A map that uses color to show elevation and landforms
Physical Map
What are the coordinates for A?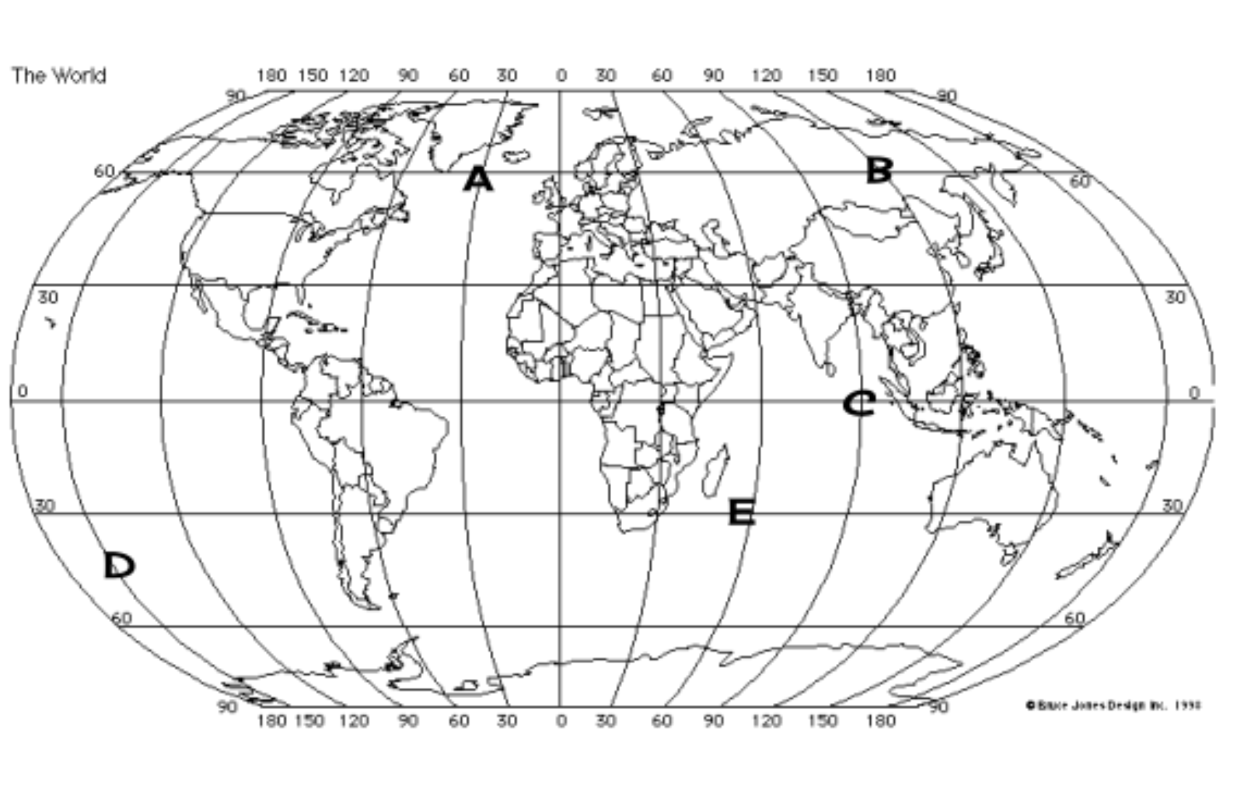
(60*N, 30*W)
Lines that run from the North Pole to the South Pole
Lines of Longitude
How people in a region live, think, and behave.
Culture
A construction company is cutting down a forest to use the trees and the wood.
HEI
A map that shows political boundaries, such as state and national borders
Political Map
What are the coordinates for B?
(60*N, 150*E)
The imaginary lines that run parallel to the Equator are called
Lines of Latitude
Cultural, economic, and political connections between different parts of the world
Globalization
The people of Venice, Italy often use river taxis to get from one point to another.
Movement
A map designed to show a specific topic, such as population density or climate
Thematic Map
What are the coordinates for C?
(0*, 90*E)
The imaginary line that circles the earth at 0° latitude
Equator
An ancient example of Globalization.
The Silk Road
Southerners in the U.S.A. are often grouped together as one because of a common accent and other common interests.
Region
Type of Map that is rectangular and distorts the size of countries near the poles.
Mercator Projection
What are the coordinates for E?
(30*S, 60*E)
The zero-degree line of longitude
Prime Meridian
A drawback of Globalization
Loss of jobs, spread of disease, and loss of unique cultures.
The U.S. is located south of Canada.
Location
A more rounded on the edges map that has curved lines of longitude that we will often use in this class.
Robinson Projection
What are the coordinates for D?
(45*S, 150*W)
The maximum number degrees latitude and longitude.
90* Latitude and 180* Longitude
Benefit of Globalization
Increased wealth from trade, spread of technology and ideas, or the sharing of culture.
The people of Ireland often wear traditional clothing, such as a kilt, during holidays or celebrations.
Place