin to a patient
What is with meals?

This type of insulin is most active 4-12 hours after injection.
What is intermediate acting insulin (i.e. insulin NPH)?

This type of insulin can last up to 24 hours.
What is intermediate acting insulin (i.e. insulin NPH)?

A type of insulin that CANNOT be mixed with other insulins in the same syringe.
What is long-acting insulins (e.g., glargine, determir)?
This is the only type of insulin that can be administered intravenously
What is regular insulin (Humulin R® , Novolin R®)?

This type of insulin takes approximately 15 minutes to start lowering blood sugar.
What is rapid-acting insulin (i.e. insulin lispro, insulin aspart)?

This type of insulin is most active 30 minutes to 3 hours after injection.
What is rapid-acting insulin (i.e. insulin lispro, insulin aspart)?

This is the amount of days that most insulin vials can be left at room temperature for.
What is up to 28 days?
This is the only type of insulin that can be mixed with short acting insulin
What is intermediate acting insulin (e.g., NPH)?
This class of medications can mask the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia
What are beta-blockers (e.g., metoprolol)?
This type of insulin takes approximately 1.5-4 hours to start lowering blood sugar.
What is intermediate acting insulin?

This type of insulin is most active 2-4 hours after injection.
What is short-acting insulin (i.e. insulin regular)?
This type of insulin last 3-5 hours.
What is rapid-acting insulin (i.e. insulin lispro, insulin aspart)?

This is the order in which insulins should be drawn up if they are to be mixed.
What is rapid/short acting insulin (clear) before intermediate -acting insulin (cloudy)?

A term that describes how much rapid-acting insulin is needed to "cover" the carbohydates in a meal or snack (i.e. how many grams of carbohydates will one unit of insulin cover)
What is insulin to carbohydrate ratio (ICR)?
This type of insulin takes approximately 30-60 minutes to start lowering blood sugar.
What is short-acting insulin (i.e. insulin regular)?

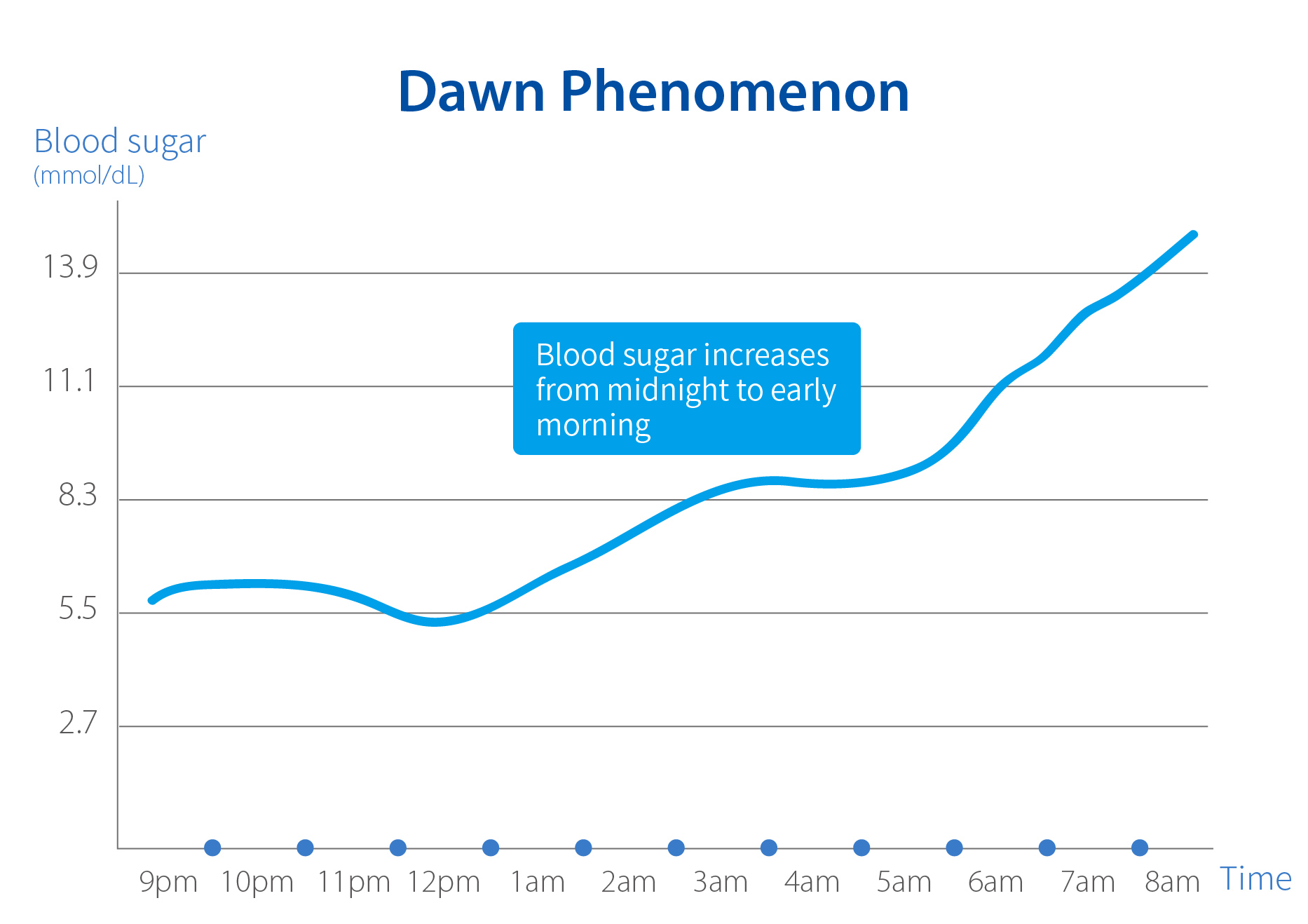
This effect/phenomenon is used to describe a normal early-morning increase in glucose, usually between 2 AM and 8 AM, in people with diabetes.
What is the dawn effect or dawn phenomenon?
This type of insulin lasts 6-8 hours.
What is short-acting insulin (i.e. insulin regular)?

The amount of time which a manually mixed intermediate and either rapid acting or short acting insulin solution must be administered by
What is 5-15 minutes?
A term that describes the amount of rapid-acting insulin needed to correct a blood glucose level (i.e. describes how much one unit of insulin lowers the glucose level by)
What is insulin sensitivity factor (ISF) or correction factor?