This is how Cranial Nerve III is tested.
pupillary reflex or raising eyebrows
This is when a patient is unable to move past a thought or a word not related to the current context.
perseveration
This neuromuscular facilitation technique is the MOST appropriate to use with a patient with Down Syndrome in order to promote normal muscle activity.
Quick vestibular stimulation
Faciliatory techniques
Children born into poverty are susceptible to this condition.
Diabetes
This is the term for the mechanism of injury when the brain hits the inside of the skull.
Direct contact
NOT Diffuse axonal injury, Blast injury, Open head injury
This cranial nerve has only an efferent function.
Hypoglossal
Accessory
Abducens
Trochlear
Oculomotor
This location in the body's circulation would potentially lead to a cerebrovascular accident if the formation of a clot occurred.
The left ventricle from bicuspid valve dysfunction
A physical therapist assistant would expect to see this reflex on the ipsilateral leg after pinching an infant's toe.
Flexion withdrawal reflex
A child extends their upper extremities forward in response to an anterior perturbation. This is the response the child would demonstrate.
Protective reaction
NOT righting response, equilibrium reaction, moro reflex
A patient is 2 weeks post a traumatic brain injury. This is responsible for progressing through recovery.
Reduction of edema
Healing of the brain tissue, acute
The majority of spinal cord tracts decussate in the central nervous system in this location.
Medulla
("decussate" refers to the crossing or intersection of nerve fibers from one side of the body to the other. The medulla oblongata is a part of the brainstem, and it contains various nerve tracts that carry signals between the brain and the spinal cord.)
Your patient is one day status post cerebrovascular accident (CVA). What is the BEST dynamic intervention to prevent the development of a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
Early ambulation
This the BEST example of functional gross motor movement of a 6 month old.
Unilateral reaching while in prone
This would be the MOST appropriate treatment technique for a patient with spastic cerebral palsy in order to promote normal muscle activity.
Rhythmic rotation
A patient is unable to complete an exercise while in a busy rehab gym, but is able to perform the same task in a private treatment room without difficulty. This patient is having difficulty with this type of attention.
Selective attention
VS Divided attention
A patient presents with a lesion to the Right Vagus nerve. When assessing the nerve, this is what the examiner should expect.
uvula deviates to the left
Hemorrhagic stroke (increases hemorrhaging)
This med is indicated for Ischemic stroke.
This describes a finding that would be MOST expected in a child with thoracic area spina bifida.
Deep Tendon Reflex of 3+/4
UMN Lesion
This clinical presentation/condition would MOST likely have serial casting as an important intervention.
Hypertonic plantarflexors
This is a neurobehavioral impairment associated with a traumatic brain injury.
Impulsivity
NOT attention, abnormal tone, paresis
"Attention" refers to the cognitive process of selectively concentrating on one aspect of the environment while ignoring others. It's a fundamental aspect of human cognition and plays a crucial role in perception, memory, learning, and other cognitive processes.
The PTA treats a patient who has a cerebellar lesion. This clinical finding is expected to be observed with this condition.
Dysmetria (timing, force, extent, direction of limb movement, unable to reach target), nystagmus (gaze-evoked, eyes drift involuntarily to neutral), dysdiadochokinesia (inability to perform rapid alternating movements)
A patient with L MCA might present with these clinical findings. List at least 2.
This is the cervical position in a patient with left sided torticollis.
Left side-bend, Right rotation and flexion
This describes athetoid type movement, as seen in some children with cerebral palsy.
Slow, twisting and writhing involuntary movements
NOT Sudden, rapid and jerky involuntary movements, Reduced amplitude of movement, Involuntary cyclical oscillations
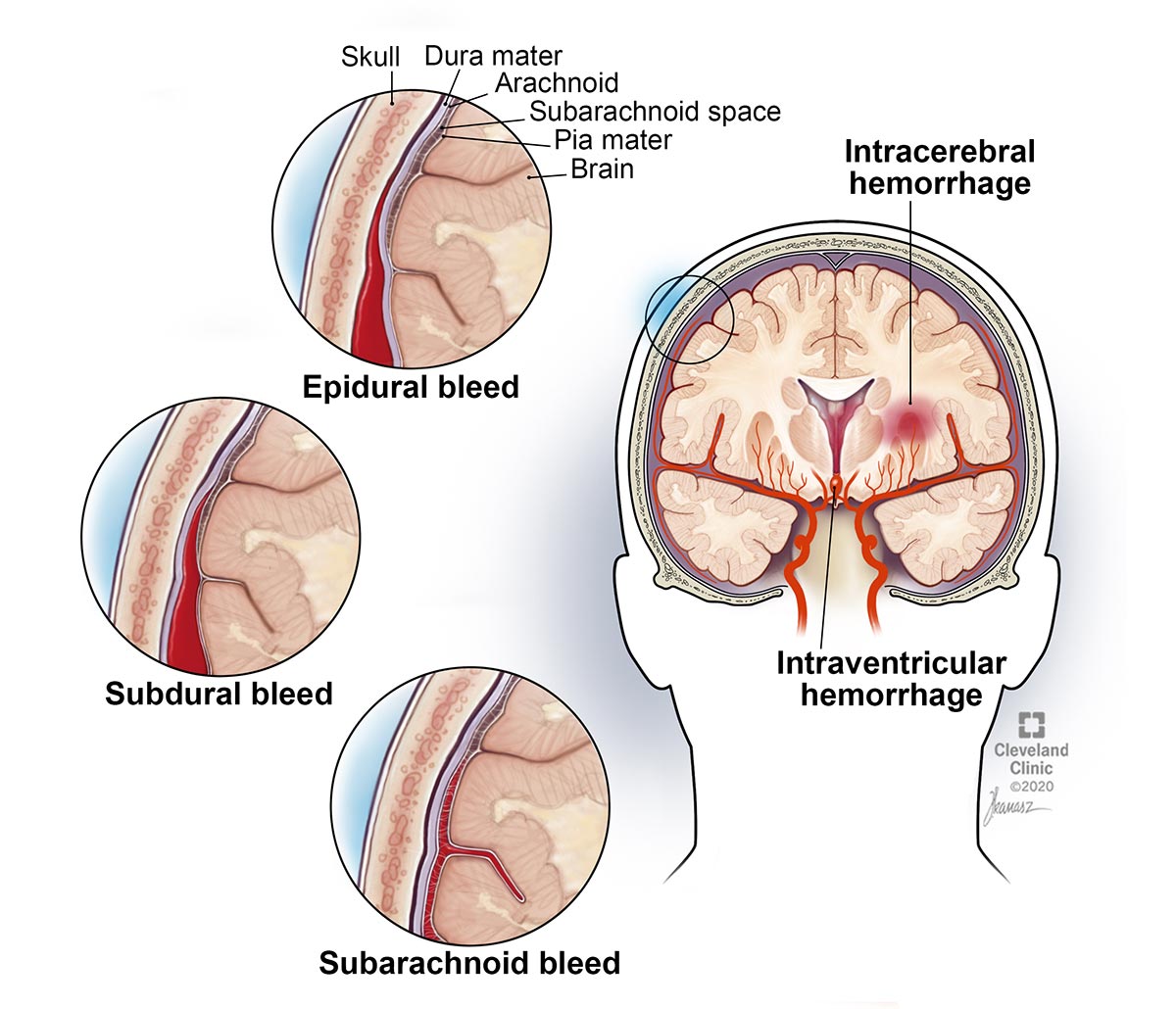
A patient is diagnosed with an epidural hematoma s/p traumatic brain injury. The bleed is located between these two tissue layers.
Bony skull and dura mater