Jeopardy! 2/8/22
Connections between the Brodmann's area 17 and Broca's area allow this higher-order function.
What is reading
A patient is unable to fixate on a point, but their H exam is normal. We might expect a defect in this nucleus.
What is the vestibular nucleus
The nerves responsible for pupillary constriction are synapsed on by axons from this nucleus.
What is the Edinger-Westphal nucleus
Large cortical representation and dual arterial supply are proposed reasons for this visual exam finding.
What is macular sparing
4 to 5 inches long, this tube is also called the oviduct.
What is the Fallopian tube
The diagram below represents someone with a lesion in this area not in the visual cortex.
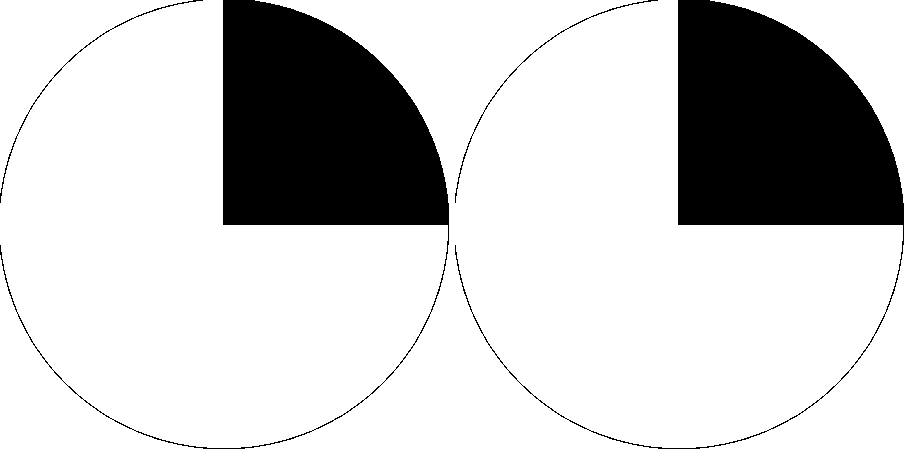
What is Meyer's loop
A 26-year-old patient with the following finding and history of temporary R arm numbness might benefit from taking this drug for spasticity.
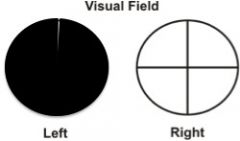
What is baclofen
The discovery of the receptor for this toxin was announced in fall 2001, around the time it was part of a terrorism scare.
What is anthrax
Fibers from the optic nerve directly synapse at these four areas of the brain.
What are the lateral geniculate nucleus (thalamus), suprachiasmatic nucleus (hypothalamus), superior colliculus, and pretectal area
Red desaturation associated with inability to comprehend speech might indicate damage to this lobe.
What is the temporal lobe
"There's no place like" this 11-letter word, the steady internal environment that organisms strive towards.
What is homeostasis
The "different" touches on Mrs. Heubner's sensory exam might be explained by the fact that this is the splenic flexure of the visual cortex.
What is the dorsal pathway
This part of the pain pathway would appear the same shade as the labeled structure from the striate cortex below.
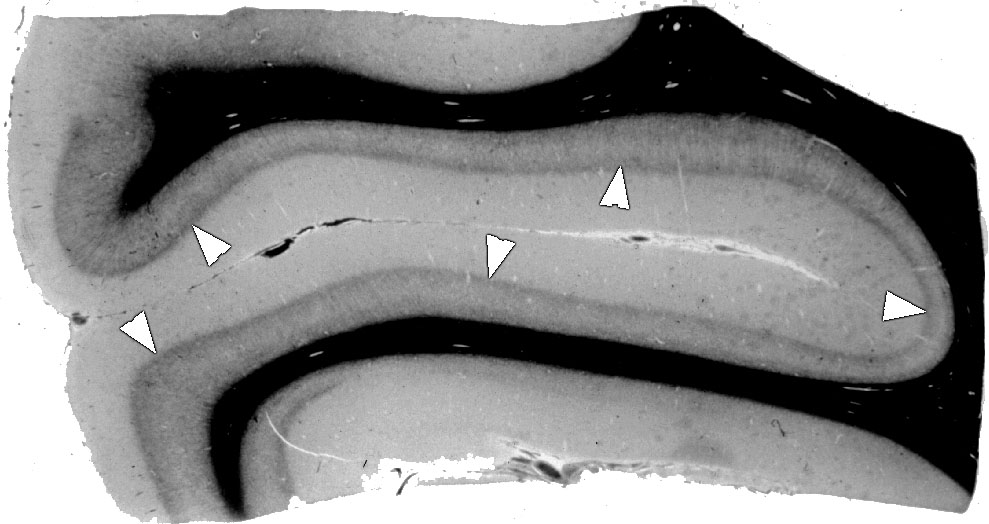
What is the spinothalamic tract
PCR, short for this, allows endless copying of tiny bits of DNA, helping identify diseases & catch killers.
What is polymerase chain reaction