Packages of genetic information bundled with proteins.
Chromosomes
Why do cells divide? (Three possible answers)
-To ensure cells do not become too large
-To produce new cells during an organism's growth
-To replace damaged cells and tissues
Cells have 'checkpoints' that ensure everything has happened that is necessary to move to the next stage of the cell cycle. What type of regulator is this an example of?
Internal regulator
What is the name of the process that allows an organism to go from a single cell to many cells of many different types?
Differentiation
What are the three limitations to cell size?
Congestions-Too much entering and leaving the cells
Overuse of the DNA
Surface are to volume ratio decreases (cells do best with a large SA to V ratio)
What is the substance made by the centrioles that aides in the progression of mitosis?
What are all the stages of the cell cycle (include the sub phases of the non-dividing phase and the dividing phase), in order?
-Interphase (G1, S, G2)
-Mitosis (P,M,A,T)
-Cytokinesis
What are the three types of cell cycle regulation? Describe Each.
Internal regulators-checkpoints within the cell cycle
External regulators-signals from outside the cell
Cyclins-proteins that speed up or slow down the cell cycle.
What are the three types of stem cells-describe each.
-Totipotent: Can become any type of tissue, including placenta and embryonic membrane
-Pluripotent: Can be any type of body cell
-Multipotent: Can be one of a few types of cell-Also known as adult stem cells
Sexual-creates genetic diversity
Asexual- Works very quickly, creates clones.
When the DNA is in interphase, it is not in its organized condensed form, but rather loose. What is this called?
Chromatin
The side of a cubical cell is doubled. How many times more nutrients would be needed and waste would be excreted?
8 times more
What can occur when there is a breakdown of the regulation of the cell cycle?
Cancer-uncontrolled cell growth
How are iPS cells different from embryonic stem cells?
iPS cells act like embryonic stem cells, however they were made from adult stem cells.
Compare the chromosomes of a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.
Prokaryotic-A single circular chromosome located in the cytoplasm
Eukaryotic-Several linear chromosomes located in the nucleus
What is the name of the protein the DNA is wrapping around in this picture?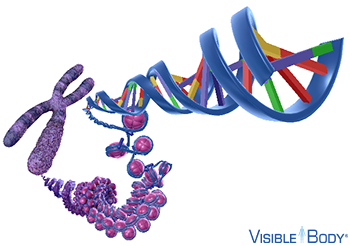
Histone
There is a breakdown on an internal regulators. During metaphase the spindle fibers fail to attach to the centrioles of the sister chromatids. How will this affect the following stages of mitosis?
The sister chromatids will not be pulled apart during anaphase. Therefore during telophase the new nuclei formed will either have too much or too little DNA.
A physician looks at a biopsy of a patients tissues to determine if it may be cancerous. What would the physician expect to see if this were a cancerous sample?
-Irregular clumping and sizes
-Undifferentiated cells
Why is stem cell therapy particularly beneficial for leukemia patients, who suffer from cancer within the bone marrow?
Bone marrow is made mostly of adult stem cells that produce different types of blood. Stem cell therapy replaces the cancerous stem cells with healthy ones.
All human body cells are diploid, meaning they contain two complete sets of chromosomes (one inherited from the mother, one inherited from the father), except for one type of cell. What is the one human cell type that contains only one set of chromosomes?
Gametes- sperm and egg cells
 What is the name of A, B and C. How are the two structures that C is pointing to related to each other
What is the name of A, B and C. How are the two structures that C is pointing to related to each other
A) Chromosome
B) Centromere
C) Sister Chromatids
The sister chromatids are genetically identical to each other.
Suppose you have two tissues cultures of eukaryotic cells, one in G1 and one in S. How would you determine which culture was in G1 and which was in S?
During S you will see replication of the DNA-so you would start to see two copies of each strand of DNA. In addition, the cells in S phase could be a bit larger.
Upon looking at a sample of an animal cells, a scientist sees that a number are undergoing apoptosis. What conclusions can the scientist make about the overall health of the animal?
The animal is likely healthy because apoptosis is a normal part of the cell cycle-although there might have been some recent cell trauma, such as exposure to UV light.
Describe the early development of a human being. Include correct terminology
Start as s single totipotent cell called a zygote. This begins to differentiate forming a hollow lopsided ball called a blastocyst. The outer part of the blastocyst will develop into the placenta, the inner part is full of pluripotent cells that will become the body.
 This picture shows the amount of time an onion root tip cell spends, on average in each phase. What conclusions can you make about this type of cell compared to others?
This picture shows the amount of time an onion root tip cell spends, on average in each phase. What conclusions can you make about this type of cell compared to others?
The onion root tip cell divides more frequently than most cells.