Name a pain scale used for the adult population
Numeric
Behavioral
Objective
Name 3 abnormal INSPECTION findings in a patient in respiratory distress (NOT VITAL SIGNS)
tripoding, inability to speak full sentences, nasal flaring, accessory muscle use, diaphoresis, agitation/restlessness/anxiety, cyanosis of mucus membranes, etc.
Demonstrate (or point to) the 5 places of cardiac auscultation

Put the following in correct order of operation: Palpation, Inspection, Auscultation
Inspection, Auscultation, Palpation
Name 2 bony prominences at high risk of developing pressure injuries
coccyx, heels, elbows, hips
What are the 4 questions we ask when assessing orientation?
What is your full name/DOB? Where are you right now? Why are you here? What year is it?
True or false. Epiglottitis (swelling of the upper throat) is considered a medical emergency.
TRUE
Edema, pulses and capillary refill are all things that we can ______ during a cardiovascular assessment
Palpate
Where is the Epigastric region?
Upper center abdomen
Mechanical soft, thickened liquids, pureed & dental soft are all examples of what?
Modified diets
What does PERRLA stand for?
Pupils equal round & reactive to light & accommodation
Name an abnormal sound associated with the UPPER airway
wheezing, stridor
Explain the pathophysiology behind pitting edema/pulmonary edema
Name 3 things you would inspect during an abdominal assessment
Abdominal Shape, Skin color, Pulsating? Guarding? Stool Characteristics, Urine Characteristics, Vomit Characteristics
Name 3 age related factors that impact dietary intake and nutrition in geriatric populations
Loss of taste, Loss of physical abilities (grocery shopping, cooking), Denture, Loneliness/depression, Loss of appetite (GI slows), Memory
Coordination
Name the abnormal lung sound associated with fluid/mucus in the alveoli causing a wet fluttering sounds
Rhonchi
Name the 5 P's of a peripheral vascular assessment
Pain, Pallor, Paresthesia, Pulse, Paralysis
Define normoactive bowel sounds
between 5-20 gurgles/sounds per minute
Stage this wound:
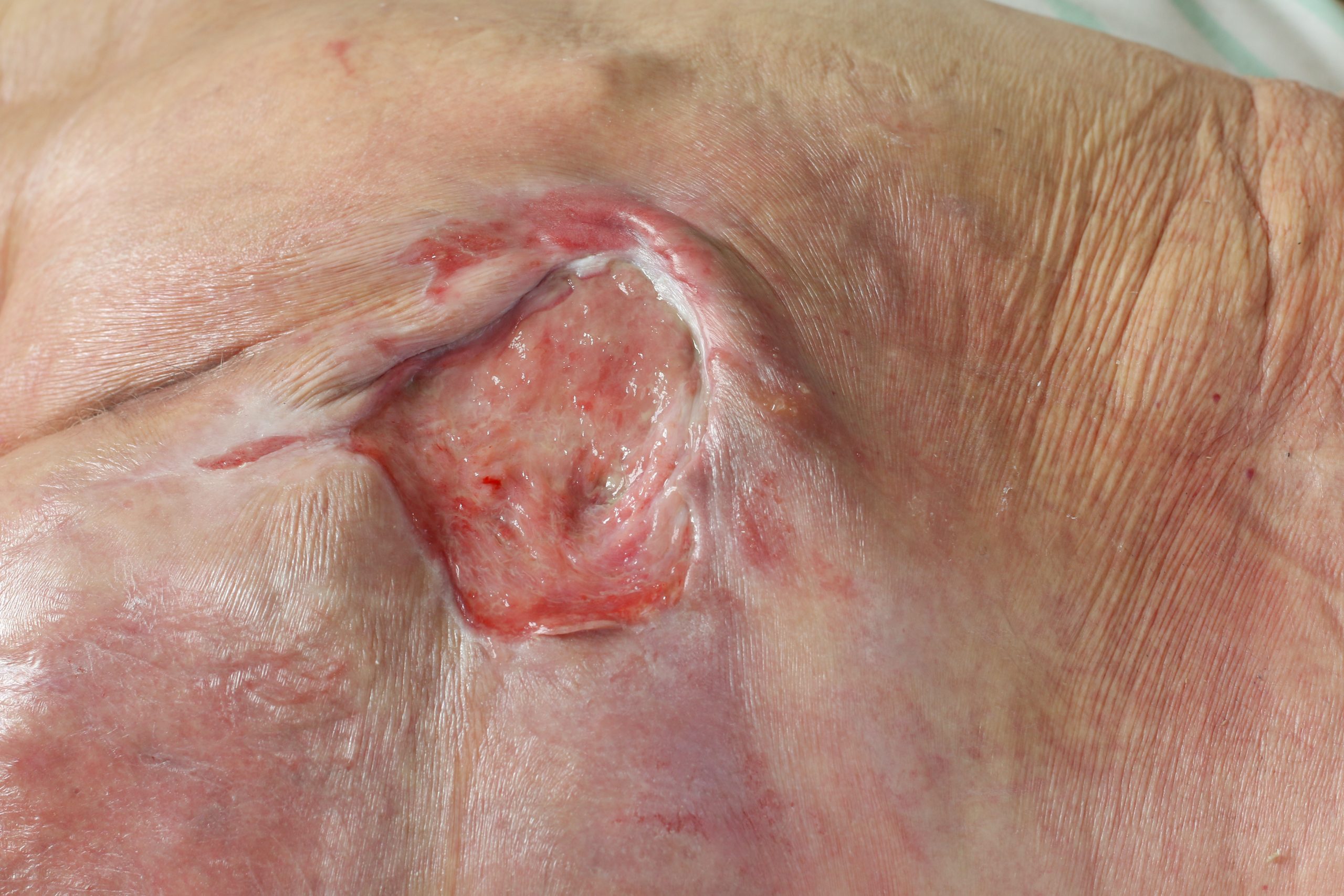
Stage 3 - full thickness, some slough present around edges, no bone or tendon visible
Glascow Coma Scale (GCS) assesses what 3 items?
Name 2 *LATE* stage signs of hypoxia
Cyanosis, Bradypnea, altered mental status, bradycardia/arrythmias
What two assessment findings differentiate an artery obstruction vs. a venous obstruction
Where is McBurney's point AND what does rebound tenderness at that location indicate?
RLQ. Rebound tenderness indicates likely appendicitis.
Describe how diabetes impacts skin integrity
Uncontrolled blood sugar can lead to:
- slow-healing wounds due to poor circulation
- increased skin breakdown r/t nerve damage
- increased risk of infections r/t high sugar content in the blood and increased skin breakdown