Almost every object that does something has to have ______ to be able to do it. Humans, animals, plants, and non-living objects all use ______ to do things.
energy
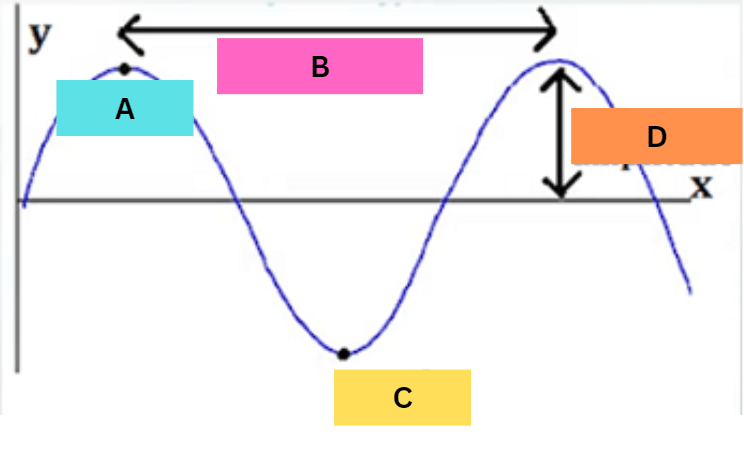
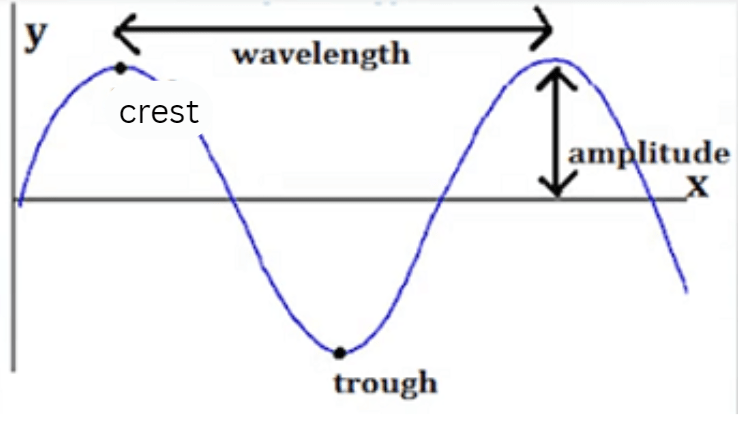
What part of a wave measures how tall the wave is?
Amplitude
What are the two main types of structures that support a plant or animal's survival?
Internal and external structures
What is the process called when rocks break down into smaller pieces?
Weathering
When an energy resource has a limited capacity, and will run out once all of it is used, it is called what?
Nonrenewable energy resource
Name one feature in most cars that keep us safe during a collision.
Air bags, seat belts, etc...
What is the distance between two wave crests called?
wavelength
How do animals process the information they receive through their senses?
By using their brains to interpret it
What is the process of moving rocks or sediment with wind, water, or snow?
Erosion
What is it called when there is an unlimited supply of a certain type of energy resource?
Renewable energy resource
A red ping pong ball is motionless. A blue ping pong ball is moving quickly towards the red motionless ball. The blue ball with motion collides with the red motionless ball. Explain what happens when they collide.
The blue ball hits the red ball. The blue ball will transfer some of its energy to the red ball. The red ball will roll away and the blue ball will roll for only a little while linger before stopping.
How do waves cause objects to move?
By transferring energy
How do plants reproduce?
Through seeds or spores
What evidence can we find in rocks to show changes in landscapes over time?
Fossils
What is one source of energy that comes from renewable energy resources?
wind, solar, or water
An orange car and a blue car are racing at the race track. The blue car is going 109 MPH and the blue car is going 125 MPH. Which car has more energy?
The blue car
How does light allow us to see objects?
Light reflects off objects and enters our eyes
Why are sensory organs important to animals survival?
They alert them to danger nearby, help them hunt, etc...
Describe a natural process that can change a landscape.
Flood, earthquake, tornado, hurricane, or volcanic erruptions
What is one way to reduce the impact of earthquakes on humans?
Build stronger stuctures
List 5 things that are evidence of an energy transfer.
Light, heat, motion, sound, and electricity
A mirror changes the path of light because it ___________ the light.
reflects
How was the Grand Canyon formed?
The Colorado River flowing through and causing weathering and erosion over a long period of time.
Name a form of nonrenewable energy.
Natural gas, nuclear, coal, or petroleum