The process of turning from a liquid into a gas due to heating.
What is evaporation?
Where 97% of Earth's water is found.
What is the ocean?
What types of water are considered fresh?
What are rivers, groundwater, glaciers, and ice caps?
The cycle of processes by which water circulates between the earth's oceans, atmosphere, and land.
What is the water cycle?
Lake Okeechobee is in Florida. The map below shows where the lake is in the state. How would water most likely move from the Gulf of Mexico to Lake Okeechobee?
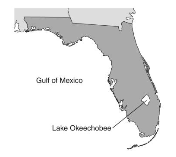
A. by ocean water flowing up a river that joins with the lake.
B. by ocean flooding and water flowing overland into the lake.
C. by ocean water evaporating and entering the lake when it rains.
D. by water seeping through the ocean floor and welling up into the lake.
C. by ocean water evaporating and entering the lake when it rains
Dew forms during what part of the water cycle?
What is condensation?
Explain why water near the equator is generally around 86 degrees F, while water near the poles can be as cold as 28 degrees F.
The angle of the Earth’s axis and relation to the sun causes sunlight to spread out more near the poles than the equator, where it is more concentrated.
True or false: Freshwater is safe for consumption.
What is false? Freshwater means there is no salt, not that it is safe to drink.
The name for the gaseous form of water.
What is water vapor?
A puddle evaporated from a sidewalk. What happened to the water that caused it to evaporate?
A. The water cooled down then evaporated
B. The water disappeared before evaporating
C. The water heated up then evaporated
D. The water soaked into the concrete sidewalk before evaporating
C. The water heated up then evaporated
Rain, snow, sleet or hail.
What is precipitation?
What consistent ocean pattern can cause a bottle from Florida to wash up on a beach in Brazil?
What are ocean currents?
Most of Earth’s freshwater is found in _____.
What is glaciers and ice caps?
A man-made place where fluid collects on Earth.
What is a reservoir?
Which process plays the greatest role in removing water from the ocean?
A. Condensation
B. Evaporation
C. Precipitation
D. Runoff
B. Evaporation
Clouds are drops of liquid formed from _____.
What is cooled water vapor?
True or false: The salinity of the ocean is the same throughout all oceans.
What is false? The salinity of Earth’s oceans varies.
Underground water supplies.
What are aquifers?
The draining away of water from the surface of an area of land or other structure.
What is run off?
Rosita makes a model of the water cycle. She placed a small cup with some warm water inside a plastic bag and sets the bag in a sunny window. Rosita checks the model after 1 day. The figure below shows what Rosita observes. Which processes of the water cycle is she observing?
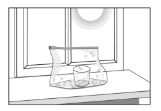
A. Cloud formation
B. Only water evaporation
C. Only water condensation
D. Both water evaporation and condensation
D. Both water evaporation and condensation
What is the largest influence on the water cycle?
What is the sun?
Scientists use names to help them identify the _____ of ocean currents.
What are locations?
What is the wetlands?
Earth’s freshwater is not evenly _____.
What is distributed?
Which of these describes a drought?
A. The Appalachian Mountains have not yet had their first rainfall of the year, despite having record snowfall.
B. Arizona is in a burn ban this month because they have not had any rain.
C. Oklahoma farmers have shown a decline in harvest sizes over the last 7 years due to below-average precipitation.
D. Derry, Maine boasts the highest rainfall levels recorded since 1985.
C. Oklahoma farmers have shown a decline in harvest sizes over the last 7 years due to below-average precipitation.