neurocutaneous disorder
seizures, intellectual disability
Non-neurologic findings include ash-leaf spots, facial angiofibromas, angiomyolipomas, and retinal hamartomas, cardiac rhabdomyomas
5-10% of patients can develop subependymal giant cell astrocytomas
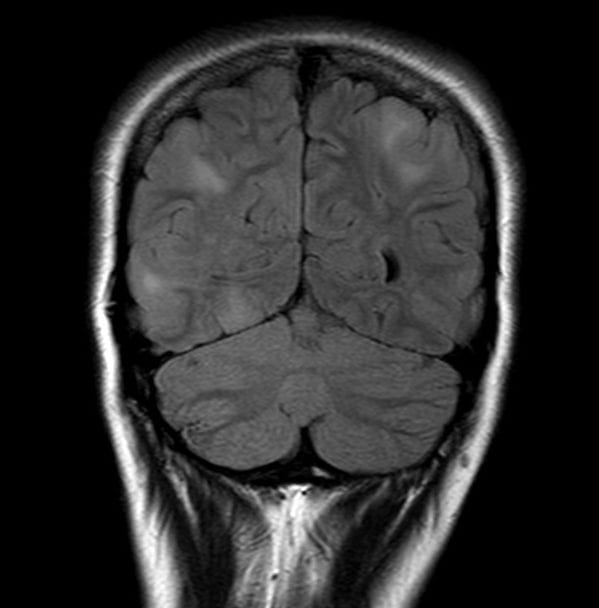
Tuberous Sclerosis
GENE:TSC1 (9q34) which encodes hamartin and TSC2 (16q13) which encodes tuberin.
myotonia as well as weakness of the face, neck, and intrinsic hand muscles
2 types
what are the genes and nucleotide repeats
Myotonic dystrophy (MD)
Type 1 MD: myotonic dystrophy protein kinase (DMPK) gene. CTG repeat
Type 2 MD: CNBP gene. CCTG repeat
EMG will show myotonic discharges (spontaneous potentials with waxing and waning amplitude and frequency)
Patients develop infratentorial hemangioblastomas and retinal angiomas
Non-CNS manifestations include renal cell carcinoma, pheochromocytomas, and pancreatic and renal cysts
Von Hippel–Lindau disease
GENE: VHL (a tumor suppressor) gene mutation
temporary, recurring episodes of muscle weakness, stiffness (myotonia), or paralysis, usually triggered by rest after exercise, cold, or high-potassium foods
Attacks typically last 15 minutes to an hour, often affecting shoulders, hips, and limbs
usually before age 10
Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis
GENE: SCN4A voltage-gated sodium channel mutation
rare genetic neurodevelopmental disorder, primarily affecting girls, that causes severe, progressive loss of motor skills, speech, and purposeful hand use
typically appear after 6–18 months of normal development
repetitive hand movements, breathing irregularities, and seizures
Rett syndrome
GENE: MECP2 gene
Optic nerve gliomas
Non-neurologic findings include café-au-lait spots, Lisch nodules, skeletal abnormalities, and axillary freckling
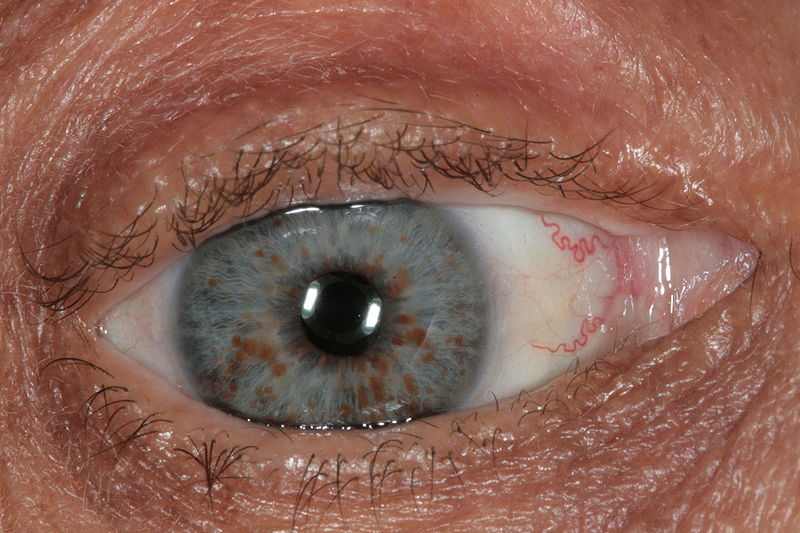
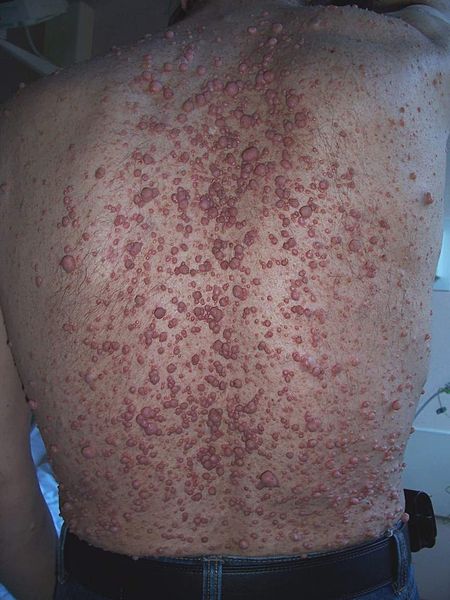
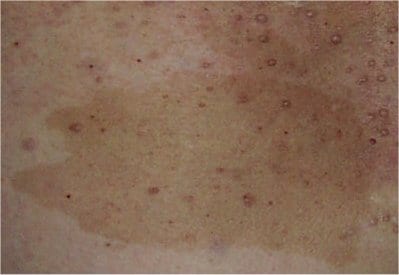
What is the disorder, gene, and what does it encode?
Neurofibromatosis type I (NF-1)
GENE: NF1 gene, which codes for neurofibromin.
Neurofibromatosis Type II (NF2): NF2 gene, which codes for merlin on chromosome 22.
Presents with vestibular schwannomas and multiple meningiomas.
- Can have bilateral acoustic neuromas. Patients usually present in their 20s with tinnitus.
NF2 is a story of 2's: 2 nerves affected (typically CN VII or CN VIII), often on 2 sides (bilateral), 2 tumors (schwannomas, meningiomas), Chromosome 22.
Onset in age 40’s with ptosis, progressing to dysphagia, then proximal muscle weakness
Mutation of what gene?
oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD)
PABPN1
Triggered by the use of anesthesia (typically succinylcholine)
Causes muscle rigidity, hyperthermia, autonomic instability, rhabdomyolysis, and altered mental status
Malignant hyperthermia
GENE: RYR1 gene (ryanodine receptor 1)
Treatment: Stop the offending agent and give dantrolene: blocks release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
temporary, recurring episodes of severe muscle weakness or flaccid paralysis, often starting in adolescence, where individuals remain conscious during attacks
Symptoms include weakness in shoulders, hips, arms, and legs—often upon awakening or resting after exercise—which can last from minutes to days.
first to third decades
Hypokalemic periodic paralysis
GENE: CACNA1S encodes L-type voltage-gates calcium channels
most common single-gene cause of intellectual disability
Presents with intellectual disability and stereotypies (hand wringing, clapping, or flapping)
Characteristic physical features include a long face, large ears, and hyperextensible joints
Gene and number of trinucleotide repeats required
Fragile X Syndrome
GENE: FMR1 gene
- Requires >200 CGG trinucleotide repeats
choreiform movements, psychiatric problems, and neurocognitive deficits.
develop depression as well
imaging: caudate atrophy

Gene, location, and trinucleotide repeats?
Bonus: MOA of the med to treat
Huntington's Disease
GENE: HD gene. Location 4p16.3
Trinucleotide repeats >40 CAG leads to full penetrance of the disease (Repeats expand with each generation in an “anticipation” pattern)
MED: Tetrabenazine VMAT2. Deutetrabenazine
Remember the rule of 4s for HD: 4p gene, >40 trinucleotide repeats, around 40 years at the age of onset, TETRAbenazine
length-dependent polyneuropathy and autonomic dysfunction
multiorgan (kidney, liver, GI) dysfunction
Congo red staining, which reveals characteristic apple-green birefringence under polarized light.
Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis (hATTR)
mutated proteins: transthyretin (TTR), apolipoprotein A-1, or gelsolin proteins
treatment:
- Diflunisal (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug)
- Tafamidis (selective stabilizer of TTR)
- Patisiran (siRNA which reduces the production of TTR proteins)
Presents with weakness or sensory loss during the first two decades of life along with distal atrophy, hyporeflexia, palpable nerves, and high-arched feet
Patients will require ambulation aids such as ankle-foot orthoses but will not lose the ability to ambulate
Pathology: Onion bulbs/hypertrophic neuropathy are the result of repeated episodes of demyelination and remyelination and are composed of concentric rings of Schwann cells
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT):
CMT type 1A (CMT1A)
GENE: duplication of gene peripheral myelin protein (PMP22). chromosome 17p
EMG will show demyelinating sensory and motor peripheral neuropathy
Presents with muscle stiffness provoked by cold, exercise, or hypokalemia
Paramyotonia congenita
GENE: SCN4A voltage-gated sodium channel

Periventricular Nodular Heterotopia
GENE: FLNA gene. Filamin A protein.
recurrent febrile seizures beyond 6 years of age
also have non-febrile generalized seizures
gene encodes sodium channel subunits
Genetic epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+)
GENE: SCN1A or SCN1B
neonatal hypotonia and weakness
Muscle biopsy will show lucent central cores on NADH stain with variably sized fibers with internalized nuclei
these patients are at a higher risk to develop malignant hyperthermia
Central core disease
GENE: ryanodine calcium channel (RYR1)
Presents with episodic ataxia, gait instability, and nystagmus.
Type I: last minutes. Triggered by startle and exercise
Type II: last hours to days. Triggered by fatigue, stress, and alcohol.
2 different genes for 1 and II, bonus if you know the treatments for each
Episodic Ataxia
Type I: Mutation to the voltage-gated potassium channel (KCNA1)
tx: Carbamazepine
Type II: Due to point mutations to the voltage-gated calcium channel (CACNA1a)
tx: Acetazolamide
fyi: Mutations to the CACNA1a gene can cause familial hemiplegic migraine and spinocerebellar ataxia type 6
Presents with normal muscle strength, myotonia, and muscle stiffness between 2-3 years of age
Patients will have normal or increased bulk, and muscle stiffness will improve with exercise
Myotonia congenita
GENE: chloride channel (CLCN1) gene.
Triad of agenesis of the corpus callosum, chorioretinal lacunae, and infantile spasms.
no gene known yet but what is the condition...not to get confused with Aicardi-Goutières syndrome (AGS)
Aicardi Syndrome
characterized by the onset of focal motor seizures, typically within the first week of life (days 2–7), in otherwise healthy infants. Seizures usually resolve spontaneously within weeks or months, with normal neurodevelopmental outcomes in over 90% of cases, though some may develop later epilepsy.
strong association with potassium channel defects
Self-limited familial neonatal epilepsy (SeLNE)
AKA Formerly called benign familial neonatal epilepsy (BFNE), benign familial neonatal seizures (BFNS), or benign familial neonatal convulsions (BFNC)
GENE: KCNQ2
Late-onset ataxia, myoclonic epilepsy, and dementia, most commonly in Japanese
Dentatorubral-pallidoluysian Atrophy
GENE: ATN1 gene
Repeat: Trinucleotide expansion (CAG)
Presents with impairment of memory and at least one other area of cognition
Early symptoms include forgetfulness for recent events or newly acquired information, disorientation, and difficulty with complex cognitive functions
What is this and what is the most common single-gene cause?
Early-onset Alzheimer’s disease
GENE: Presenilin 1
Most common single-gene cause of AD. It is autosomal dominant with 100% penetrance and located on chromosome 14
Presenilin 2:Located on chromosome 1.
Amyloid precursor protein (APP): Located on chromosome 21.
- People with Down syndrome (trisomy 21) have a higher risk of Alzheimer’s disease due to the overproduction of APP
Presents in childhood as progressive dystonia of the lower extremities without any other significant comorbidities
females
Symptoms are usually mild in the morning and worse at the end of the day (“diurnal”)
Dopa responsive dystonia
Symptoms are usually mild in the morning and worse at the end of the day (“diurnal”)
GENE: Mutation of the gene GTP cyclohydrolase I (GCH1)