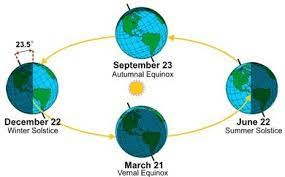
what causes seasons on Earth
Distance from the sun as the Earth tilts away from the Equator
another Word for a net force Fnet
Resultant Force
What is a force
Why is Australia in Winter around June
The N hemisphere is tilted towards the sun S Hemisphere is tilted away
Separtating Sand from Magnets
Magnetism
A variable that changes on its own
dependant variable
________ rocks are formed by great heat and pressure. They are generally found inside the Earth's crust where there is enough heat and pressure to form the rocks.
Metamorphic Rocks - Metamorphic
calculate the net force
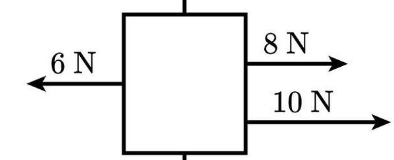
(8+10) - 6= 12N to the Right
Make Right + and Left -
What are the units for measuring force
N (Newtons)
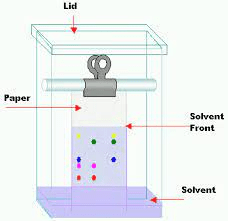
Separating Coloured substances
C____phy
Chromatography Chroma means colour in Greek
Variables that must be kept the same
controlled variable
Hardened magma or lava is called i_______rock. Examples of i_____rocks include basalt and granite.
hardened magma or lava is called igneous rock. Examples of igneous rocks include basalt and granite.
As a liquid is heated it become----- Dense than the surounding liquid so it will _____. This is called convectional curents
Less dense------ Rise
Calculate the resultant force
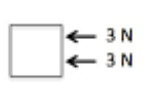
3+ 3 = 6N
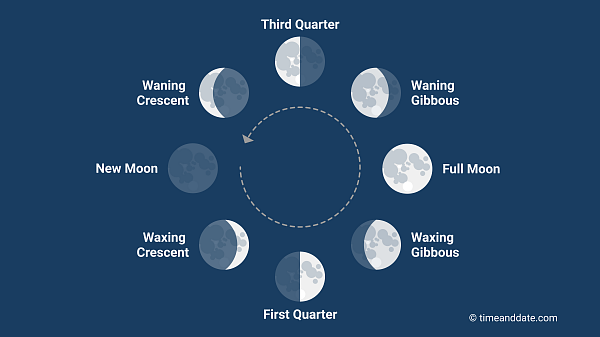
The moon phases are caused by A______ of S_______ that is reflected to the earth from the moon
Amount of Sunlight
Pure Substances are either
Compounds or elements
the grapgh shows how size of crystals vary with time to cool for igneous rocks. What does the graph show
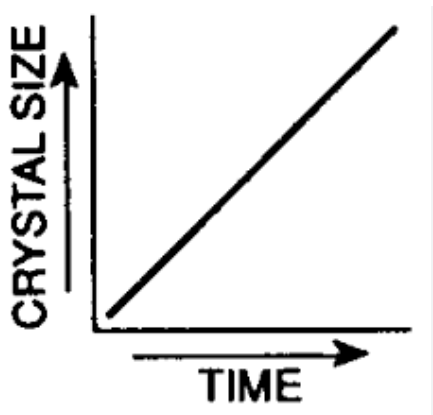
the longer the cooling time the bigger the crystals
S_______ rocks are formed by years and years of sediment compacting together and becoming hard
Sedimentary
3 states of matter are S---- L---- and Gas
Solid, liquid and gas
Another word for resultant Force
Net Force
Moon phases include
N____Moon, Waxing G_____, F____moon
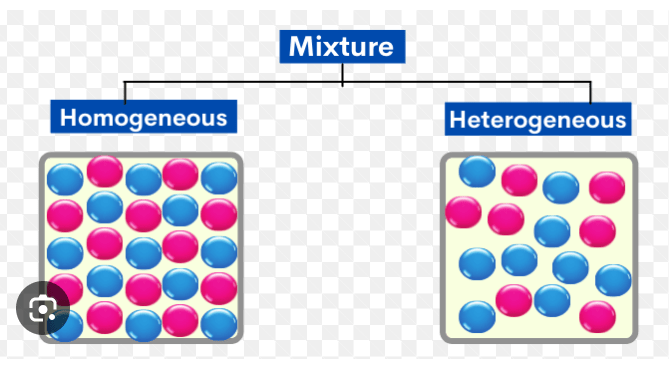
Mixtures can be Ho___ or Het_____
why must any experiment have many controlled variables
to make it fair or valid
Rocks are constantly changing in what is called the R---C ------
Rock Cycle
When water seeps throgh porous layers of the land but is unabl to pass through the _____ layer. It can end up forming A_______
Zero Net force mean all forces in opposing directions are _________
Equal so the object will not move (or move at a constant speed
draw and label Inner Core Outer Core Mantle and Crust
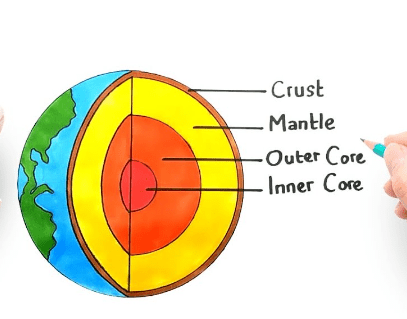
_______the thin outer later of the Earth where we live.Variesin thickness from around 5km thick (in the ocean floor) to around 70km thick on land.
CRust
The 2nd layer of the Earth is called the M__________. The M______ is much thicker than the crust at almost 3000km deep. It's made up of slightly different silicate rocks with more magnesium and iron.
Mantle
The I____C___ is so deep within the earth that it's under immense pressure. So much pressure that, even though it is so hot, it is solid. The i___c____ is the hottest part of the Earth, and, at over 5000 degrees C, is about as hot as the surface of the sun.
Inner Core
The Earth's O---- C----- is made up of iron and nickel and is very hot (4400 to 5000+ degrees C). This is so hot that the iron and nickel metals are liquid! The outer core is very important to earth as it creates something called a magnetic field. The magnetic field the outer core creates goes way out in to space and makes a protective barrier around the earth that shields us from the sun's damaging solar wind.
OUTER CORE
What is an object at rest
Not Moving