Sierra sorts items into the following categories. How was she categorizing her items?
1: styrofoam, wood, rubber
2: metal spoon, wire, nail
Conductors versus Insulators
Fill in the blank:
To increase the speed of an object, you should apply a force in the _____ direction you want to go. To slow an object, you should apply a force in the ______ direction the object is moving.
To increase the speed of an object, you should apply a force in the SAME direction you want to go. To slow an object, you should apply a force in the OPPOSITE direction the object is moving.
What is the difference between weather & climate?
Weather describes what is happening on a specific day. Climate is the average weather an area experiences.
Name 3 living and 3 nonliving parts of an environment that an animal might interact with.
Living - grass, trees, bacteria, other plants, other animals
Nonliving - rocks, water, air, sunlight, wind, soil
What is a life cycle?
Describes the steps that a plant or animal goes through as it matures from a seed or egg to an adult.
Beans, sand, and iron filings are combined into a jar. What tools can you use to separate each item?
Beans: Tweezers
Iron filings: Magnet
Provide an example of mechanical, light, thermal, electrical, and sound energy that you can see in the classroom.
Mechanical - pencil sharpener sharpening
Light - ceiling lights
Thermal - bricks getting warm after charging iPads
Electrical - wires used to charge iPads
Sound - students talking
Explain the water cycle. What is the role of the sun and the oceans?
Using energy from the sun, water is evaporated. It condenses into clouds and then falls to the earth as precipitation (snow, sleet, rain, etc.). The water can accumulate in ponds, lakes, and rivers. The ocean is the biggest source of water for evaporation.
Humans often bring in new plants and animals to an ecosystem that do not belong. These are known as invasive species. How do invasive species affect native plants and animals?
They often compete with native plants and animals for resources like food and water, but there are often no natural predators to keep populations in check.
Name two structures cacti have to help them thrive in a desert environment. How do these structures help them?

Spines instead of traditional leaves, waxy coating.
Prevent water loss in the desert.
James puts a red block and green block into a container of water. The red block floats while the green block sinks. How do the densities of the red and green block compare?
The red block is less dense than the green block. The green block is more dense than the red block.
Describe the difference between reflection, refraction, absorption, and transmission.
Reflection - light bounces back
Refraction - light bends
Absorption - light is absorbed & cannot be seen anymore
Transmission - light moves through with no change
How are sedimentary rocks and fossil fuels formed?
Sedimentary rocks - sediment is compacted and cemented in layers over long periods of time
Fossil Fuels - organic material is buried in these layers and transforms into fuel over long periods of time.
Describe the flow of energy in this food web. Where does all the energy come from?
Compare the teeth in these two skulls. Which skull belongs to a carnivore and which skull is an herbivore? How do you know?
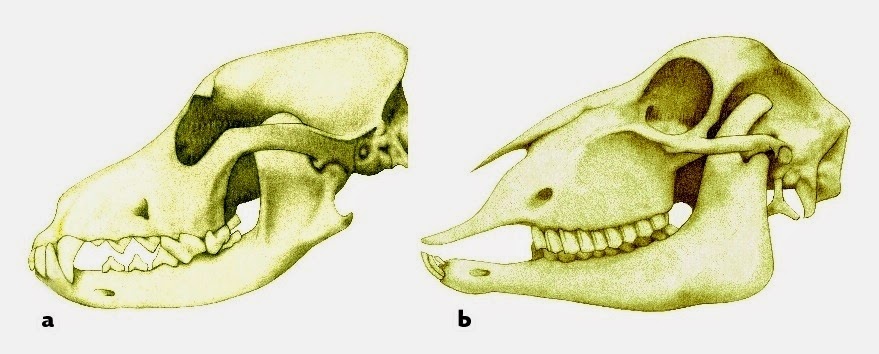
Skull a is carnivore. Teeth are sharp and pointy which is necessary for eating other animals.
Skull b is an herbivore. Teeth are flatter which is good for chewing plants.
What phase changes must water vapor go through to become ice?
Water vapor condenses to become water. Water freezes into ice.
Which switches need to be closed to light bulb A only?
Switches A & C
Name 3 landforms that are formed as the result of wind, water, or ice.
Wind -
Water -
Ice -
Wind - Sand dunes, arches
Water - deltas, canyons
Ice - U-Shaped Valleys
Identify the producers, consumers, and decomposers in this food web. 
Producers: Cactus, Star Cactus, Grass
Consumers: Kangaroo Rat, Tarantula, Rattlesnake, Rabbit, Grasshopper, Lizard, Hawk
Decomposer: Bacteria
Name two inherited traits and two learned behaviors you might expect to observe in a dog.
Inherited - fur color, herding skills, prey drive, self grooming, etc.
Learned - fetch, sitting for food, begging, walking on a leash, etc.
How do you know if something is soluble?
Give an example and a non-example of something soluble.
Substances that are soluble in water will dissolve in water. An example is sugar. A non-example is a coin.
A student wants to test the affect of friction on motion. How would they change their initial setup to test this?
Change the surface they are dragging on
What is happening in this image? What is caused by this movement? How long does it take?

The Earth is rotating on its axis, which causes day & night and the apparent movement of the sun across the sky. The Earth takes 24 hours to rotate.
A geologist is examining some fossils in a rock layer and he notices that there are fossilized shells and coral fragments within the rock layer. What can the geologist infer about the environment when this layer was formed?
Which birds spend at least part of their lives in water? How do you know?

Birds G, K, I, F
There is at least partial webbing in their feet.