
What is ejection fraction?
Via catheterization, a small balloon is used to reopen a blocked artery to increase blood flow. A small stent is left in place to keep the artery open.
What is percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)?
Three nursing considerations prior to a patient going to an interventional procedure.
What is NPO after midnight, shaving access sites, assessing PIV, undressing patient, and reviewing which medications should be held?
Combined administration of Aspirin and P2Y12 inhibitor.
What is dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT)?
Your patient underwent a catheterization via the femoral artery. Upon assessment, you identify a new hematoma. This is your FIRST action.
What is hold firm manual pressure 2-3 cm above the skin puncture site?
This type of valve replacement is made of durable, long-lasting material. However, most patients will require lifelong anticoagulation after receiving it.
What is a mechanical valve?
Using endoscopy, ultrasound transducer is inserted into the esophagus to take images of the posterior aspect of the heart.
What is transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE)?
This is what the nurse should do if they are concerned that a patient is ordered for anticoagulation inappropriately prior to a procedure.
What is contact the provider?
This is why a patient undergoing cardioversion should not have their anticoagulation held.
What is the risk of blood clot?
Antibiotic prophylaxis prior to dental work and invasive procedures is recommended for patients with prosthetic valves to prevent this complication.
What is endocarditis?
These two veins are both utilized for right heart catheterizations.
What is internal jugular vein and basilic vein?
Small implanted chip is attached to the mitral valve to help it close more completely
What is a MitraClip (Transcatheter Mitral Valve Repair)?
Patient education following PPM placement
What is do not lift arms over head for 2 weeks and do not lift anything heavier than 10 pounds for 1 week?
These are three examples of a P2Y12 inhibitor.
Clopidogrel (Plavix)
Ticagrelor (Brillanta)
Prasugrel (Effient)
Ticlopidine (Ticlid)
Cangrelor (Kengreal)
This is how you confirm pressure to a bleeding groin site is fully occlusive.
What is confirm that no dorsalis pedis or posterior tibialis pulses are dopperable?
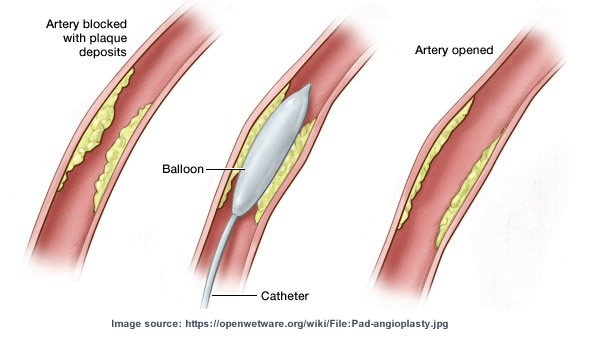
What is a POBA (Plain Old Balloon Angioplasty)?
Minimally invasive procedure during which a catheter is threaded through an artery to place a new valve inside the diseased aortic valve. Minority of patients will require temporary pacing wires.
What is a transcatheter aortic valve repair (TAVR)?
Procedure prep will include shaving of the back and chest. Defib pads will be placed on patient in the procedural area. Following procedure, anticipate patient to be NPO x1 following administration of viscous lidocaine.
What is a TEE/CV?
This is typically how long anticoagulation should be held following permanent pacemaker placement.
What is 48 hours following?
Your patient underwent LHC via the femoral artery earlier today and now reports new onset back pain. Other symptoms of this complication include hypotension, tachycardia, abdominal distention, and the Grey Turner's Sign
What is Retroperitoneal Bleed?
Normal range for pulmonary artery wedge pressure.
What is 6-12 mmHG?
Parachute-shaped device is inserted into the patient's Left Atrial Appendage, decreasing the risk of blood clot formation.
What is the Watchman Procedure?
Five nursing considerations prior to patient undergoing a CABG.
What is...?
-Advance directives/HCP
-Patient education materials
-Consents (CABG, Hospital, Anesthesia)
-Bilateral BPs
-Surgical Scrub PM and AM
-Mepilex
-Place EKG leads laterally (AM)
This is the indications for stopping IV cangrelor.
What is oral antiplatelet therapy is established?
Your patient underwent a pacemaker placement earlier today and is now in acute distress. Symptoms of this complication include sharp chest pain, SOB, tachycardia, hypotension, muffled heart sounds, & distended neck veins.
What is cardiac tamponade?