A child presents to the emergency room with his father, who states that the child has been sick with a cold and recently started drooling. The nurse notices the child is sitting in a tripod position, and when the nurse hears the child making this sound knows it is a medical emergency.
Stridor
This structure covers the larynx during swallowing and helps keep food out of the lower respiratory tract, and can become involved in several pathologic conditions in children.
Epiglotis
Treatment for this disease often includes the use of a mechanical vest to loosen thick mucus in the airways
cystic fibrosis
"If your child has this, sometimes taking them outside at night and exposing them to cool air will help"
Acute Spasmodic Croup
This movement is often seen in children with respiratory distress who are using accessory muscles, such as the intercostals, to breathe. The areas below the ribs, between the ribs, and in the neck sink in with each attempt to inhale.
Retractions
What is the hallmark lung sound for asthma?
Wheezing
Premature infants born before 34 weeks might experience respiratory distress because of the lack of this phospholipid & protein compound in the lungs.
Surfactant
Intramuscular injection of palivizumab (Synagis) can be given monthly during peak season for this disease to children who are at higher risk for hospitalization, such as preterm infants, and children with chronic lung disease or congenital heart disease
"It is imperative that you use your controller medications daily for this condition. Follow your action plan closely to know when to escalate medications, and when to seek emergency care."
Asthma
A serious sign of air hunger demonstrated by widening of the nares to enable an infant or a young child to take in more oxygen.
Nasal Flaring
This low-pitched expiratory sound is present with respiratory distress.
Grunting
This is the neonate's major respiratory muscle.
Diaphragm
Surgical placement of tympanostomy tubes is an option for children who have this recurrent infection
Acute otitis media
"This is an autosomal recessive disorder. Both parents contributed one copy of the defective gene, and the child was born with it."
Cystic Fibrosis
This is the medical term for a respiratory rate greater than 60 breaths per minute.
Tachypnea
This lung sound is often associated with pneumonia
Crackles (or rales)
These are relatively horizontal in children, which increases the risk for bacteria entering the middle ear.
Eustachian tubes
Use of the H. influenzae type B (Hib) vaccine has reduced the incidence of this life-threatening, rapidly progressive condition that can cause complete airway obstruction within a few hours of onset.
epiglottitis
"Cough suppressants for this disease is not recommended. Assist your child to take deep breaths and cough several times each hour to loosen up mucus and get it out of your lungs."
Bacterial pneumonia
One of the classic signs of epiglottitis is that the child insists on sitting upright, often in this position
Tripod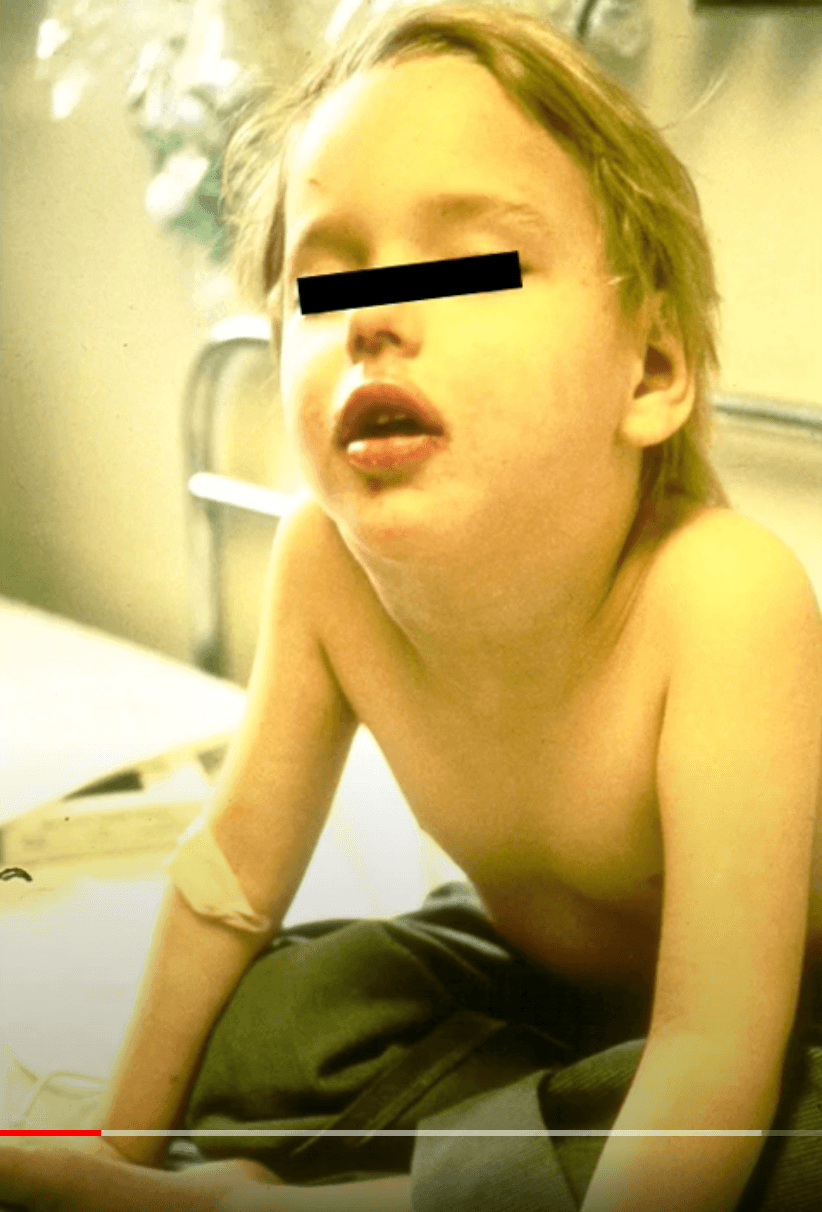
A harsh, barking cough is the hallmark of what viral illness?
Croup
In asthma, these small air passages become inflamed and cause a characteristic wheezing sound
Bronchioles
Treatment for this condition is symptomatic, focusing on pain relief and rest. Acetaminophen or ibuprofen is used for pain; older children may find gargling with warm saline solution comforting. Cool, bland liquids are tolerated best because of the discomfort caused by swallowing solids or irritating liquids. Antibiotics should be restricted to those children who test positive on rapid detection tests or cultures..
pharyngits
"Brief periods (10-15 seconds) of this is normal in the newborn. You should be concerned if this lasts longer than 15 seconds and is associated with the child turning blue, poor feeding, or excessive sleepiness."
Apnea - AKA periodic breathing
This is a shrill, harsh sound that can be heard during inspiration, expiration, or both; produced by the flow of air through a narrowed segment of the upper respiratory tract, it is often a sign of significant respiratory distress.
Stridor