Onset = 15 minutes
Peak = 1 hour
Duration = 2-4 hours
lispro or aspart (generic name)
Humalog (brand name)
(fast-acting)
Excessive thirst caused by high blood sugars.
Polydypsia
What is the pathologic change in the retina can a person with diabetes experience?
Diabetic Retinopathy
(microvascular change)
Hormone secreted by beta cells in the pancreas to reduce blood glucose levels.
Insulin
Name 4 signs and symptoms that result from low blood sugar.
Neurologic (from a lack of glucose in the brain) - confusion, fatigue, seizure, coma, blurred vision, slurred speech, poor coordination, headache.
Autonomic (from release of epinephrine) - tremors, palpitations, anxiety, hunger, diaphoresis, paresthesias.
Onset: 30 minutes to 1 hour
Peak: 2 to 3 hours
Duration: 4 to 6 hours
Regular Insulin
(short acting)
Excessive urination caused by elevated blood glucose.
Polyuria
Life-threatening complication in T1DM noted by hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and increased serum ketone concentration.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
What acids are created when fat is metabolized for energy?
Ketone Bodies
Serves as an indicator of overall glycemic control and a reflection of the average blood sugar over the last 90 days.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
Adequate control is reflected by an A1c of 7% or less.
Onset: 1 to 3 hours
Peak: 4 to 8 hours
Duration: 10-18 hours
NPH Insulin
(intermediate)
Which type of diabetes is know to cause unintentional, sudden weight loss?
Type 1 Diabetes
Macrovascular damage to large blood vessels causes endothelial inflammation and a build-up of arterial plaques (atherosclerosis).
What organs are affected by macrovascular disease associated with diabetes?
Heart. Brain. Peripheral Arteries.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Over 70% of people >65 y.o. with DM will die from some form of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) i.e. heart attack or stroke.
This boy is experiencing what kind of breathing?
Kussmaul Breathing
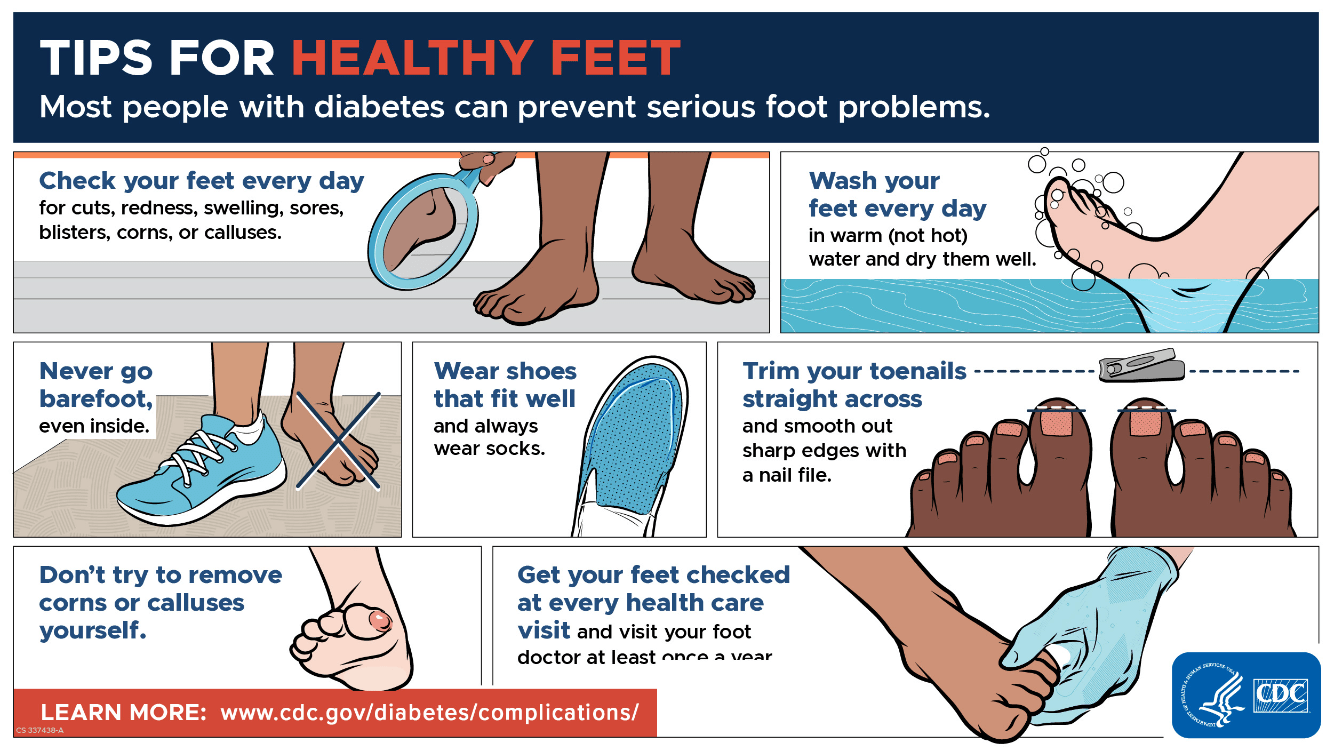
What are 5 things a diabetic patient needs to know about foot care?
Mimics bodies basal secretion of insulin.
Last 24 hours
Has no peak
insulin glargine (generic name)
Lantus (brand name)
(long-acting)
In this type of diabetes, symptoms develop slowly or be so mild that they are unnoticed until they become severe.
Type 2 diabetes
The hallmarks of this disease are progressive reduction of kidney function, proteinuria, and hypertension
Diabetic Nephropathy
What hormone is secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreas in response to hypoglycemia?
This hormone stimulates the liver's glucose production to maintain adequate plasma glucose concentrations.
Glucagon
What would you teach a patient about storing insulin?
Avoid extreme heat or extreme cold.
Unopened bottles are stored in the refrigerator.
Opened bottles can be stored at room temp (77F) for 1 month.
Check the expiration date before using.
Opened insulin expires 28 days after opening.
Examine the bottle for particles or discoloration.
Syringes filled with a single type of insulin can be stored for a month.
In prefilled syringes keep the needle pointing upwards to prevent insulin from clogging the needle opening
This oral anti-diabetic medication is not insulin. It works by reducing the amount of glucose produced by the liver and improving the body's sensitivity to insulin.
Biguanides (generic name)
Metformin (Brand name)
Excessive hunger caused by hyperglycemia.
Polyphagia
Chronic hyperglycemia in diabetics causes microvascular complications. What condition causes damage to small vessels resulting in nerve impairment that contributes to foot ulcers and amputations.
Diabetic neuropathy
Other microvascular changes are retinopathy, nephropathy
What electrolyte imbalance may occur in patients receiving insulin?
Hypokalemia
If a patient is experiencing hypoglycemia they should have 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrate to raise their blood sugar. What are examples of a 15-gram fast-acting carbohydrate?
1/2 cup (4 ounces/118 milliliters) of fruit juice.
1/2 cup (4 ounces/118 milliliters) of regular soda. Do not drink diet soda.
Hard candy, jelly beans or gumdrops. Check the label to see how many grams of carbohydrate these contain.
1 tablespoon of sugar, honey or corn syrup.
Glucose tablets or gel. Check the label to see how many grams of carbohydrate these contain.