What word means the movement of people from the countryside into cities?
Urbanization
In rural Mexico, what happens to many small farmers’ jobs and income during rural decline?
Poverty and unemployment increase and they lose their farms
Julio César Cu works in an overloaded part of the city where he dives to remove trash. What system is this?
The sewer system
In Mexico City, which group enjoys the highest standard of living: haves, have-nots, working poor, or middle class?
The “haves”
On the “Mexico’s Urban and Rural Population” bar graph, what does the red bar stand for?
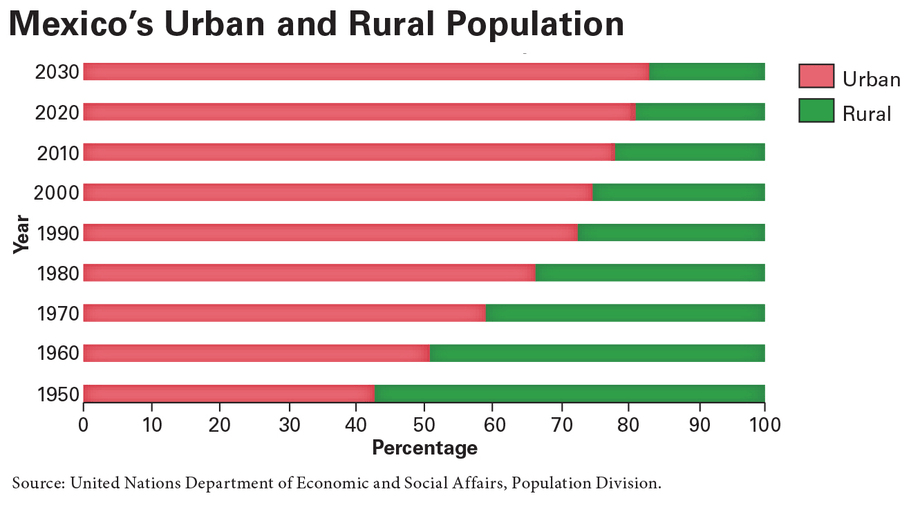
The percentage of the population living in urban areas
What do geographers call an uneven spread of money and resources so some areas are richer than others?
Spatial inequality
What is one major effect of rural decline on Mexico City’s population?
More people move to the city, increasing urbanization
Which basic resource is often in short supply in Mexico City, making sanitation hard and spreading disease?
Clean water
Who is most likely to live in tiny, crowded shacks made from scrap materials on the edge of the city?
Recent migrants to the city
In which decade was Mexico’s population last more rural than urban according to the graph?
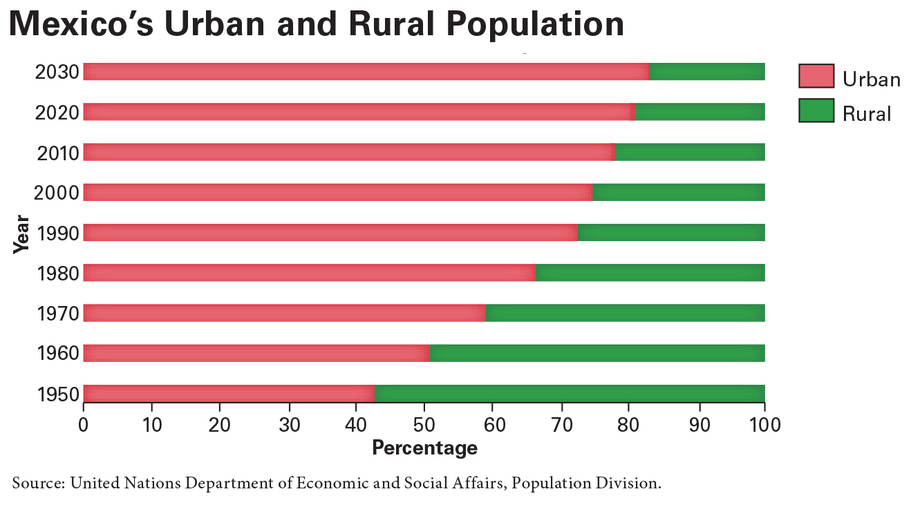
The 1950s
What phrase means the overall level of comfort and well-being people enjoy in a place?
Standard of living
What is the main “pull factor” that attracts farm families to Mexico City?
Economic opportunity (better-paying jobs)
As Mexico City has grown, which of these has NOT increased: crime, air pollution, average family size, or slum neighborhoods?
Average family size
Which group usually lives in houses or apartments and can afford some luxuries like eating out and entertainment?
The middle class
What time periods do the maps cover?
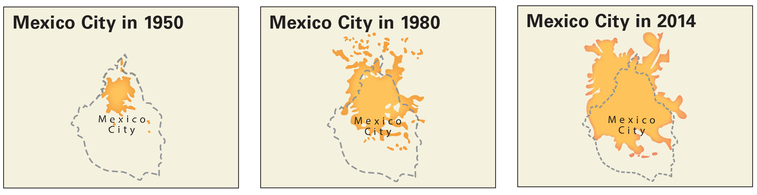
From 1950 to 2014
What do we call worsening conditions in the countryside, with more poverty and fewer jobs?
Rural Decline
When farmers migrate to the city, what is one big hope they have for their children?
Getting a better education and escaping poverty
OR
A better standard of living
Since 1950, how has Mexico’s population changed according to the urban–rural graph?
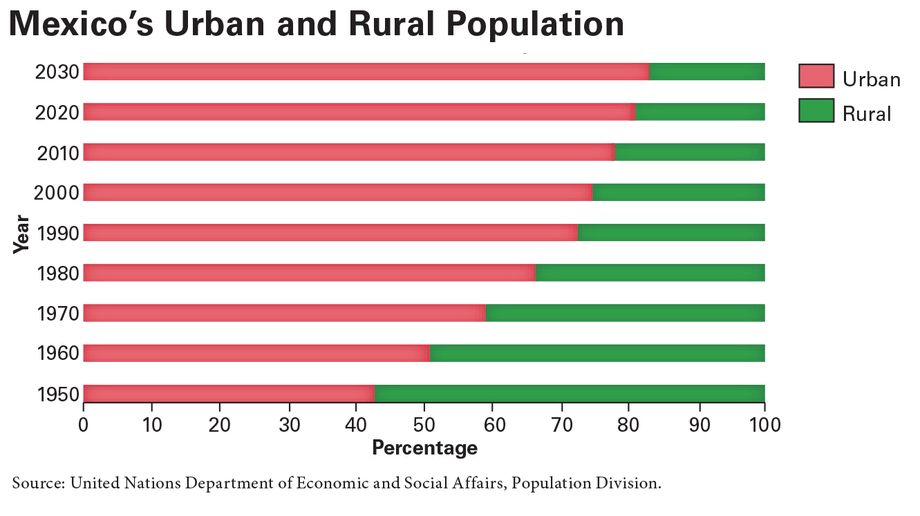
It has become more urban, but urban growth has slowed since about 1990
Why does slum housing show a low standard of living? Give two reasons.
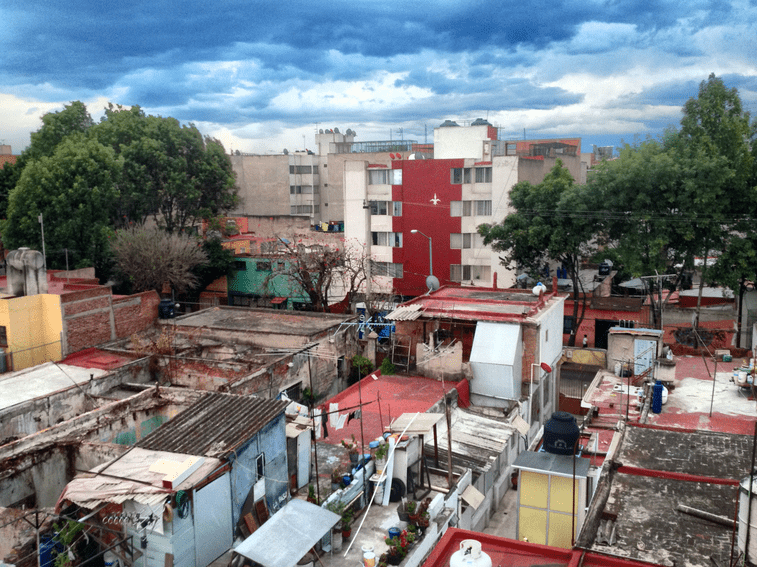

Houses are made of poor materials and often lack electricity and running water
Comparing the three maps, what happened to the size of the Federal District (the dashed lines) between 1950 and 2014?

It stayed the same size while the urban area spread beyond its borders
What compares how well people live in different countries using life expectancy, education, and income?
Human Development Index (HDI)
Why has Mexico City’s growth slowed down in recent years?
Fewer people are migrating from rural areas to the city
OR
Family sizes are smaller today than they used to be
As urbanization increased, what two social problems also increased in Mexico City?
Poverty and crime
Based on the neighborhood data table, which area—Benito Juárez or Milpa Alta—has the higher standard of living overall?
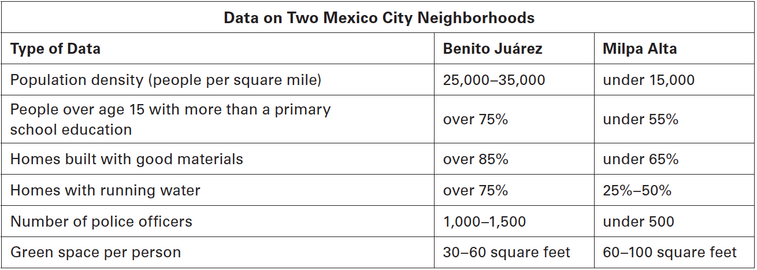
Benito Juárez
Comparing the three maps, how did the area of Mexico City itself (the orange) change between 1950 and 2014?

It more than doubled by 1980 and then almost doubled again by 2014
The Human Development Index (HDI) uses three main things to judge how well people live in a country.
Name TWO of the three things HDI measures.
Any two of: life expectancy, education level, average income.