What are the three states of matter?
What is a mixture?
A combination of two or more substances
What materials are good conductors of electricity?
Metals like copper and aluminum
What is energy transformation?
The change of energy from one form to another.
What is force?
Force is a push or pull
Name two slow changes to Earth’s surface.
Weathering and erosion.
What causes day and night?
Earth’s rotation on its axis.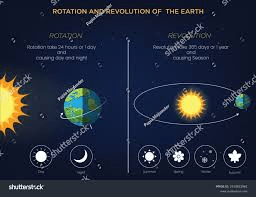
What does it mean to conserve resources?
Using resources wisely to avoid waste.
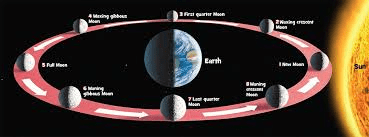
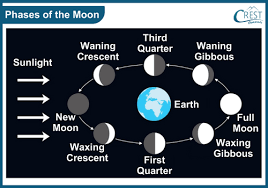
What causes the Moon to appear to change shape?
Moon phases caused by positions of Moon, Earth, and Sun.
As the Moon orbits the Earth, the Sun lights up different parts of it, making it seem as if the Moon is changing shape.
What do plants need to survive?
Water, sunlight, air, nutrients.
What is a food chain?
A series showing how energy passes through organisms
What tool would you use to measure the mass of an object?
Triple Beam Balance or Digital Scale
How can you separate sand from water?
By using a coffee filter or letting it settle.
What is a simple circuit?
A path that allows electricity to flow.
Give an example of electrical energy changing to light energy.
Lightbulb turning on.
What tool is used to measure force?
A spring scale.
What causes an earthquake?
Movement of tectonic plates.
What causes the seasons?
Earth’s tilt and revolution around the Sun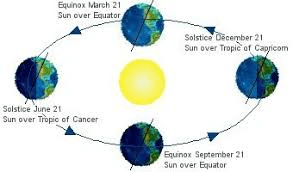
Name one way to reduce water use at home.
Turn off water when brushing teeth.
Shorter showers.
There are eight moon phases, name at least four. Double your points if you name all eight.
For 200 points: New Moon, First Quarter, Full Moon, Last Quarter.
For 400 Points: New Moon, Waxing Crescent, First Quarter, Waxing Gibbous, Full Moon, Waning Gibbous, Last Quarter, and Waning Crescent.
What is an adaptation?
A trait that helps survival.
the process where a species or an organism gradually becomes better acclimated to its environment.
Examples include a camel's hump for storing water, a bird's beak shape for eating specific foods, and a polar bear's white fur for camouflage.
What is a producer in an ecosystem?
An organism that makes its own food (e.g., plant)
How does temperature affect the state of matter?
It causes matter to change state (e.g., melting or boiling)
What is the difference between a mixture and a solution?
A solution has substances evenly mixed that cannot be easily separated, but a mixture can be easily seperated.
What happens when you add a switch to a circuit?
It allows control over the circuit flow.
What energy transformations happen in a flashlight?
Chemical to electrical to light energy
How does friction affect motion?
It slows down or stops motion
How do volcanoes change the Earth's surface?
They build/construct new landforms by depositing lava and ash and can cause destruction through eruptions, landslides, and other hazards.
Describe the water cycle (4 parts).
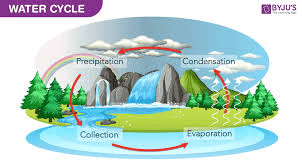 Evaporation (Liquid to Vapor/gas), condensation (gas to liquid), precipitation (rains, sleet, snow, hail), collection/accumulation (rivers, ponds, lakes, oceans)
Evaporation (Liquid to Vapor/gas), condensation (gas to liquid), precipitation (rains, sleet, snow, hail), collection/accumulation (rivers, ponds, lakes, oceans)
What are renewable and nonrenewable resources?
Renewable: sunlight, wind, and water.; Nonrenewable: Fossil Fuels, oil, coal, natural gas, etc.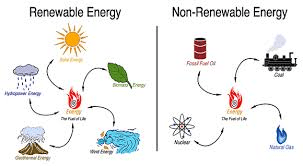
Why do stars appear to move across the night sky?
Stars appear to move across the night sky due to the Earth's rotation on its axis.
How do animals survive in the desert?
They store water, stay cool, and are active at night
Describe the role of a decomposer.
Breaks down dead matter and recycles nutrients
Describe a physical change and give an example.
A change in size, shape, or state; e.g., ice melting
Give an example of a solution and explain how it can be separated.
Saltwater; evaporate the water to get salt.
How does light behave when it hits a mirror?
It reflects in a straight line.
Describe how energy changes form in a toaster.
Electrical to thermal energy
Describe the effect of gravity on a falling object.
Gravity pulls it down to Earth.
Describe how a canyon is formed.
By water erosion over time.
Water, ice, and wind contribute to the weathering and erosion of rock, gradually wearing down the canyon walls. This process can create unique features like slot canyons or widening the canyon over time
Rivers play a crucial role by carving deep valleys through rock, while the surrounding land is uplifted and eroded, contributing to the formation of steep canyon walls.
How do the sun and ocean interact in the water cycle?
When energy from the Sun reaches the Earth, it warms the atmosphere, land, and ocean and evaporates water.
How does recycling help the environment?
Reduces waste and saves energy.
How does the position of the Sun change throughout the day?
It rises in the east and sets in the west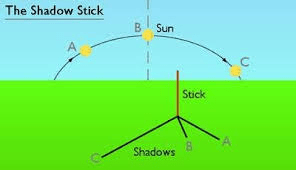
Explain how camouflage helps animals survive.
It helps animals blend into surroundings
What happens if one part of a food web is removed?
It can affect all organisms in the web
Explain the difference between a physical and chemical change with examples.
Physical changes don't form new substances, chemical changes do.
Describe how physical properties can help separate mixtures.
By using size, magnetism, solubility, or density.
Describe how electrical energy is transformed into light and heat energy.
Electrical energy → light and heat energy in a bulb.
Explain energy transformations in a roller coaster ride.
Potential energy (going up) → kinetic energy (going down) → thermal (friction) and sound (gears & chains)
→ thermal (friction) and sound (gears & chains)
Explain how unbalanced forces change the motion of an object.
They cause changes in motion, speed, or direction.
Explain the difference between weathering, erosion, and deposition.
Weathering breaks, erosion moves, deposition drops.
Explain how the rotation and revolution of Earth affect the environment.
Earth's rotation causes day and night, while its revolution around the sun causes the seasons. 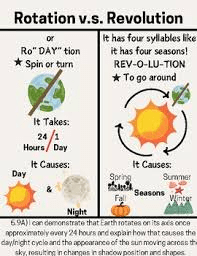
Explain how human activities can impact natural resources positively and negatively.
Positive: planting trees, renewable energy sources, reforestation, wildlife preserves, conservation measures.
Negative: pollution, deforestation, invasive species
Explain how Earth’s rotation affects what we see in the sky.
As Earth orbits the Sun, it moves around the host star by approximately one degree a day and at the same time is completing one rotation every 23 hours and 56 minutes.
Because Earth rotates every 24 hours
Describe how traits can be inherited or learned.
Inherited (passed down genetically from parents): eye color, skin color, hair color;
Learned (acquired through experience and observation): riding a bike, observations and consequences.
Explain the flow of energy from the Sun through an ecosystem.