What interventions will be helpful with a client who has a somatic disorder? How would we evaluate effectiveness?
Assertiveness training
Case Management
Psychotherapy (trauma-focused)
Pharmacological to treat co-morbid anxiety / depression
ECT in extreme cases and other attempts at treatment have failed
Remember, small progress is better then no progress
Patient's experiencing a mood disorder are at a high risk for ____________?
What nursing intervention would be the highest priority?
Suicide
Safety Assessment
Recurrent episodes of eating in a discrete period of time an amount of food that is larger than what most individuals would eat (i.e.- more than 5,000 cal) at least 2 days a week for 6 months without purging behaviors
Binge Eating Disorder
Check facts on Anorexia and Bulimia as a review
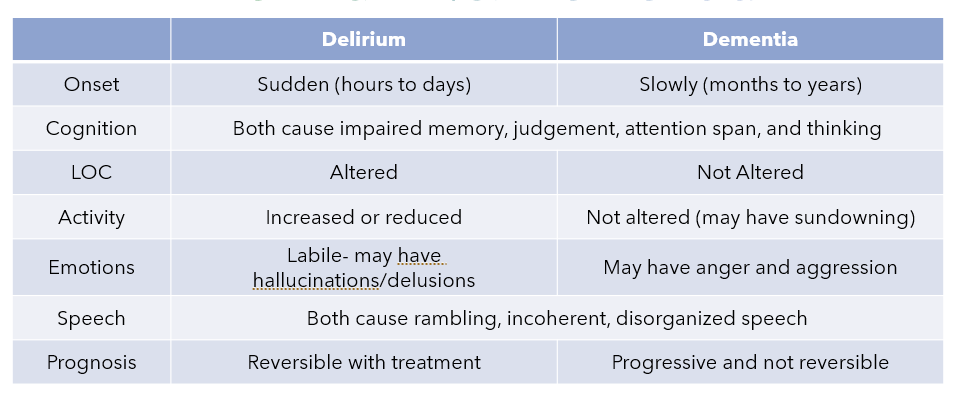
What are some of the similarities and differences between delirium and dementia?
Interventions to use with children/adolescents diagnosed with Autism spectrum disorder include?
Weighted Blankets (helps with wanting the pressure)
Social Stories (A social story is a narrative made to illustrate certain situations and problems and how people deal with them. They help children with autism understand social norms and learn how to communicate with others appropriately )
Noise Canceling Headphones (help decrease stimulation )
Sensory objects (helps with the desire to chew on objects or wanting to "feel" a certain sensation)
Visuals Schedules (PECS)
Medication (antipsychotics to help manage aggression)
What is the best way to describe malingering?
What are some examples of how a patient may present if they are malingering?
Patietns exaggerating their pain to gain access to more medications
Saying anxiety is worse then it is to have a prescriber give them a benzo instead of an antianxiety
Stating they are suicidal to gain a place to stay inpatient (if they are currently homeless)
How might a patient present with HYPOmania?
Cheerful, enthusiastic, abnormally elevated or especially irritable mood
•Does not impair ability to function (no psychotic features)
•Excessive and pressured speech
•Decreased need for sleep and increased activity and/or psychomotor agitation
What is a symptom of purging?
Discoloration of teeth and/or tooth decay; rupture of the esophagus
Priority nursing interventions for patient's with dementia include?
SAFETY!
Locks on doors if needed
Assisting with ADL's
Ensuing they are eating/drinking
Education for parents and children with ADHD regarding medication should include what?
Common: methylphenidate (Ritalin) and an amphetamine compound (Adderall)
• Sustained-release methods reduced the need for
dosing during the school day:
(Vyvanse lisdexamfetamin)
Certain antidepressants or antihypertensives may be used if stimulants aren’t tolerated (Clonidine, intuniv, and straterra are some options)
• Most common side effects are insomnia, loss of
appetite and weight loss
Interventions to help with side effects:
•Encourage a good breakfast before taking the medication
• Monitor weight using appropriate growth charts
• Do not take late in the day ( no dosing after 3 usually to help prevent insomnia)
What are the disorders and provide a brief explanation of each?
llness anxiety disorder
Functional Neurological Disorder (Conversion Disorder)
Factitious Disorder (Munchausen Syndrome)
Factitious Disorder Imposed on Another
Lithium level ranges are?
What signs or symptoms would lead the nurse to suspect lithium toxicity?
Ranges 0.8-1.2 (ideally around 1)
Mild Toxicity
<1.5 mEq/L
(Exaggeration of expected side effects)
Metallic taste in mouth, nausea, polyuria, polydipsia, diarrhea, muscle weakness, weight gain, edema
Moderate Toxicity
1.5-2.5 mEq/L
Severe diarrhea, dry mouth, nausea and vomiting, ataxia, incoordination, tinnitus, slurred speech, vertigo, muscle twitching, asymmetric deep tendon reflexes
Severe Toxicity
> 2.5 mEq/L
Fasciculations, nystagmus, coarse tremors, cardiac arrhythmias, hallucinations, oliguria, peripheral vascular collapse, confusion, seizures, coma
This is the most common type of therapy for virtually all types of eating disorders
cognitive therapy
Management of patient's with delirium include what interventions?
Try to determine the causes for anger/aggression
Use a soft, reassuring, calm tone
Respond with simple, brief explanations
Use memory aids (clocks, notes, calendars, etc.) and pictures
Modify the environment (decrease noise and stimuli, maintain a schedule, etc.)
Break complex tasks down into smaller steps
Distract the patient with positive outlets for their energy
Don’t argue, become defensive, take things personally, or become frustrated
Communication strategies to use with clients with ADHD include what?
Ensure the patient makes eye contact before you start talking or giving directions
Short, simple directions
Have them repeat back what was said
Offer positive reinforcement/praise for completing the tasks
Case management goals for patients with a somatic disorder include what?
Develop a trusting relationship
Provide education related to their disorder
Emphasize client strengths
Explore problem-solving strategies
Promote relaxation techniques
What are examples of foods we would want to make sure are available for a patient experiencing mania?
Finger foods
High calorie
High protein
NO CAFFEINE
Interventions to include when a patient is on an in-patient unit for treatment for an eating disorder include what?
Blind weights- daily
Mirror Meals
Bathroom restrictions after eating
Physical activity restrictions
Monitoring conversations to avoid triggering topics
Encourage reflection/journaling of feelings
Safety interventions to monitor for self-harm or suicidal ideations
Medications used to slow the progression of dementia include?
•Galantamine hydrobromide (Razadyne)
•Rivastigmine tartrate (Exelon)
•Donepezil hydrochloride (Aricept)
What are warning signs/symptoms of bulimia?
Examples of compensatory behaviors
Taking laxatives and over exercising, purging, abuse of stimulants
What medication class would you anticipate a patient with a somatic condition having prescribed?
Antidepressants or Antianxiety
Not anything addictive (no benzo's or narcotics)
What are some interventions we can encourage with patients who have depression and lack motivation?
Self Help/Peer Support Groups
Making short-realistic goals
Work to identify cognitive distortions
Encourage activities to raise self-esteem
Explore/encourage physical activity
If interested, connect with local spiritual/religious groups
Risk factors for the development of an eating disorder include?
Female, athletes, adolescents
Anorexia- tend to come from strict/high achieving homes
Bulimia- tend to come from chaotic homes
What information is the nurse concerned with when using the confusion assessment method (CAM)?
1.Acute onset and fluctuating course
Acute change from baseline that fluctuates during the day
2. Inattention
Difficulty focusing attention, easily distracted
3. Disorganized thinking
Rambling speech, irrelevant conversations,
unclear thinking
4. Altered level of consciousness
Hyper-vigilance, lethargic, stuporous, comatose
Reasons for concerns related to an eating disorder ( requiring immediate attention)
Low heart rate
Low B/P
Electrolyte imbalances
Cardiac issues
Extreme weight loss
Dehydration