Phonemes
The smallest classes of sound that make a difference in meaning. Phonemes are also categorized as speech sounds.
Morphemes
The smallest unit of meaning 
Enculturation
The process by which people learn the requirements of their surrounding culture and acquire values and behaviors appropriate or necessary in that culture. 
Kinesics
The study of communication by non-verbal means, including posture, mannerisms, mody movement, facial expressions, signs and gestures. 
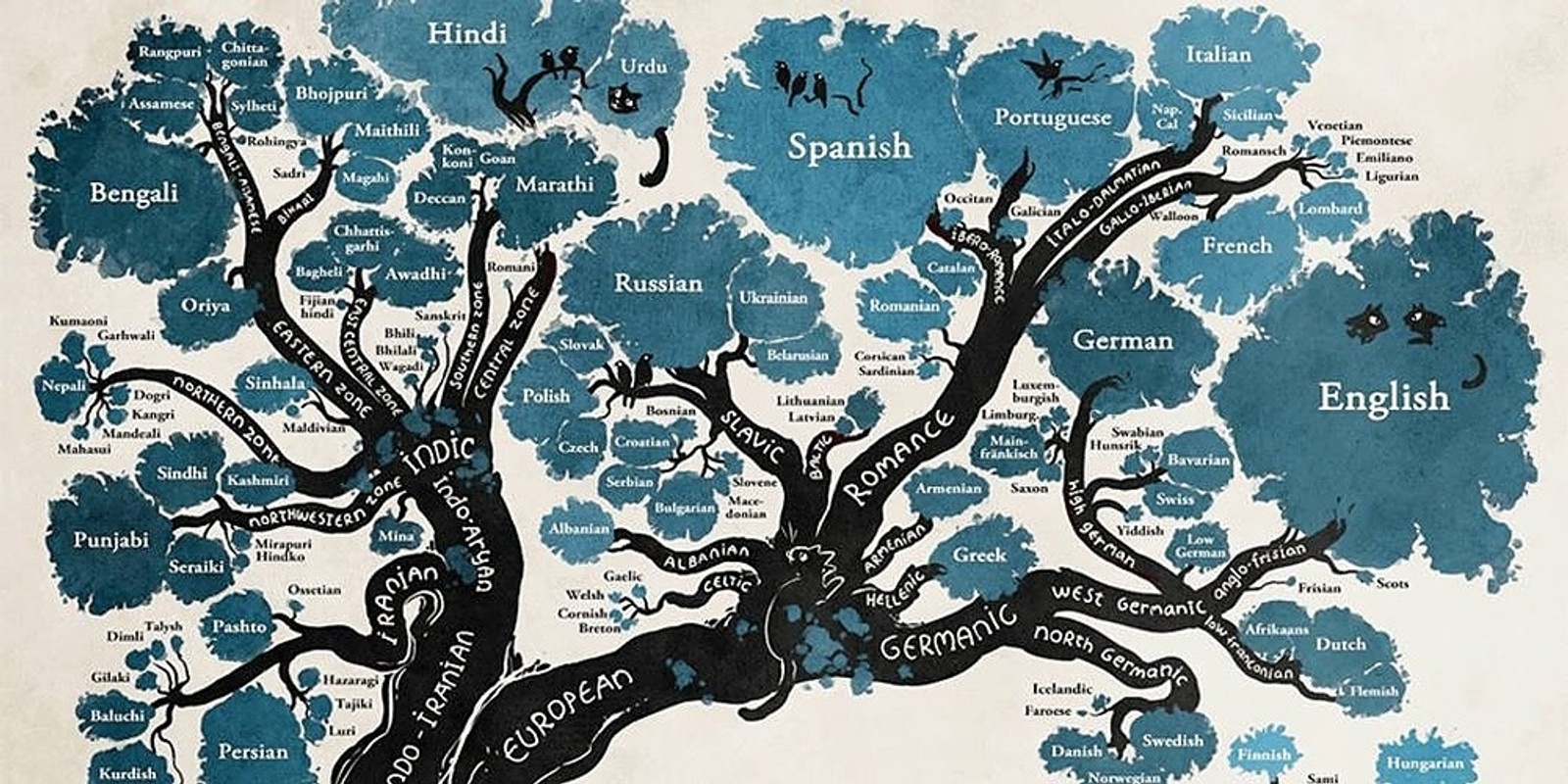
Historical Linguistics
Study languages over time that includes extinct languages as well as the evolution and migration of languages.
Code-Switching
More than one language in the course of conversing.
pragmatics of language
rules for using language in different contexts
Language instinct
The belief that humans are born with an innate capacity for language and all human language shows evidence of a universal grammar. Language is unique to humans, produced by evolution, to solve the problem of communication among social hunter-gatherers
Organized sound that is created by voice, instruments, or body noises that convey meaning through poetry, song, or storytelling.
Music
Sociocultural linguistics
Study of the relationship between language and sociocultural systems, for example, speech behavior and miscommunication between male and female 
Protolanguage
Language ancestral to several daughter languages 
The semantic system
explores the standards by which people select particular words and expressions to convey certain meanings.
Primitive Art
The term used by the Western art world for the art of non-Western, "tribal" societies.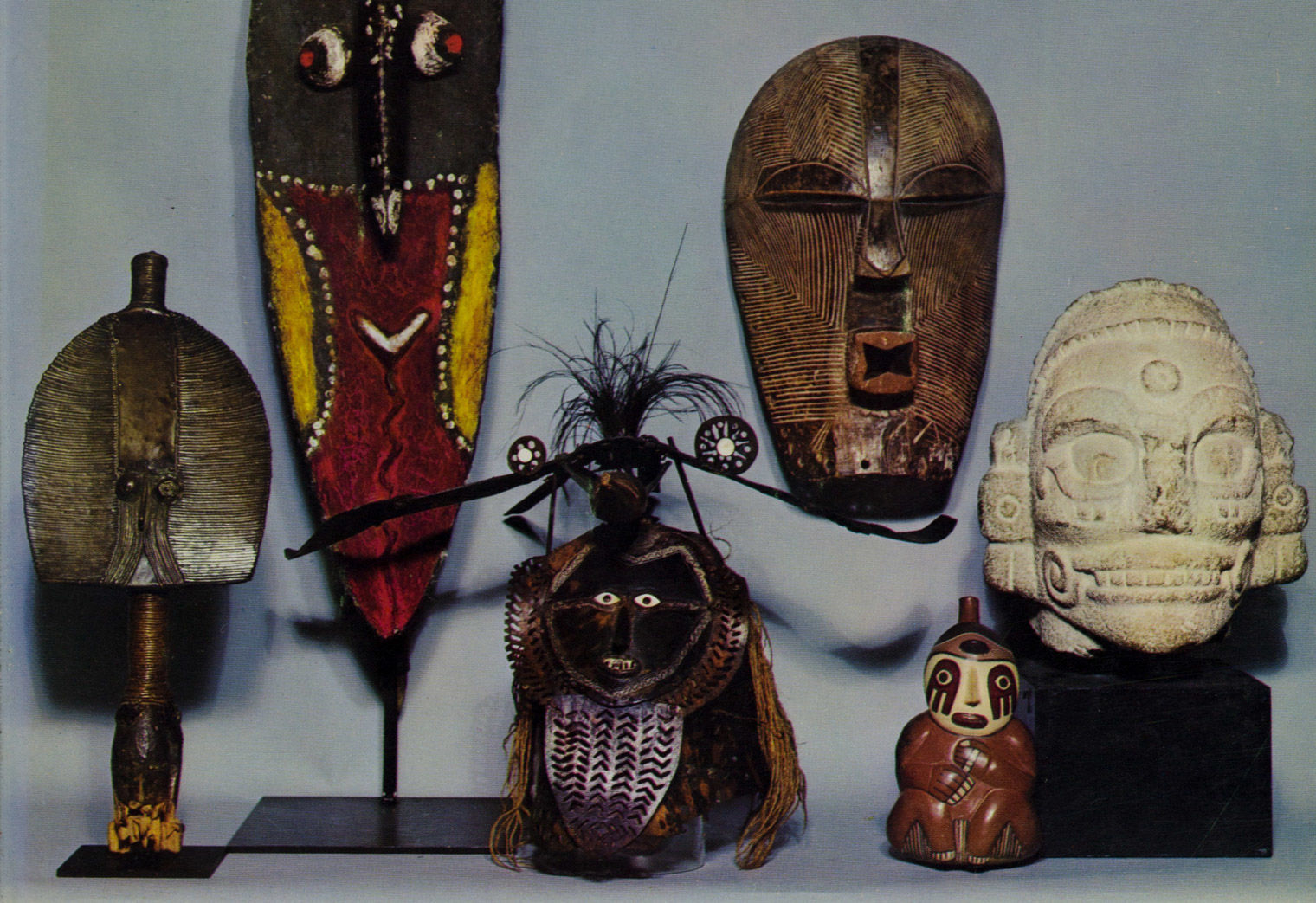 
Paralanguage
Refers to all the optional vocal features or silences apart from the language itself that convey meaning.
Descriptive linguists
study the morphology of word, syntax, and meaning of sentences, as well as physical qualities (phonetics) and structure (phonology) of speech. 
The phonological system
The standards for discriminating the differences in sound, intonation, and stress that are consistently associated with differences in meaning
The morphological system
Built up from combinations of languages, phonemes are the minimal units that carry specific meanings in that language. These minimal meaningful units are called morphemes 
Permanent body modification and decoration
Things that we decorate our body with that cannot be removed, like tattoos, scarifications, permanent body changes (such as foot binding), piercings, and removal of body parts.
Gesture/ (Body language)
Body language is a form of communication humans share with other primates. Body language uses subtle embodied messages to demonstrate emotions.
Linguistic Anthropology
Study of language whether spoken, written, or non-verbal (gestural) that allows anthropologists to better understand the human condition across time, space, and culture 
Cognates
Words of different morphs that belong to different languages but have similar sounds and meanings.
Daughter languages
Languages that share a common parent language
Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis
the idea that different languages create different ways of thinking
Call system
Vocal system that consists of a limited number of sounds -calls- that are produced only when particular environmental stimuli are encountered
Computational linguistics
is an interdisciplinary field concerned with the statistical or rule-based modeling of natural language from a computational perspective, as well as the study of appropriate computational approaches to linguistic questions